Draw and label a DNA nucleotide
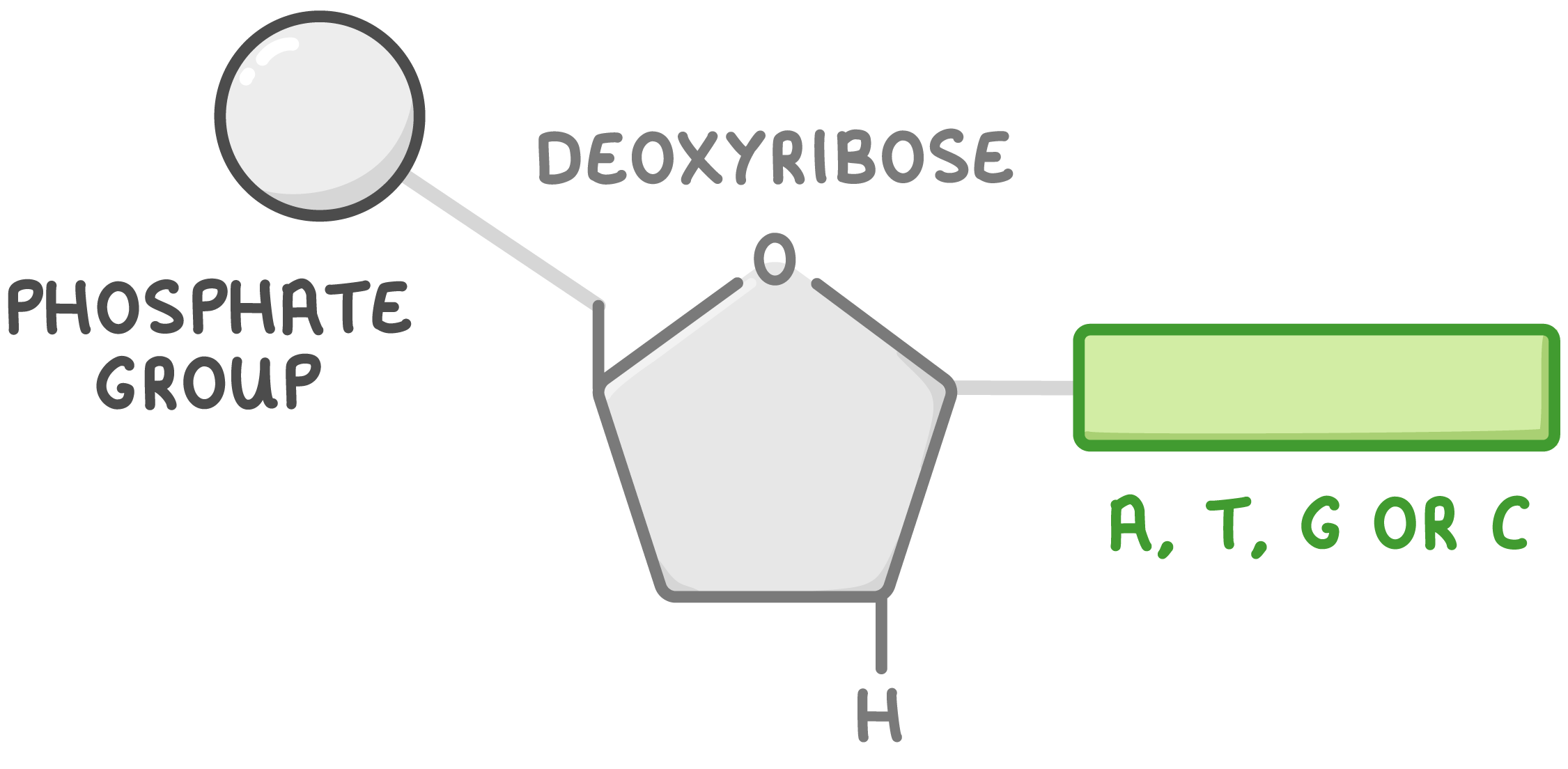
Name the three types of RNA.
mRNA (messanger RNA)
tRNA (transfer RNA)
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
State the stages of Mitosis in order.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
(Hint: Remember PMAT)
State the different between sexual and asexual reproduction, giving an example of each.
Asexual reproduction - creates genetically identical offspring. Examples: binary fission in bacteria, budding in yeast, bulbs of onions, etc.
Sexual reproduction - combines genes from two parents to create non-identical offspring. Examples: sperm + egg in humans, pollen + ovule in flowering plants, etc.
State the two categories of nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Purine and Pyrimidine
Helicase - separates strands by breaking hydrogen bonds
DNA Polymerase - adds nucleotides to template strand to make new strand
HL (Also accepted)
DNA Ligase - connects Okazaki fragments
DNA Primase - adds primers to template strand
Start Codon: AUG
Amino acid: MET
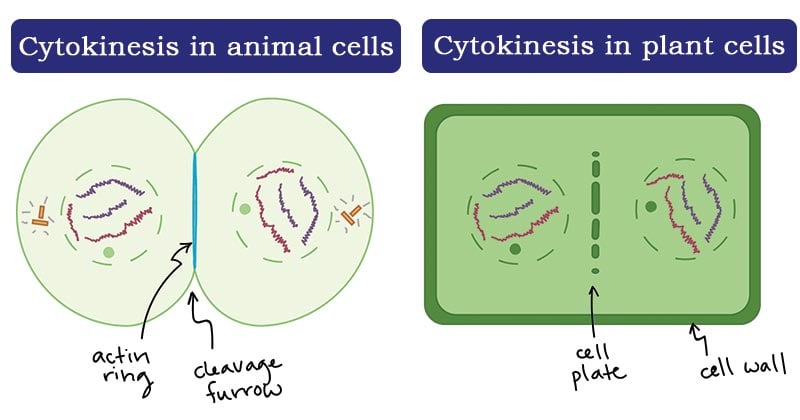
Outline how cytokinesis is different in plant cells and animal cells.
In animal cells the membrane pinches into a cleavage furrow, and eventually fully pinches off into two cells, splitting the cytoplasm.
In plant cells, since the cell wall prevents pinching, a cell plate forms between the two nuclei and eventually merges with the cell walls, separating the cytoplasm.
List three adaptations of seeds for dispersal, including their method of transport.
1. Feathery/winged - move by wind
2. Fleshy fruit - eaten by animals and moved
3. Hooks/barbs - attach to coats of animals
4. Dry and explosive - "explosion" propels them further away
Fill in the blanks:
___________ are formed by DNA wrapping around octomer proteins called __________.
NUCLEOSOMES are formed by DNA wrapping around octomer proteins called HISTONES.
Define: Frameshift mutation
When a base is inserted or deleted in a DNA sequence, shifting the following "reading frame", affecting the codons coming after and producing a very different protein.
Translate the following mRNA sequence:
UUAUGUCCAAGUGA

UUAUG UCC AAG UGA
MET-SER-LYS-Stop
Describe the events occurring in Metaphase I.
Metaphase I - Meiosis
Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along the equator. They are randomly assorted (random order to which side the maternal or paternal chromosomes go). Spindle fibres attach to the centromeres.
Outline self-incompatibility mechanisms in plants.
To prevent flowers from fertilizing the ovule with their own pollen, plants prevent inbreeding with genes.
If the pollen has the same combination of the self-incompatibility genes as the style, the pollen tubes will not form. If they are different, it can form, leading to fertilization.

Outline the process of pre-mRNA splicing.
Non-coding regions called introns are removed, and the remaining exons are spliced together.
Describe how DNA's structure is essential for its replication.
- DNA made of two strands held together by hydrogen bonds.
- During replication, the strands can fully separate by breaking the hydrogen bonds, allowing complementary strands to be created, with the old strands as templates.
- The new DNA is one strand old, one strand new (semi-conservative replication)
Outline how complementary base pairing is used in translation.
tRNA anticodons match to complementary mRNA codons as they are read by the ribosome. This tells the tRNA which amino acid to deliver.

Outline two methods through which meiosis leads to variation.
1) Crossing over - homologous chromosomes pair up in prophase I and cross over, forming a chiasmata, and exchange sections of the chromosome. The resulting chromosomes are non-identical, providing variation.
2) Random assortment in metaphase I - homologous chromosomes line up in pairs, with a random organization of paternal vs maternal chromosomes on either side. When they are pulled apart, there will be a different mix of maternal and paternal genes in each cell, providing variation.
Draw and label the human male reproductive system.

Describe how methylation affects epigenetics.
Epigenetics is the sum of gene expression in the body - which genes are turned off and on.
Methylation is the addition of methyl tags to DNA, which will inhibit the transcription of a gene. (This often occurs in the promoter region, with the methyl tag on cytosine.)
By inhibiting transcription, the gene is not expressed - the protein cannot be made.
Outline how gel electrophoresis can separate DNA fragments for comparing two samples.
Restriction enzymes cut the DNA into fragments.
A positive electrode on the opposite end pulls the negatively charged DNA towards it.
Shorter fragments will move further.
The different bands showing the fragments can be compared.
1) RNA polymerase binds at the start of a gene to DNA and separates the strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds.
2) RNA polymerase uses the template strand and attaches complementary RNA nucleotides.
3) The finished mRNA strand leaves the nucleus, and the RNA polymerase leaves the DNA, allowing the strands to reattach.
Describe how gametes can end up with an even number of chromosomes. Include key terms, and phases in your answer.
Meiosis produces haploid gametes with 23 chromosomes. If non-disjunction occurs, gametes will end up with 22 or 24 chromosomes instead.
Non-disjunction can occur in two phases:
1) Anaphase I - when homologous chromosomes do not separate, both going to one cell
2) Anaphase II - when sister chromatids do not separate, both going to one cell
Outline two examples of feedback loops in the menstrual cycle (positive or negative)
1) Positive feedback - In the follicular phase, FSH stimulates oestriadiol, which is secreated by follice walls. Oestriadiol causes an increase in FSH receptors, which boosts again oestriadiol production.
2) Negative feedback - At very high levels, Oestriadiol inhibits FSH and stimulates LH until ovulation.
3) Positive feedback - LH promotes development of broken follicle post-ovulation into the corpus luteum, which secretes oestriadiol and progesterone.
3) Negative feedback - Progesterone inhbits FSH & LH in the luteal phase.
Outline how CRISPR can be used to treat single based mutations such as cystic fibrosis.
RNA transcript of the desired gene is attached to the CAS9 enzyme. The CAS9 finds the gene in the DNA and cuts it, allowing a replacement to be made, possibly using a guiding template. This can fix a single base mutation.