Define gene
Genes are sections of DNA that code for a specific trait.
Other than the events occurring during meiosis, what are two other things that produce variation.
1. Mate choice
2. sexual reproduction
3. environment
4. mutations
5. fertilisation
What sort of cell would these chromosomes be found in?
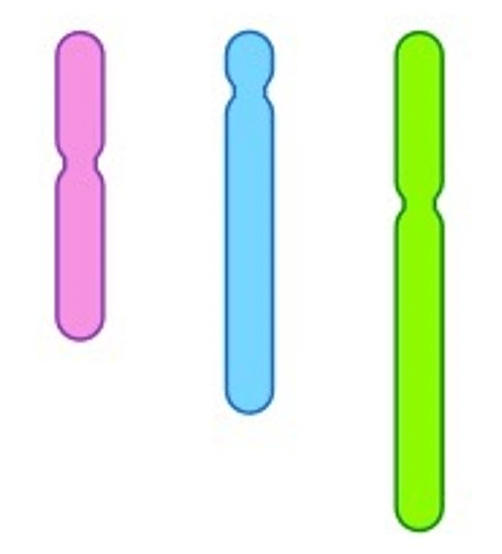
A haploid cell e.g., a gamete.
What sort of letter indicates a dominant allele?
A capital letter.
Meiosis is a type of cell division which produces gametes.
List the 3 events during meiosis that produce variation.
1. Crossing over
2. Independent assortment
3. Segregation
What sort of cell would these chromosomes be found in?
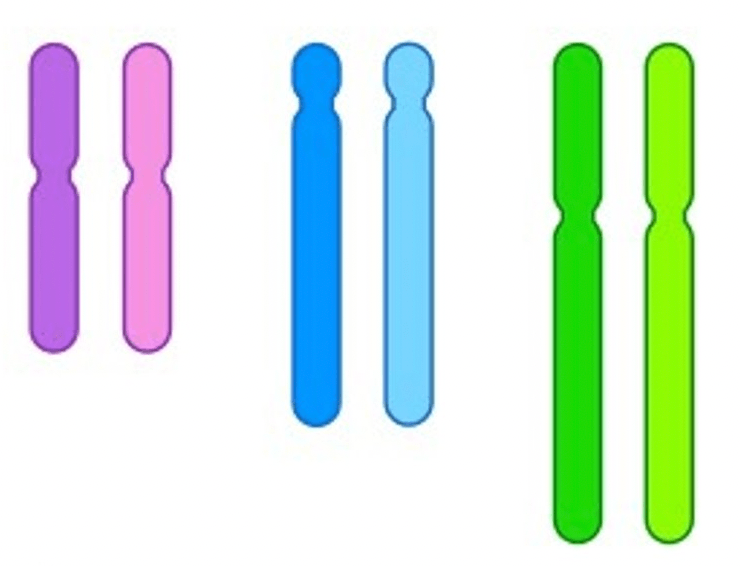
A diploid cell e.g., a body cell.
What is the genotypic ratio?
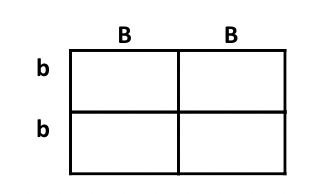
100% dominant
Diploid
A cell with 2 sets of chromosomes. e.g., body cells.
Define crossing over
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes can swap pieces of chromosome.
This breaks up gene combinations that were inherited together.
This increases variation between gametes.
What is this event called?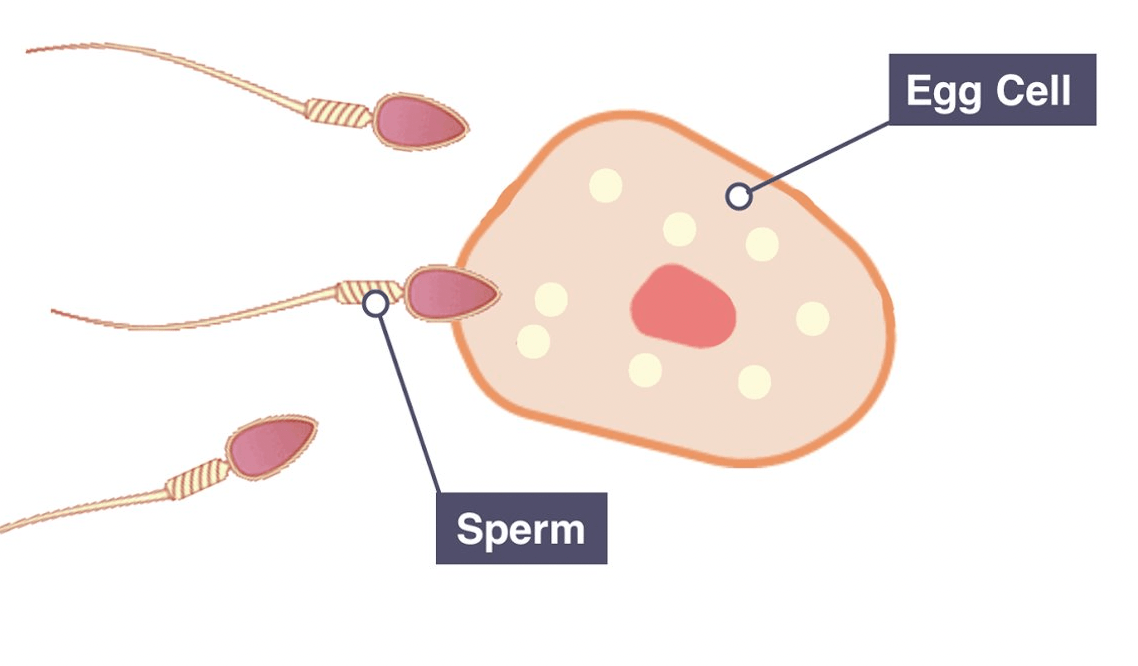
What is the phenotypic ratio?
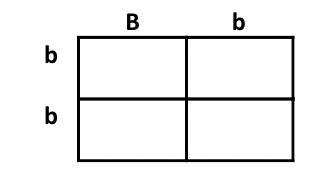
1 dominant: 1 recessive
Define nucleotide (explain what it is made of, and what it makes).
A gene is made up of repeating units called nucleotides.
Nucleotides are made up of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
There are 4 types of bases;
adenine (A)
thymine (T)
cytosine (C)
guanine (G)
Define independent assortment
During metaphase, homologous chromosomes line up randomly.
Therefore, the combination of alleles in the resulting gamete is different.
In humans, as there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, this leads to 8 million possible combinations.
What event is this?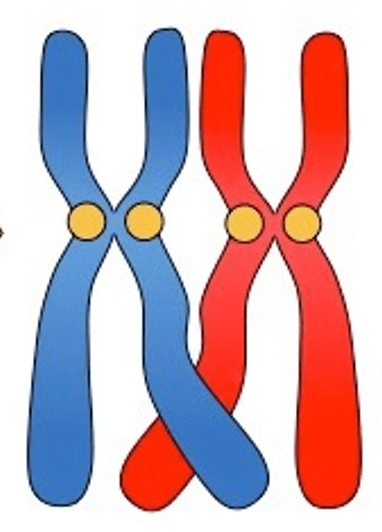
Crossing over
What is the percentage of each of the 4 squares in a punnett square?
25%
Define homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes of the same length and genes in the same place but alleles may be different.
Similar but not identical.
Define segregation
During meiosis, it is random which allele goes into which cell during anaphase.
As each chromosome has two alleles - there is a 50% chance an allele will end up in either gamete.
Result is variation in gametes.
What event is this showing?
Independent assortment.
Parent 1 is Bb. They express the dominant phenotype. Each letter represents an allele. But what do the letters actually represent?
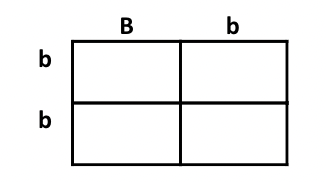
Gametes