A 66-year-old woman is evaluated during a wellness visit. She reports no symptoms. She does not recall the last time she had a Pap smear, and medical records from her previous physician are not available. She has no history of sexually transmitted infection, gynecologic cancer, or surgical history.
Which of the following is the most appropriate cervical cancer screening strategy for this patient?
Cervical cytology with human papillomavirus testing
Cervical biopsy
Colposcopy
Discontinue cervical cancer screening
A 58-year-old woman is evaluated for a 5-week history of an itchy rash on the low back. She was recently diagnosed with hepatitis C virus infection, for which she has just initiated ledipasvir-sofosbuvir. Her medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she takes no other medications.
Skin findings on the low back are shown.
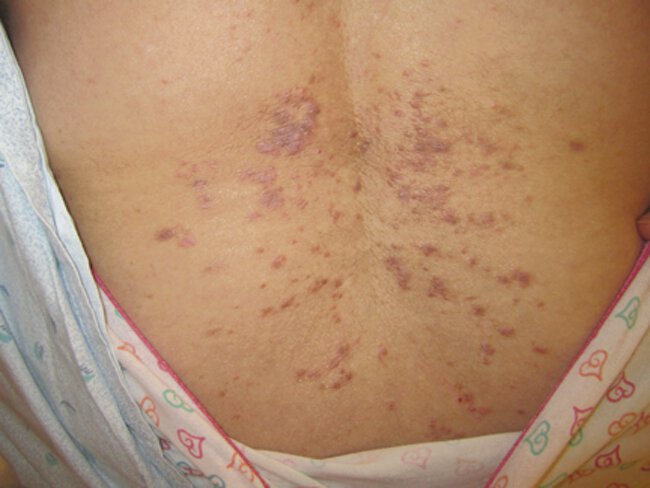
The volar wrists have lesions similar to those on the back. There is no lymphadenopathy.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Lichen planus
Pityriasis rosea
Psoriasis
Secondary syphilis
A 44-year-old woman is evaluated for a 4-week history of worsening rash. She used clobetasol cream for 1 week, but the rash worsened.
Skin findings on the volar aspect of the wrist are shown.
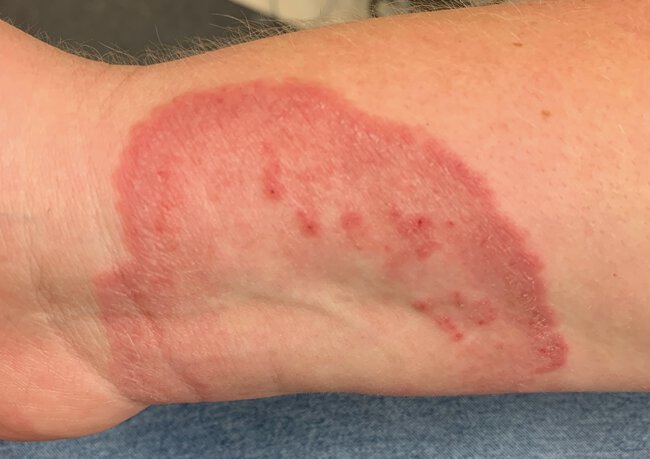
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test?
Potassium hydroxide preparation of skin scraping
Mineral oil preparation of skin scraping
Shave biopsy
Wood lamp examination
A 65-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for hypertension. He reports that he eats fruits, nuts, and vegetables daily and red meat once weekly. He drinks artificially sweetened soda daily and one alcoholic beverage most evenings with dinner. He does not smoke cigarettes. He lives alone and does not maintain social relationships and describes himself as lonely. Depression screening is negative.
In addition to traditional risk factors, which of the following is also a contributor to cardiovascular risk in this patient?
Social isolation
Alcohol consumption
Artificially sweetened soda consumption
Red meat consumptionD
A 48-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-month history of a painless lesion on his left shoulder that has been increasing in size and is now 2 cm in diameter. Medical history is unremarkable.
Skin findings are shown.
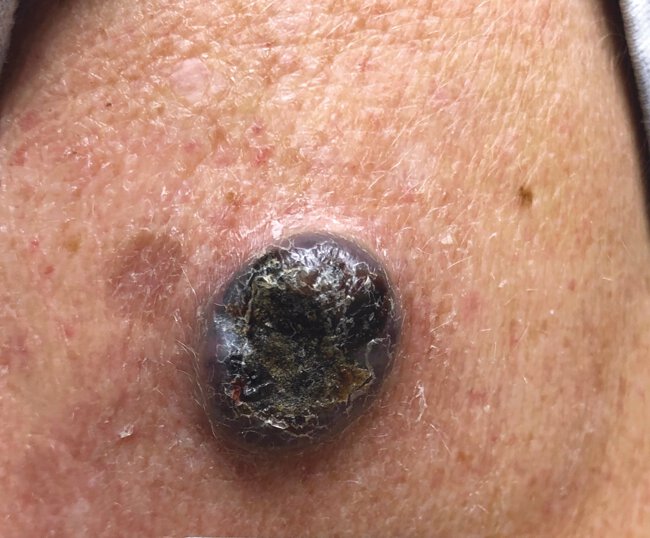
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Nodular melanoma
Hemangioma
Keratoacanthoma
Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
A 39-year-old woman is evaluated for a 6-month history of irregular, heavy menstrual periods. She reports having a menstrual period every 6 to 8 weeks and that her periods now last 9 days and are heavier than usual. She has no other symptoms. She birthed two children. Her last Pap smear was obtained 3 year ago and was normal; human papillomavirus testing was negative. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 36. The bimanual pelvic examination shows blood in the cervical os and normal findings.
Laboratory studies reveal a normal complete blood count. A pregnancy test result is negative.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Obtain an endometrial biopsy
Obtain a follicle-stimulating hormone level
Obtain a Pap smear
Start oral contraceptive pills
A 28-year-old woman is evaluated for a painless breast lump she noticed 1 week ago. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her grandmother was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 72 years. Her only medication is a combined hormonal contraceptive pill.
Breast examination reveals a 1-cm, nontender, smooth, mobile, round mass on the medial aspect of the right breast. The overlying skin is normal. There is no lymphadenopathy. The left breast is normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Breast ultrasonography
Mammography
Repeat clinical breast examination in 6 weeks
No further evaluation is indicated
A 68-year-old woman is evaluated for reduced vision and flashing lights in her left eye that began this morning. This was preceded by floaters in her left eye, first appearing several days ago and now with increasing frequency. She has no other symptoms. Medical history is significant for myopia. She takes no medications.
On physical examination, she has an inferior visual field defect in her left eye. Visual fields in the right eye are normal. Pupils are equally round and reactive to light and accommodation. Visual acuity is 20/60 in the left eye and 20/20 in the right eye. Nondilated funduscopic examination is normal.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Retinal detachmen
Age-related macular degeneration
Central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal vein occlusionDt
A 77-year-old man is seen for a preoperative medical evaluation before elective aortofemoral bypass. He has exercise-limiting claudication despite participation in supervised exercise programs and pharmacologic intervention. Medical history is also significant for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and aortic stenosis. His last echocardiogram 2 years ago showed moderate aortic stenosis with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Medications are atorvastatin, aspirin, metoprolol, benazepril, amlodipine, metformin, liraglutide, and cilostazol.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Cardiac examination reveals a grade 3/6 systolic ejection murmur at the right upper sternal border that radiates to the right carotid artery. The lower extremities are cool, with no palpable pulses.
Transthoracic echocardiography findings are compatible with severe calcific aortic stenosis with left ventricular ejection fraction of 45%, meeting the criteria for valvular intervention.
Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation regarding surgery?
Aortic valve replacement prior to aortofemoral bypass
Aortic valve replacement plus aortofemoral bypass
Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty prior to aortofemoral bypass
Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty plus aortofemoral bypass
A 56-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. He reports that he is concerned about his cardiovascular disease risk. His father had a myocardial infarction before the age of 55 years, as did his younger brother. Has a 35–pack-year smoking history but quit smoking 3 months ago. He is sedentary. He has no other medical problems, including no history of gastrointestinal bleeding, upper gastrointestinal pain, uncontrolled hypertension, chronic kidney disease, NSAID use, or thrombocytopenia. Medications are varenicline, metformin, lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 28. The remainder of the physical examination is normal.
His 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk is 25% using the Pooled Cohort Equations.
The patient receives counseling on therapeutic lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and weight control and encouragement regarding continued smoking cessation.
Which of the following is the best advice regarding antithrombotic therapy for this patient?
Low-dose aspirin
Aspirin and clopidogrel
Clopidogrel
Rivaroxaban
No antithrombotic therapy
A 27-year-old woman is evaluated for a 2-week history of hives that burn and sting. Individual wheals resolve with darkening of the skin in 1 to 2 days. She also has associated fever and joint pain. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Other than acetaminophen for fever and joint pain, she takes no medications.
On physical examination, temperature is 38.3 °C (101 °F); other vital signs are normal. There are 2- to 3-cm wheals with pale red flares on the arms, legs, upper chest, and back. There is faint hyperpigmentation in areas where wheals have resolved. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Urticarial vasculitis
Chronic idiopathic urticaria
Hereditary angioedema
Urticarial drug reaction
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated for a 3-month history of white patches around the eyes, legs, and feet. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Skin findings are shown.
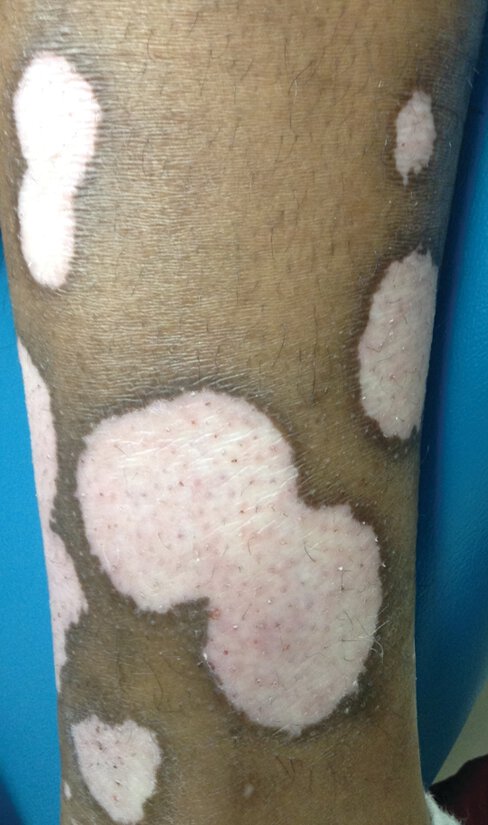
Which of the following tests should be obtained?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Antinuclear antibody
Hepatitis C antibody
HIV testing
A 20-year-old woman is evaluated for a 2-day history of sore throat, nonproductive cough, nasal congestion, headache, and malaise. She has no other medical problems and does not smoke.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. The nasal mucosa is boggy and inflamed, with clear discharge. The pharynx is erythematous. Tonsils are normal appearing. Tympanic membranes are clear. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
A SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test result is negative.
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Acetaminophen
Amoxicillin
Guaifenesin
Intranasal zinc
A 46-year-old woman is seen for a routine evaluation after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery 2 months ago. She is doing well and has lost 13.6 kg (30 lb). She recently initiated an exercise program. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Her current medications are metformin, low-dose insulin glargine, chlorthalidone, lisinopril, atorvastatin, vitamin B12, vitamin D, thiamine, calcium, and a multivitamin with iron and folate.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 132/78 mm Hg; the remainder of the physical examination is normal.
Home glucose monitoring data for the previous 7 days show average fasting blood glucose of 108 mg/dL (6.0 mmol/L). She has experienced no episodes of hypoglycemia.
Which of the following medications should be discontinued for this patient?
Insulin glargine
Atorvastatin
Lisinopril
Metformin
Vitamin D and calcium
A 56-year-old man is evaluated for erectile dysfunction that began insidiously 1 year ago. He reports that his libido and mood are good. He is in a monogamous relationship with his wife. He runs on a treadmill for 30 to 45 minutes three to four times weekly, and he has no cardiovascular symptoms. The patient's medical history is also significant for coronary artery bypass graft surgery 4 years ago, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension. Medications are metoprolol, losartan, aspirin, and atorvastatin.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 24. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show an early morning serum total testosterone level of 380 ng/dL (13.18 nmol/L).
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Oral sildenafil
ECG
Exercise stress test
Intramuscular testosterone
A 60-year-old woman is evaluated for bone health during a routine wellness visit. Her mother was treated for a hip fracture after a fall at the age of 65 years. The patient is sedentary and has a 30–pack-year history of cigarette smoking but quit smoking 2 months ago. She has no medical problems and takes no medications.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal. Her weight is 56 kg (123 lb); BMI is 21.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Assess fracture risk with a clinical assessment tool
Bone mineral density measurement
Initiate alendronate
Serum vitamin D measurement