The temporary molecule made from copying DNA.
What is RNA?
The location of translation.
What is the ribosome?
Two differences between DNA and RNA.
What are stability, sugar, strands, heritability, location?
What is semiconservative?
The stage of mitosis shown in this picture.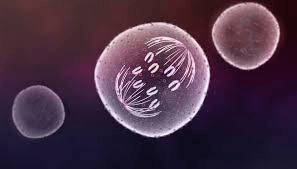
What is anaphase?
The DNA sequence that would result in the following mRNA sequence: AUUCGGAC
What is TAAGCCTG?
What is leucine?
A mutation in which there is a single nucleotide change that results in one amino acid of the protein changing.
What is missense?
The stages of interphase in order.
What is G1, (Go), S, G2?
The stage of mitosis in which the nuclear envelope begins to disappear.
What is prophase?
The location of transcription.
What is the nucleus?
Two names for the end production of translation.
What are protein and polypeptide?
A mutation that results in the incomplete formation of a protein.
What is nonsense?
The stage in which the cell is performing protein synthesis and expressing its genes.
What is G1?
The stages of mitosis where sister chromatids are still fused at the centromere.
What are prophase and metaphase?
The enzyme responsible for making mRNA.
What is RNA polymerase?
The amino acid attached to the tRNA if the anticodon read CCC.
What is glycine?
The mutation type that tends to lead to new variations of a trait.
What is missense?
The way in which you know a cell is in interphase when examined under the microscope.
What is its DNA will be in chromatin form?
What are spindle fibers?
The purpose of transcription.
What is to ensure that DNA remains protected in the nucleus?
The amino acid brought if the DNA read TTA.
What is asparagine (asn)?
The name of the enzyme responsible for mutations.
What is DNA polymerase?
The amount of cells expected to be in interphase if you counted 673 onion root cells under the microscope.
What is 606?
The purpose of mitosis NOT cytokinesis.
What is to ensure the DNA is divided equally between the two daughter cells?