The four major ones are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic.
What are oceans?
This is the specific job title for a person who creates maps.
What is a cartographer?
This set of imaginary lines runs north-south and measures distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
What is longitude?
Earth's spinning on its axis causes day and night; this is called this.
What is rotation?
Because this landform's flat, fertile soil is deposited by rivers, it is excellent for farming.
What is a plain?
A large, continuous landmass, like Africa or Asia, as opposed to a self-governing political unit like Canada or Brazil.
What is a continent?
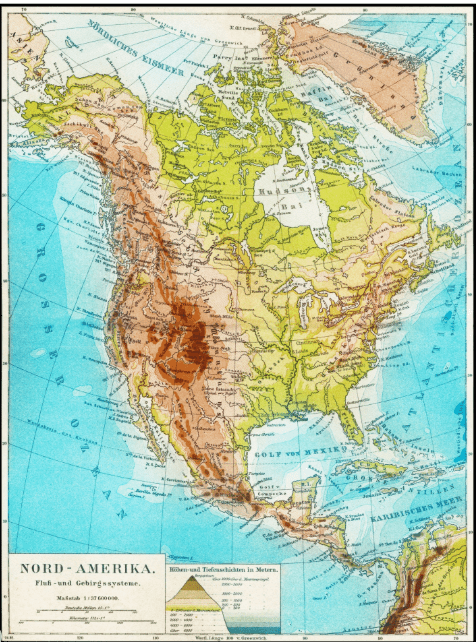 A map that shows mountains, deserts, and rivers is this type, named after the natural world.
A map that shows mountains, deserts, and rivers is this type, named after the natural world.
What is a physical map?
This theme of geography focuses on how people, goods (like those in a supply chain), and ideas move from one place to another.
What is Movement?
The tilt of the Earth's axis, combined with its revolution around the Sun, is the cause of this annual change.
What are seasons?
A supply chain is an example of the Movement theme, but growing food in a river valley is an example of people relying on this.
What is the environment?
The imaginary line called the Equator divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern, or Western and Eastern, halves.
What are hemispheres?
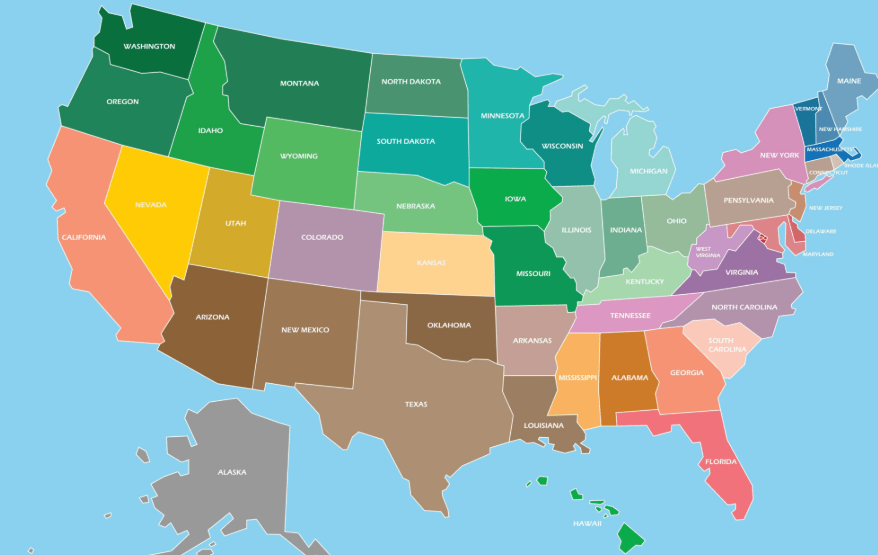 A map that focuses on state borders, capital cities, and country lines is called this.
A map that focuses on state borders, capital cities, and country lines is called this.
What is a political map?
The mental skill of understanding the location of objects and their relationship to one another in space.
What is spatial reasoning?
Areas that share similar temperatures and precipitation patterns, such as the tropical wet zone or the arid zone, are categorized as this.
What are climate zones?
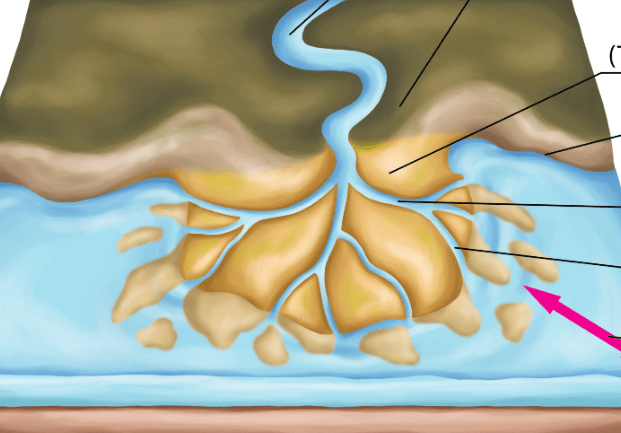 This triangular landform is created at the mouth of a river as it slows down and deposits soil into the ocean or a larger body of water.
This triangular landform is created at the mouth of a river as it slows down and deposits soil into the ocean or a larger body of water.
What is a delta?
Japan, the Philippines, and Hawaii are all examples of this group or chain of islands.
What is an archipelago?
This type of map uses colors and symbols to show specialized data, like population density or rainfall.
What is a thematic map?
Place, Location, Human-Environment Interaction, Movement, and Region make up this core concept in geography.
What are the 5 themes of geography?
The higher you go up a mountain, the colder the temperature gets; this is an example of elevation acting as a factor for this.
What is climate?
The act of building a dam to control a river's flooding, or draining a swamp to create new farmland are all examples of people modifying the environment under this theme.
What is Human-Environment Interaction
This hemisphere is home to the continents of Australia and Antarctica, as well as the Tropic of Capricorn.
What is the Southern Hemisphere?
If you are hiking Southwest and then turn to head North, the change in your direction is equivalent to $135$ degrees on this navigational tool shown on most maps.
What is a compass rose? (simply compass)?
On a mountain near the Equator, you can go from tropical Tierra Caliente at sea level to snowy Tierra Helada at the peak, showing that the effect of this on climate is often more important than the distance from the equator.
What is elevation (or height)?
This astronomical event, combined with the Earth's revolution around the Sun, is the primary reason different regions experience summer, fall, winter, and spring.
What is the tilt of the Earth's axis
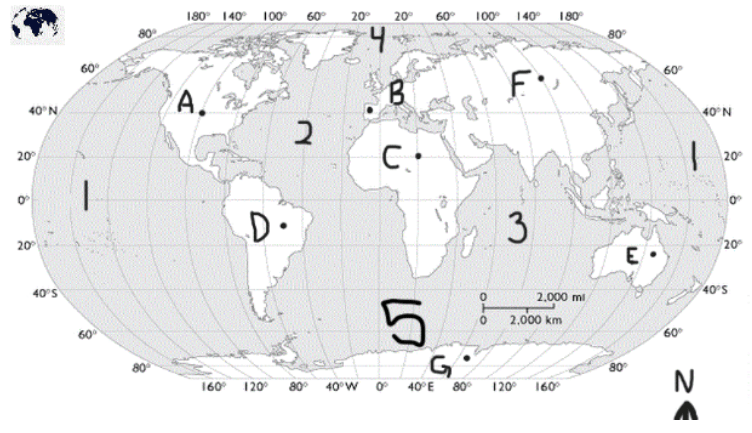
A, B, 2
What is North America, South America, Atlantic Ocean