A 60 year old patient with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, HTN, Polycythemia Vera presents with sudden onset painless loss of vision of one eye. Fundoscopic exam show is show below. What is the diagnosis?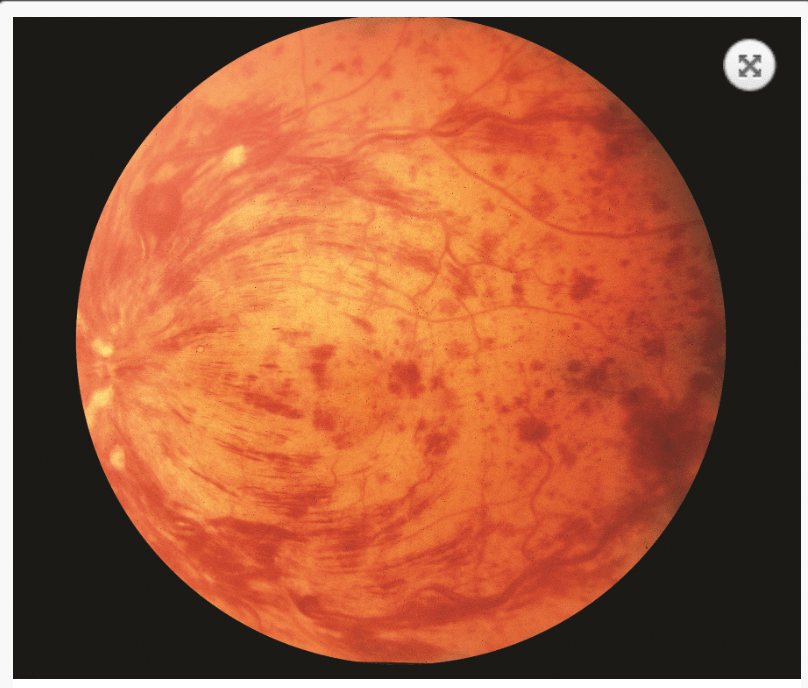
Retinal Vein Occlusion
Patient with asymptomatic LBBB, planned for surgery. What is your next step in management?
Clear for surgery
Patient presents to clinic with a whitish/gray spot on her conjunctive. Fasting blood sugar is normal. A photo of the spot is shown. What is the diagnosis?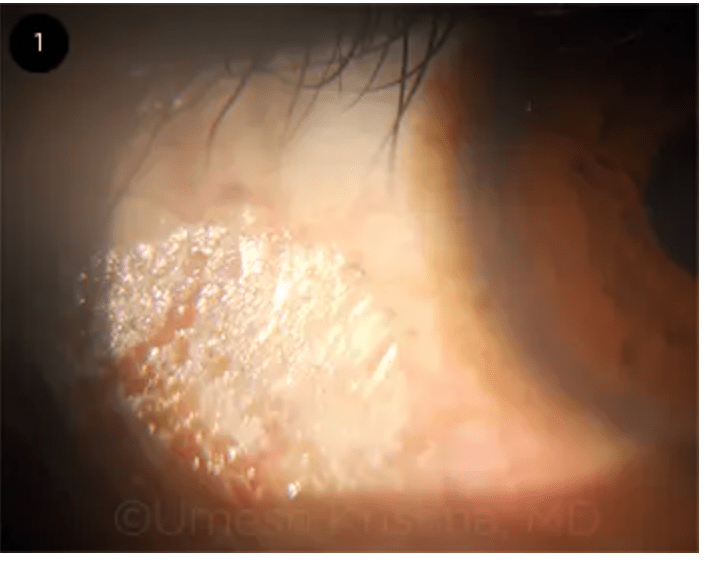
Vitamin A deficiency causes Bitot’s spots through metaplasia of the conjunctival epithelium and tangles of keratin admixed with Corynebacterium xerosis, which dwell in the stratum corneum of the conjunctiva. The typical foamy appearance is due to gas produced by these bacteria.
Are antipsychotics (typical and atypical) FDA approved for management of delirium?
No
The USPSTF recommends that all persons planning to or who could become pregnant take a daily supplement containing how much folic acid?
Grade A recommendation: Take a daily supplement containing 0.4 to 0.8 mg (400 to 800 mcg) of folic acid.
Patient presents with sudden new onset flashes or streaks of light, showers of black dots & a wavy curtain for the past three days. On Fundoscopy: Retina appears folded or elevated. What is the next step in management?
This patient has retinal detachment. Next step in management is emergent ophthal evaluation treatment to reattach the retina. Ex. Pneumatic Retinopexy
Name 2 commonly used cardiovascular risk scores to risk stratify patients pre-operatively?
The Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI)
The American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP)
Patient presents with from a rural area with diarrhea and on exam you notice vertical white lines on his nails as show. 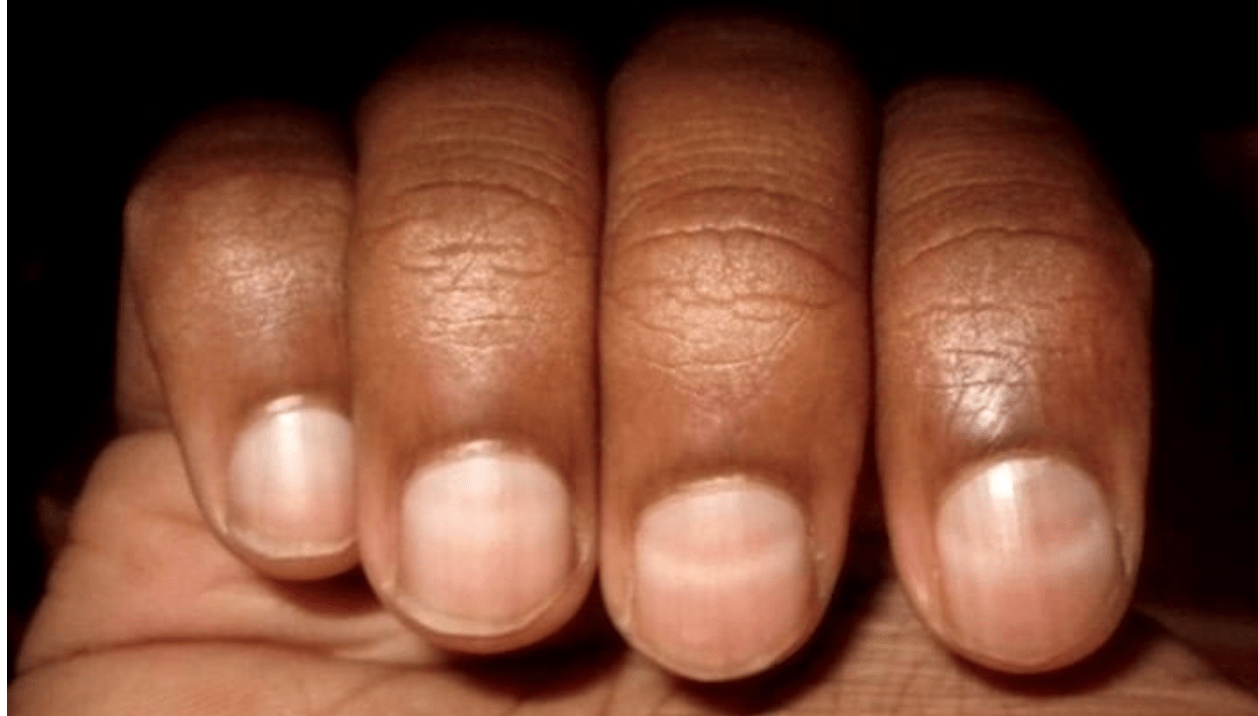 What is the diagnosis?
What is the diagnosis?
Arsenic poisoning
A young patient with multiple complaints referrable to multiple organ systems >8. Exam reveals no matching physical findings to symptoms. What is the course of treatment for this patient?
Schedule monthly appointments with PCP for reassurance and decrease utilization of healthcare resources.
The USPSTF recommends screening for gestational diabetes in asymptomatic pregnant persons at how many weeks gestation?
Grade B recommendation to screen at 24 weeks of gestation or after.
Patient present to clinic for annual exam. Fundoscopic exam reveals A-V nicking as seen below. What are your next steps in managment?
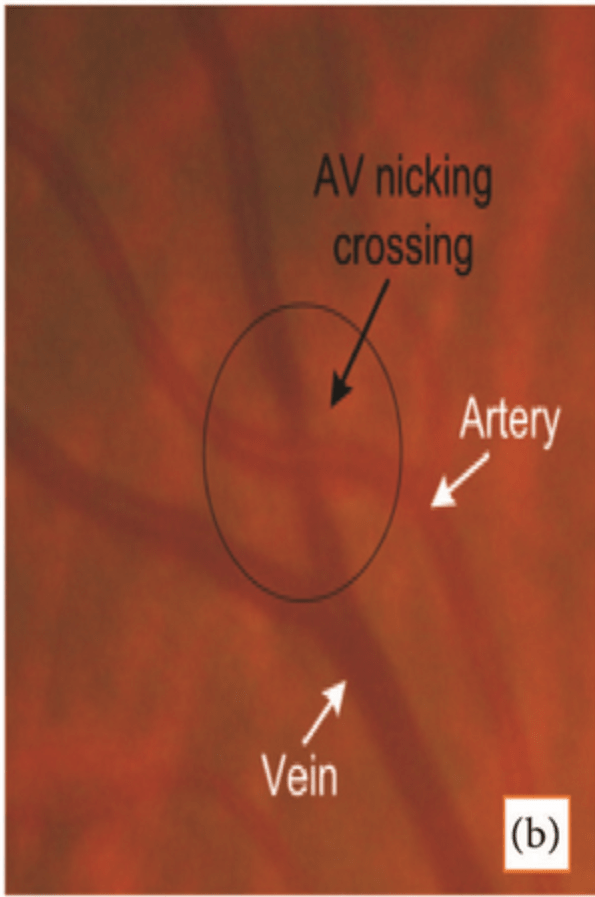
Begin antihypertensive treatment. Indicator for hypertension, and patient is at increased risk for stroke.
Patient presents for follow up prior to her scheduled surgery. She is on anti-TNF medications for a rheumatological condition that is well controlled. What recommendation do you tell the patient prior to surgery?
Hold anti-TNF medications for 2 weeks before surgery and restart 2-4 weeks after the surgery. As this increases the risk for would dehiscence.
Patient with a complicated ICU stay on TPN develops alopecia, periorificial pustular rash, anemia and loss of taste. What is the diagnosis?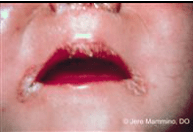
Zinc Deficiency
Elderly patient with hx of anxiety gets admitted and request a medication to relieve her anxiety. Overnight she develops hyperthermia, tachycardia, and decreased bowel movement and urinary retention. What caused the patient mental status change?
Anticholinergic delirium likely due to Benadryl.
An otherwise healthy pregnant women presents at 14 weeks. Routine prenatal visit has S3 sound and a II/IV systolic murmur at the apex.
What is your next step in management?
DO NOTHING and continue present care, no Echo is needed. This is a functional heart sound and murmur due to normal volume overload of pregnancy.
SAVE THEM SOME SMONEY!
Patient presents with sudden onset of painless unilateral vision loss, has hx of HTN, Afib, DM, CKD, PVD. Fundoscopic exam is notable for cherry red spotin the mucula. What is the most likely etiology of his presentation?
Patient has a retinal artery occlusion likely from emboli.
Patient with a bileaflet mechanical aortic on warfarin planned to undergo endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy for cystic pancreatic lesion. Has hx of epistaxis requiring nasal packing for 2 days one year ago. Cardiac workup 2 months ago was unremarkable. what is the next best step in management of this patient AC prior to surgery.
Stop Warfarin, then proceed with biopsy when INR < 1.5.
Mechanical bileaflet aortic valve is considered moderate thrombotic risk or hihg risk when 1 or more additional risk factor like HTN present
Recommendations: Patient with moderate to high thrombotic risk should hold warfarin for 5 days until INR <1.5 and then perform the procedure.
Compared to very high thrombotic risk patients ( mechanical mitral valve) requires peri-operative bridging with LMWH or unfractionated heparin. Started once INR <2.0
Patient is post-op in the ICU, and develops nausea and is given phenothiazine and IVF. The following day the patient develops horizontal nystagmus and diplopia, and ophthalmoplegia. What is the likely diagnosis?
Wernicke Encephalopathy 2/2 thiamine deficiency. Always ask about ETOH use!
A 70 year old male reports his wife passed a few years ago. He has a loss of appetite with weight loss for the past 6 months. He appears depressed. He also reports he is hearing voices and seeing things on the wall. What is the likely diagnosis?
Depression with psychotic features
Patient presents at 9 weeks gestation presents with increased frequency and urgency. She is febrile to 102F, BP 124/84 mmHg, pulse 96/min and RR 18/min. There is mild tenderness to palpation in the suprapubic region, however no CVA tenderness. Labs are notable for peripheral leukocytosis and marked pyuria. She is admitted for acute pyelonephritis and is started on antibiotics. Which antibiotics should you avoid prescribing this patient?
Macrobid (avoid in first trimester )an association with birth defects has been reported including oral clefts.
Bactrim (avoid in first and at term) an association with esophageal atresia.
Patient is status post cataract surgery one week ago and presents with eye ache and decreasing vision, however otherwise feels well. He is afebrile, and conjunctiva is injected with white deposits in the anterior chamber. Slit lamp reveals intraocular WBCs. What is the diagnosis?
Endophthalmitis
A 80 year old patient presents for pre-operative assessment prior to his elective hip replacement. What is the best metric for determining the likelihood of 30 day post-operative complications and discharge to a nursing facility?
Frailty determination
Frailty independently predicts postoperative complications, length of stay, and discharge to a skilled or assisted-living facility in older surgical patients and enhances conventional risk models.
Patient presents with nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, and abdominal pain. Labs are notable for Ca level 11 and elevated LFTs. Fundoscopic exam reveal blurring of the disk margin (papillary edema). On further questioning, patient reports taking multiple vitamins. What is the diagnosis?
Vitamin A toxicity
Young patient with new onset upper GI bleed at a party. Labs are notable for Na 136, K2.7, Cl 80, Bicarb 35, Urine Cl- <15. BMI 24. What is the likely diagnosis and what pharmacotherapy is FDA approved for treatment?
Bulimia Nervosa and Fluoxetine
A pregnant women presents with malaise, headache, nausea, poor appetite and abdominal pain, has moderate elevation of LFTs ~ 150's. PT, Direct bilirubin, and ammonia are elevated. Liver biopsy shows microvesicular fatty change. What is the diagnosis and treatment?
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy and resolved rapidly after delivery of the baby.
-Due to impaired mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and abnormal accumulation of fat within liver cells (microvesicular steatosis)