Eye color, presence of dimples, hairline shape, and height are all ___, which are the characteristics passed down from parents to offspring through genes.
Complete the Punnett square.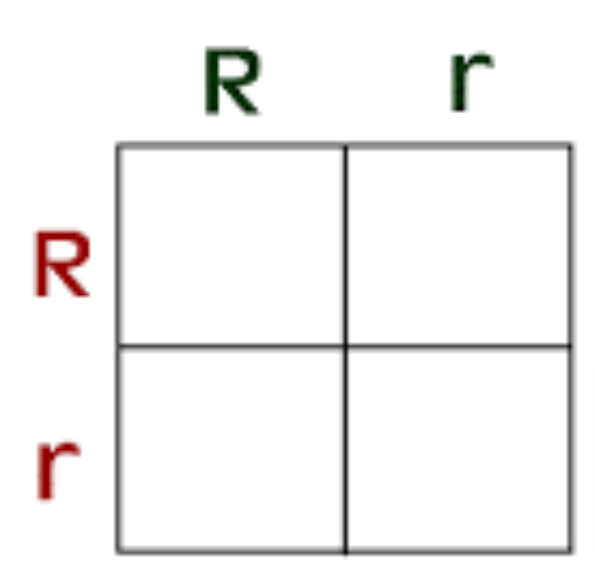
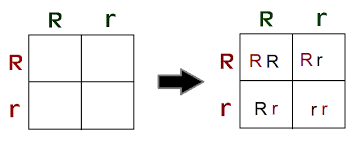
A purebred tall pea plant is crossed with a hybrid pea plant. Create a Punnett Square to represent this cross.
A unicellular organism is made of one cell. A multicellular organism is made of many cells.
This man is known as the “father of genetics” because of his discovery of the principles of heredity from his experiments with pea plants.
Gregor Mendel
What is the difference between a dominant allele and a recessive allele?
A dominant allele is one whose trait always shows up when the allele is present. A recessive allele is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present.
What is the probability of the offspring phenotype?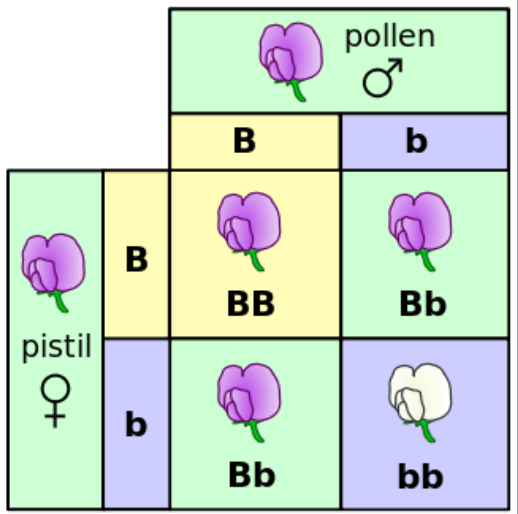
75% purple
25% white
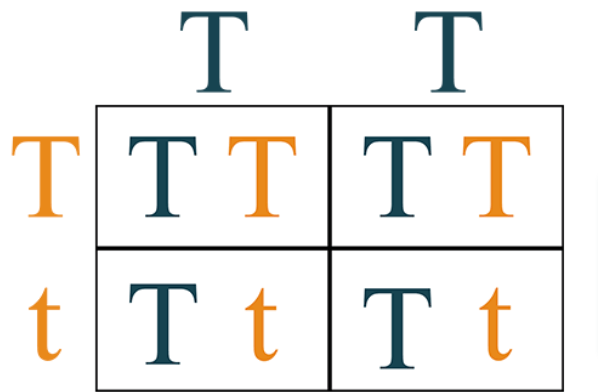
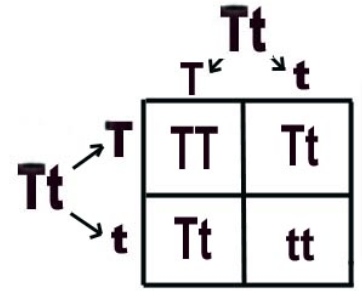
Cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for height. (T = tall and t = short)
What is the probability of the offspring’s genotype?
25% homozygous dominant (TT)
25% homozygous recessive (tt)
50% heterozygous (Tt)
Explain one difference between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction: unicellular organisms, 1 parent contributes genetic info, offspring identical to parent, little parental care
Sexual Reproduction: multicellular organisms, 2 parents contribute genetic info, offspring have variations compared to parents, more parental care
Give an example of an acquired characteristic and an example of an inherited characteristic.
Acquired Characteristics: scars, dyed hair, playing the violin
Inherited Characteristics: skin color, freckles, length of tail
A purebred organism has a __ genotype, whereas hybrid organism has a __ genotype.
A purebred organism has a HOMOZYGOUS genotype, whereas hybrid organism has a HETEROZYGOUS genotype.
In rats, grey fur color (G) is dominant over white. Cross two heterozygous rats. Find the probability of the offspring genotype and phenotype.
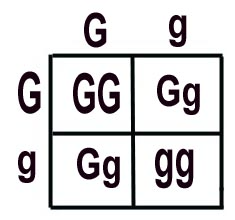
Genotype:
25% GG
50% Gg
25% gg
Phenotype:
75% grey
25% white
In a rare species of dragons, having an Adam’s apple (A) is dominant to not having and Adam’s apple (a).
Cross a homozygous dominant parent with a homozygous recessive parent.
What % will have an Adam’s apple?
100% have an Adam’s apple.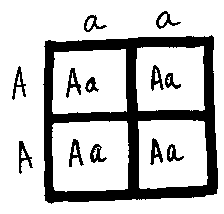
The average dolphin is 8 feet long and 250 pounds. A male dolphin and a female dolphin mate. The female dolphin gives birth to one dolphin offspring. The offspring will nurse from its mother for 2-3 years, providing nourishment and also protection. Do dolphins reproduce by asexual or sexual reproduction? Use the evidence to explain your reasoning.
Sexual Reproduction: multicellular organisms, 2 parents contribute genetic info, offspring have variations compared to parents, more parental care
Mendel crossed two purebred pea plants: one with smooth seeds and one with wrinkled seeds. The F1 generation had all smooth seeds. What seed texture did the F2 generation have?
75% smooth and 25% wrinkled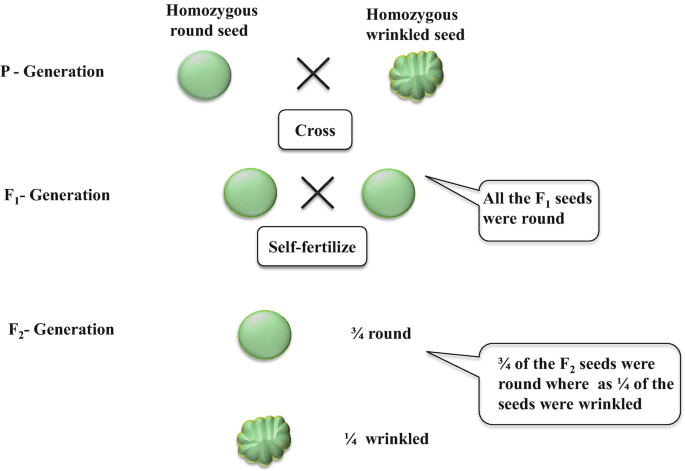
Define probability and give an example.
Probability is a number, expressed as a fraction or %, that describes how likely an event is.
Example: You have a 1/2 or 50% of landing a heads when flipping a penny.
Which pea plant seed color is dominant? Explain.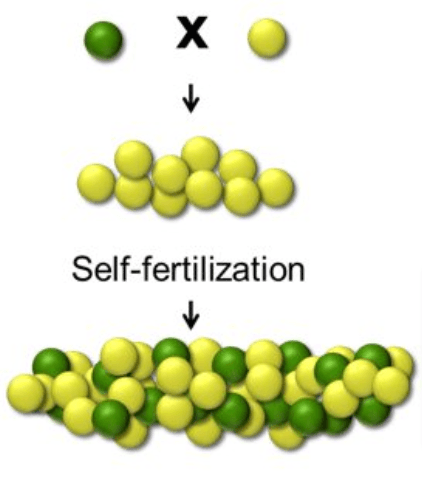
Yellow is dominant over green. Why? When yellow and green are crossed (P generation), the yellow appears and the green is hidden (F1 generation).
In flowers, red color (R) is dominant over white. Cross a hybrid flower with a white flower. Find the probability of the offspring genotype and phenotype.
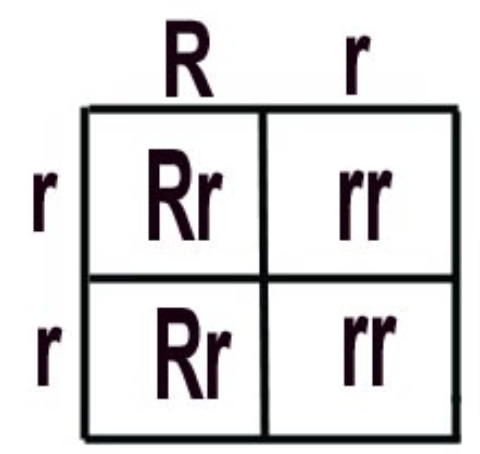
Genotype:
50% Rr
50% rr
Phenotype:
50% red
50% white
Give an example of one organism that reproduces asexually and one organism that reproduces sexually. For each example, give two pieces of evidence supporting your claim.
Asexual Reproduction Examples: bacteria, amoeba, etc.
Evidence: unicellular organisms, 1 parent contributes genetic info, offspring identical to parent, little parental care
Sexual Reproduction Examples: dogs, trees, etc.
Evidence: multicellular organisms, 2 parents contribute genetic info, offspring have variations compared to parents, more parental care
In humans, dimples are dominant over no dimples. List all genetic crosses that will result in all children having dimples. Use the following vocabulary: heterozygous, homozygous dominant, and/or homozygous recessive.
homozygous dominant x homozygous dominant
homozygous dominant x homozygous recessive
homozygous dominant x heterozygous
Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype.
Genotype is an organism’s genetic makeup, or combination of alleles. It determines the organism’s phenotype, or physical appearance.
Having dimples is dominant over not having dimples. A woman with dimples marries a man without dimples. Their child has his father’s phenotype. What are the genotypes of all 3 people?
Mother: heterozygous
Father: homozygous recessive
Child: homozygous recessive
In a certain species of insects, having antennas (A) is dominant over not having antennas (a). Cross an insect without antenna and an insect with antenna who has a parent without antennas. Find the probability of the offspring genotype and phenotype.
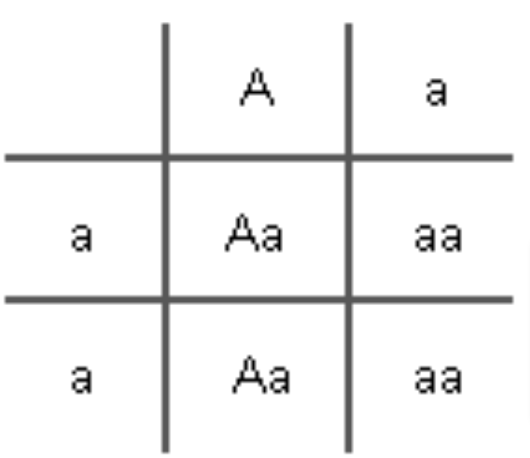
Genotype:
50% Aa
50% aa
Phenotype:
50% antennas
50% no antennas
Do humans reproduce asexually or sexually? Support your claim with 4 pieces of evidence.
Humans reproduce sexually. Evidence: humans are multicellular, have 2 parents contribute genetic info, their offspring have variations from their parents, and more/longer parental care is given
In humans, having a widow’s peak is dominant and having a straight hairline is recessive. Two parents have several biological children. Half of the children have widow’s peaks and half have straight hairlines. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of both parents?
Parent #1
Genotype: heterozygous
Phenotype: widow’s peak
Parent #2
Genotype: homozygous recessive
Phenotype: straight hairline