What types of genes make up about 80% of the human genome?
Regulatory genes (control expression, replication, stability, and transposons)
(~2% encode proteins and 20% are junk)
I should skip learning the scientific names of the model organisms because it is a waste of time
No, that is literally the most important thing to know
In plants that do not undergo alternation of generations, what are the pistil and stamen equivalent to? (sporophyte or gametophyte)
Gametophyte
If a couple plans to have 4 children, exactly how many of them will have the recessive phenotype. The parents genotypes are Hh and Hh.
Cannot determine
Is this trait dominant or recessive?
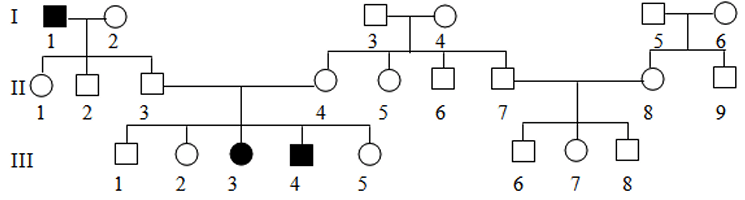
Recessive
What is a multifactorial trait?
Trait determined by multiple factors other than genetics (ex- environmental conditions)
The scientific name for Soil Nematode is
C. elegans (Caenorhabditis elegans)
What are two other names for a tetrad?
Synaptonemal Complex, Bivalent, and Synapsis
What are keywords for multiplying and adding in probability problems?
Multiply "and"
Add "or"
ex- What is the P the child will be born with Red OR Green hair?
What is the genotype of II-3?
Ee
What is the difference between gene expression and regulation?
Expression: How genes are read and used.
Regulation: Mechanisms to control gene expression (When, where, how much)
A scientist looking to study the amount of energy that can be made in an hour by a cluster of chloroplasts would likely study...
A. thaliana
What cell type is described: germ-line cell that is haploid and has replicated chromosomes. It will undergo one more meiotic division and has unequal division of cytoplasm.
Secondary oocyte
What is a test cross and what is it used for?
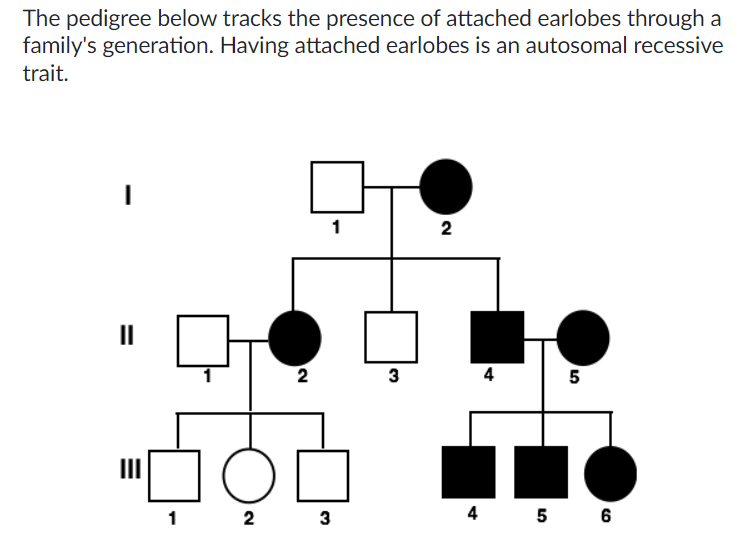
What is the probability that a mating event between III-2 and III-5 will produce a child with attached earlobes?
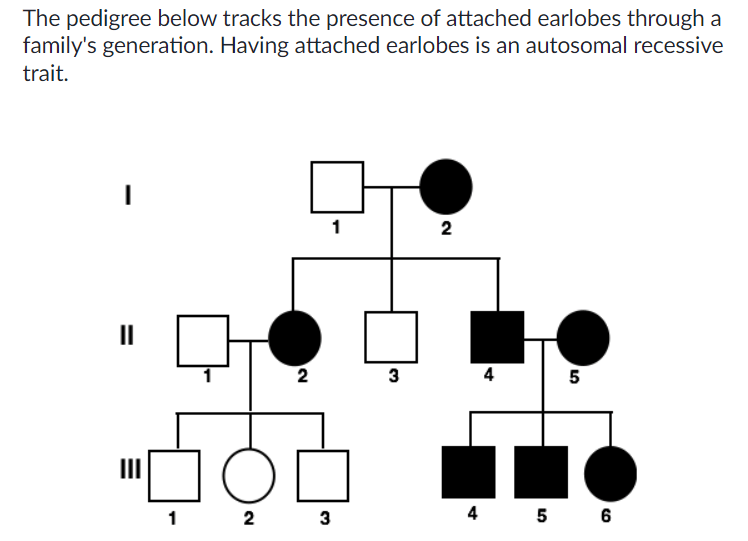
1/2 or 50%
What type of gene is used to make tRNA?
Functional genes
(protein-coding genes are the other class, which is divided further into two more types)
The best model organism to study human diseases is...
M. musculus
What phase of the cell cycle could chromosomes that look like this be found:
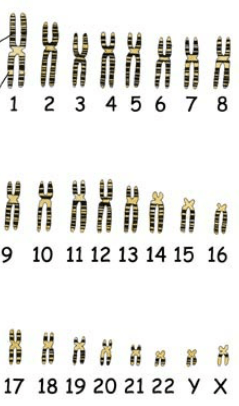
Any phase that is haploid with replicated chromosomes. Telophase 1 (iffy), Prophase 2 (safest answer), Metaphase 2
What is the probability that a blue-eyed woman with brown-eyed parents and a brown-eyed man with a blue-eyed mother has a brown-eyed child?
1/2
What is the probability that in a mating between individuals II-1 and III-6, the child has attached earlobes?
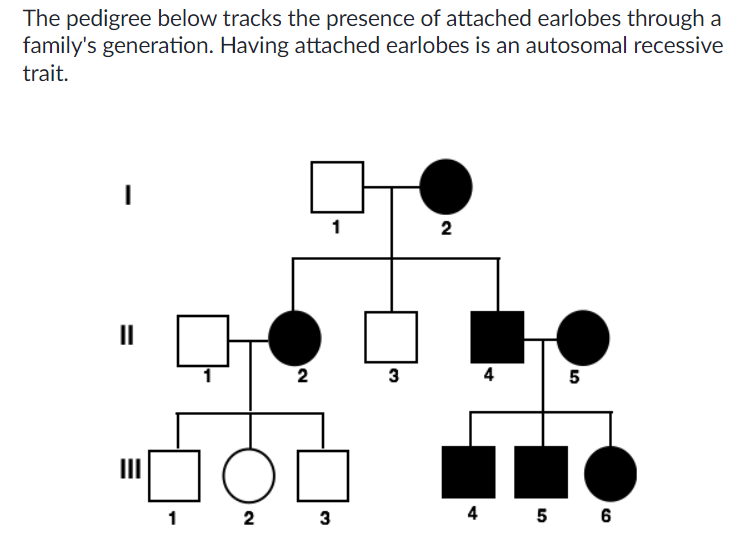
1/4
Determine which subdivision of genetics the following situation applies to:
A researcher is studying how a giraffe population's neck length changes over time by looking at mutations in the GRYA4 gene.
Molecular genetics (since we are looking at the DNA makeup)
If this was just about the necks and not genes, it would fall under population. If it was based on inheritance (such as by making pedigrees) it would be transmission genetics.
The model organism with the least amount of genes is...
E. coli
A kangaroo has 2n=16 chromosomes. During prophase 1, prophase 2, and in the gametes, how many chromatids and chromosomes are there?
prophase 1: 16 c.somes, 32 c.tids
Prophase 2: 8 c.somes, 16 c.tids
Gametes: 8 c.somes, 8 c.tids
What is the probability of a Gg man and Gg woman to have three total children. 2 children with the dominant phenotype and 1 child with the recessive phenotype?
27/64
This is caused by a rare allele. Determine the mode of inheritance. What is the probability that if person IV-1 mates with person IV-8, a child that is affected will be born?
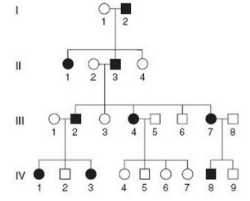
Dominant. 3/4