What drives ATP synthase to add a phosphate onto an ADP?
What is a proton gradient?
This process allows organisms capable of cellular respiration to regenerate NAD⁺ in the absence of oxygen, enabling glycolysis to continue producing ATP.
What is Fermentation?
This molecule is the primary energy currency of the cell, produced during cellular respiration.
What is ATP?
An animal that can REGULATE its own internal osmotic pressure.
What is an Osomoregulator?
This green pigment is essential for capturing light energy in photosynthesis.
What is chlorophyll?
How many ATP are produced in the ETC?
What is 28-34 ATP?
This phase of glycolysis involves the use of ATP
What is the investment phase?
This is the first stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the cytoplasm, where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
What is Glycolysis?
A strong and durable way for animal cells to stay close?
What is a tight junction?
This enzyme is responsible for the initial fixation of CO₂ in the Calvin cycle.
What is RuBisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase)?
This letter is pointing at the mitochondrial matrix
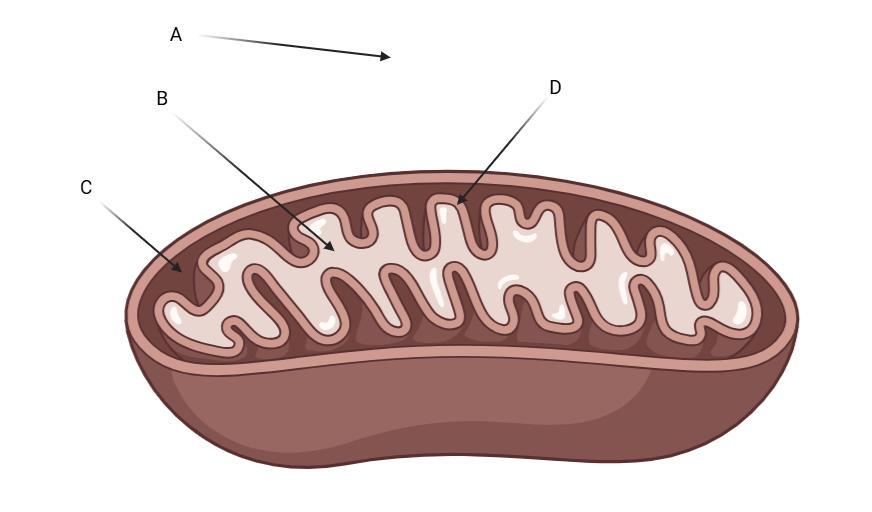
What is letter B?
The first pathway that produces NADH2.
What is Glycolysis?
This pathway occurs in the mitiochondrial matrix and produces an abundance of NADH, FADH2, GTP/ATP, and CO2.
What is the Citric Acid Cycle?
A nice way for plant cells to communicate with one another, and maybe even share some materials.
Extra 100: What is its counterpart in Animals and Fungi (Need to get both)
What is a plasmodesmata?
Animals: Gap Junctions
Fungi: Pores
This stage of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membranes and produces ATP and NADPH.
What is a light-dependent reaction?
This electron carrier creates 2.5-3 ATP after it donates to the ETC.
What is NADH?
This molecule, produced during pyruvate oxidation, enters the citric acid cycle to be further oxidized for energy production.
What is Acetyl-CoA?
Help I'm out of oxygen but still need energy, what type of respiration am I undergoing?
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
This type of aquatic create drinks plenty of water, but loves to pump out electrolytes.
Extra 100 points: Type of water environment
What are Marine Bony Fish?
What is Saltwater/Seawater?
This process, occurring in the chloroplast stroma, converts inorganic carbon dioxide into organic molecules using ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
What is the Calvin cycle?
The addition of a phosphate through an electro-chemical gradient built up by e- carriers.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
This type of fermentation produces lactate as an end product, while this other type produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.
What is lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation? 250 points for both
This enzyme, which catalyzes the first step of glycolysis, is a key regulatory point and is inhibited by high levels of ATP.
What is phosphofructokinase?
This term describes the combined effects of solute concentration and pressure on the movement of water in plant cells, and differences in its value (+, -, 0) determine the direction of water movement.
What is water potential?
These specialized cells in C4 plants surround the vascular bundles and are the site of the Calvin cycle.
What are bundle sheath cells?
This letter shows where the highest proton concentration is?
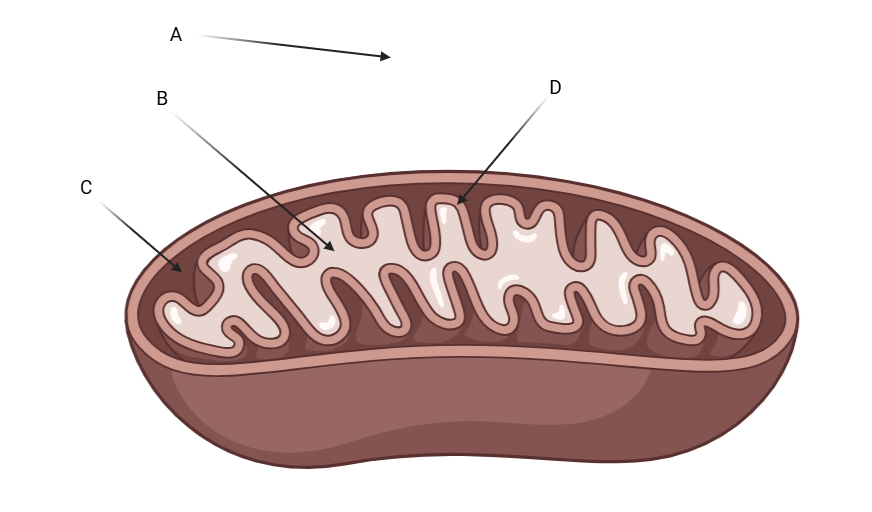
What is letter C?
What letter depicts where pyruvate oxidation, glycolysis, and fermentation occur?
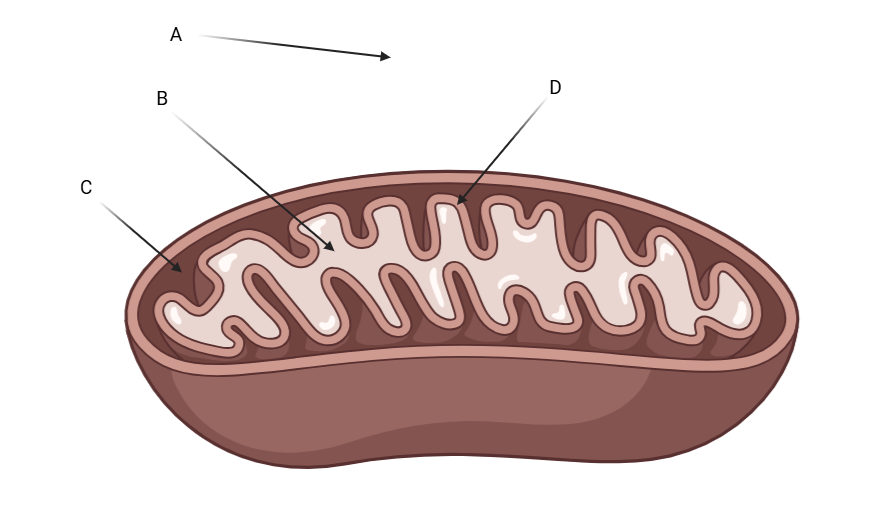
What is
Pyruvate Oxidation = Letter B (Matrix)
Fermentation = Letter A (Cytoplasm)
Glycolysis = Letter A (Cytoplasm)
This enzyme complex, is responsible for the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, linking glycolysis to the Citric Acid cycle.
What is pyruvate dehydrogenase?
These plants use a temporal separation of carbon fixation and photosynthesis. Plus name the structure they use to regulate water loss.
Extra 100 points: When do they open and close this structure?
What are CAM plants? What is a Stomata?
What is Closed during the day, open at night.
This term describes the phenomenon where oxygen competes with carbon dioxide for the active site of RuBisCO, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis.
What is photorespiration?