Blood type is an example of what type of inheritance?
Multiple alleles
What does a capital letter indicate
dominance
What do we call a heterozygous individual who do NOT have a disease?
Carrier
An organism with 2 different alleles for a trait is called a ______.
heterozygous
The tool used to show all of the possible outcomes of a genetic cross.
Punnett square
What percent of offspring will be homozygous dominant?
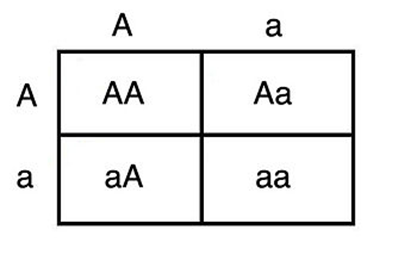
25%
What percent of the offspring of heterozygous parents will be homozygous recessive?
25%
Hair color is an example of which type of inheritance, when groups of alleles control the trait?
polygenic inheritance
Cross a homozygous dominant parent with a heterozygous parent. What are the genotypes
75% homozygous dominant, 25% heterozygous
Neither trait is dominant over the other and the two blend together.
Incomplete Dominance
A segment of DNA, controls inherited traits
gene
