The LDL level above which you can start high intensity statins without calculating ASCVD risk
> 190 mg/dL
The mechanisms of action of tramadol (must have at least two, be specific)
Weak agonist for mu opioid receptor
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake (SNRI)
(Very weak delta and kappa opioid receptor agonist)
The diagnostic test of choice for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, how it is performed, and what sign you are looking for (2/3)
 The Dix-Hallpike maneuver
The Dix-Hallpike maneuver
Turning the patient's head in the pictured way (towards the right) will result in upbeat and torsional nystagmus to the affected ear
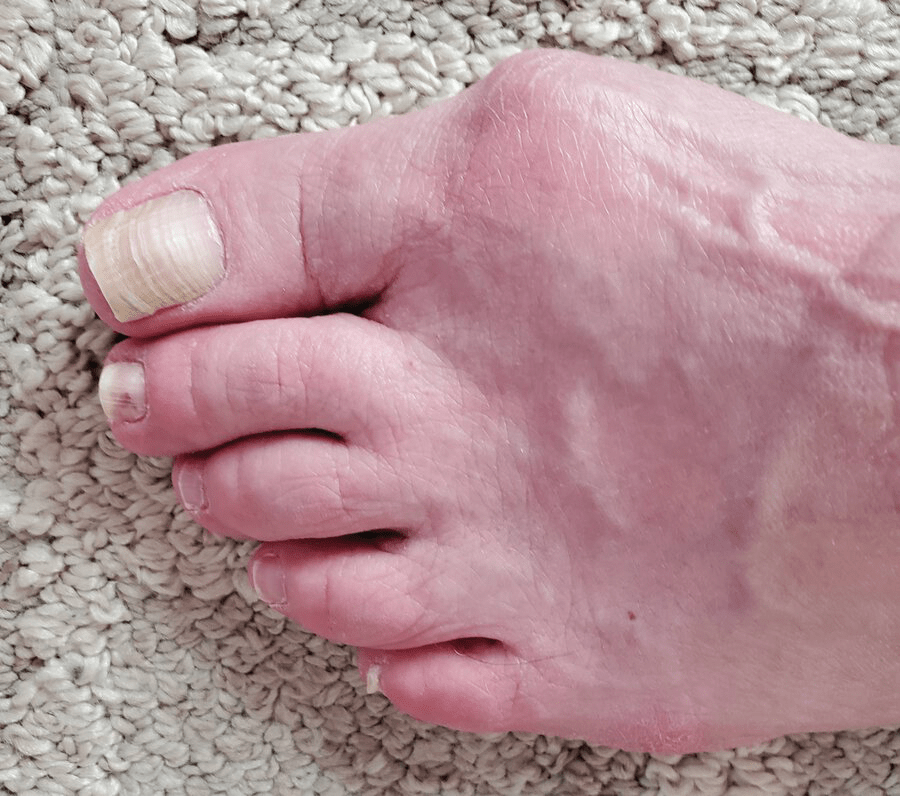
Bunion
Name causes of chronic cough (at least four)
Upper airway cough syndrome (aka post nasal drip), GERD, asthma, smoking, ACE inhibitor use, non asthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis
A 45-year-old man is evaluated during a routine examination. He does not exercise. He has never smoked and drinks one to two beers, 4 nights per week. There is no family history of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. For the purpose of calculating the patient's risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the patient reports that he is Black.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg. BMI is 28, and waist circumference is 106 cm (42 in).
LDL 148 mg/dL, HDL 38 mg/dL, Triglycerides 160 mg/dL, fasting BG 106 mg/dL
ASCVD risk score is 4.3%
The proper next step is...
Intensive diet and exercise regimen
Medications that are high risk to take with opioids (name at least three)
Benzodiazepines, sedative/hypnotic agents (zolpidem, eszopiclone, etc.), muscle relaxants (carisoprodol, chlorzoxazone, or methocarbamol), antipsychotics (haloperidol, quetiapine, or risperidone), pther central nervous system depressants (alcohol or street drugs)
Vertigo cause distinguished by sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, episodic vertigo that lasts minutes-hours but less then 24 hours, normal MRI, and Dix-Hallpike maneuver without vertigo or nystagmus
Meniere Disease

Initial treatment of cervical radiculopathy
Conservative treatment with simple analgesia, exercises, and physical therapy (as long as symptoms do not progress!!!)
Disorder that is characterized by medically unexplained symptoms that cause emotional distress and psychosocial impairment
Somatic symptom disorder
A 58-year-old man is evaluated at a follow-up appointment. He is feeling well and has no symptoms. Medical history is significant for hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He exercises by walking 4 miles daily. He has never smoked and drinks one or two glasses of wine per day. Current medications are lisinopril, metformin, canagliflozin, and aspirin. He is also receiving maximum-dose therapy with atorvastatin and ezetimibe. His baseline LDL cholesterol level before starting atorvastatin and ezetimibe was 220 mg/dL (5.70 mmol/L).
On physical examination, blood pressure is 124/73 mm Hg. BMI is 28.
HDL 35 mg/dL, 140 mg/dL, total cholesterol 190 mg/dL, triglycerides 100 mg/dL
The most appropriate additional treatment is...
Proprotein converts subtilizing/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) monoclonal antibody
First line and second line Medications that can be used for treatment of opioid induced constipation in chronic opiate patients, first line
First line: laxatives (miralax, Senna, etc.)
Refractory: methylnaltrexone
The three components of the HINTS exam are

Posterior hip pain caused by the FABER (Flexion, ABduction, and External Rotation) test suggests this problem
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
The FABER (Flexion, ABduction, and External Rotation) test may cause posterior hip pain in the presence of sacroiliac joint dysfunction, groin pain with an intra-articular cause, and lateral hip pain with greater trochanteric pain syndrome.
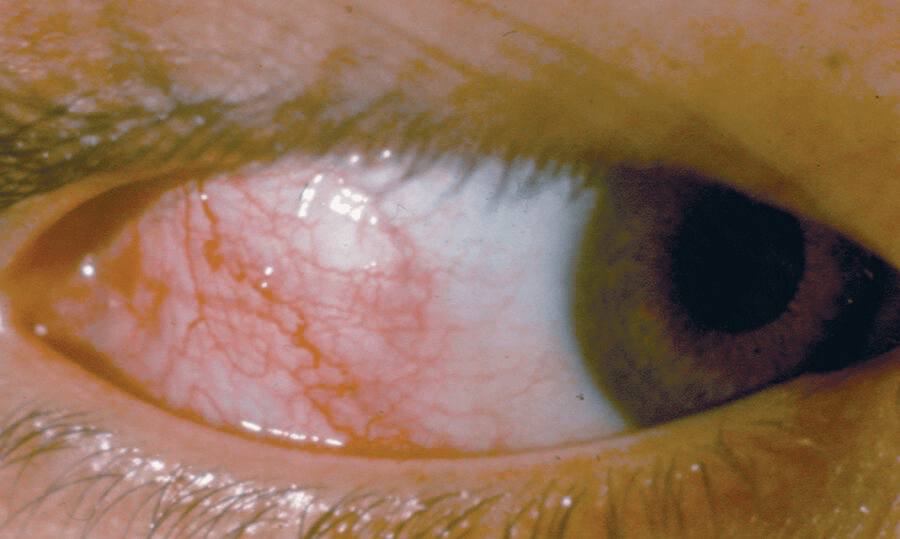
Patient has redness, tearing, irritation of right eye that began 1 day ago. No other symptoms, no past medical history.
Name this pathology
Scleritis
The classic presentation of episcleritis is an abrupt onset of unilateral eye redness due to dilated episcleral blood vessels, irritation, and tearing, with no pain, photophobia, or change in vision.
The cardinal sign of scleritis is edema of the sclera often associated with an underlying violaceous discoloration of the sclera and intense dilation of the episcleral blood vessels, accounting for the red eye.
A 72-year-old woman is evaluated during a routine follow-up visit after an acute myocardial infarction and coronary artery bypass surgery. Medical history also includes diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. She has been adhering to a Mediterranean low–trans fat diet and daily maximum-dose atorvastatin. Other medications are aspirin, clopidogrel, empagliflozin, lisinopril, metformin, and metoprolol.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 36
Total cholesterol 215 mg/dL, LDL 85 mg/dL, HDL mg/dL, triglycerides 128 mg/dL
The most appropriate next step is...
Add ezetimibe
To discharge a patient from an acute care hospital WITHOUT being required by law to check the CURES database, a patient should be sent with fewer than this number of days supply of opioid
Seven days
Vertigo cause distinguished by preceding viral infection, sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, either episodic or persistent vertigo
Labrynthitis
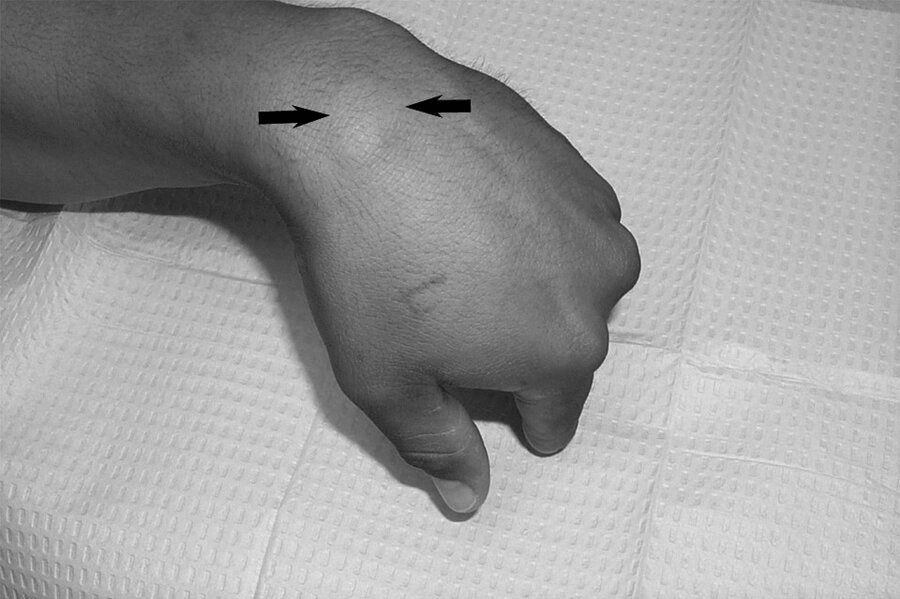 Initial treatment for the pictured pathology
Initial treatment for the pictured pathology
Ganglion cysts may be treated with aspiration. if they recur, surgery may be indicated.
Criteria for bariatric surgery referral
Recent guidelines from 2022:
BMI >=35 kg/m^2
OR
BMI >=30-34.9 kg/m^2 with metabolic related comorbidities (DM, HLD, etc)
OR
BMI >=27.5 kg/m^2 and Asian ethnicity (Chinese, Indians, Japanese, etc.)
(Many question banks may not have these updated guidelines, but your boards will!)
A 48-year-old man is evaluated following a recent hospitalization for hypertriglyceridemia-related acute pancreatitis. Evaluation for acquired hypertriglyceridemia is negative. He consumes a very-low-fat diet and avoids refined carbohydrates and alcohol. Medications are simvastatin and an omega-3 fatty acid supplement.
On physical examination, BMI is 25. Bilateral xanthelasmas are present. Fasting triglyceride level is 630 mg/dL (7.12 mmol/L).
The most appropriate treatment is...
Fenofibrate
California law requires that a prescription for naloxone be offered to a patient when chronic opioid dosage is greater than how many MMEs per day
90 miligram morphine equivalents
Vertigo cause distinguished by preceding viral infection, either episodic or persistent vertigo, and without hearing loss
Vestibular neuritis
Syndrome that presents with nonradicular and anatomically widespread symptoms (weakness, numbness, paresthesia, and pain) affecting the arm, neck, and shoulder; symptoms worsen with repetitive overhead activities.
Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome
Treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis in contact wearer
Ophthalmic fluoroquinolone (e.g. ofloxacin)
Pseudomonas should be covered when patients wear contacts
In patients without contacts, trimethoprim-polymyxin ophthalmic solution can be used instead