Phenotype(s).
The dominance represent by two upper case or capital letters:
Example: FF
Homozygous dominant
The "Father of Genetics."
Gregor Mendel.
True or False: Hh is homozygous.
False: heterozygous
The two-letter combination which represents genetic make up.
This roan cow is an example of _________ dominance.
Codominance
The type of plants Mendel studied/experimented with.
Pea plants.
What we call the two-letter combinations to help us complete our punnett squares.
Genotypes.
Homozygous
 When we cross a red flower and a white flower, we get a pink flower.
When we cross a red flower and a white flower, we get a pink flower.
This is an example of ____________ dominance.
incomplete
What we call different versions of a gene.
Alleles.

Percentage of Green pea plants.
50%
Term which means "different".
Heterozygous
Incomplete dominance
Mendel was an Austrian ________.
Monk.

Percentage of homozygous dominant genotypes.
50%
Study of how traits are determined and passed down from one generation to the next.
Genetics
Describes a phenotype where both inherited traits are visible in an offspring.
Codominance
Yellow and green.
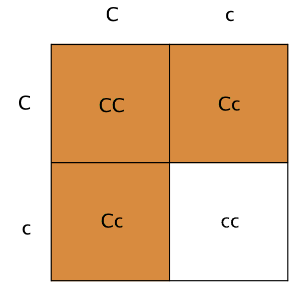
The genotype with the lower case c's (cc) is what we would call...
Homozygous recessive.