The reason why winds in the Northern Hemisphere are deflected to the right, causing high-pressure systems to spin clockwise.
Coriolis Effect
Describe the difference between Dew Point and Relative Humidity
Dew point: actual amount of water vapor in the air (temperature)
RH: amount of water vapor relative to the maximum amount the air can hold at the temperature (percentage)
What is the "Ice Age" epoch, characterized by repeated glacial cycles?
The Pleistocene
The primary force responsible for both a rockfall and the gradual, slow process of creep that deposits colluvium. (not gravity)
Mass wasting
What are the 3 main cloud types (describe them)?
Cirrus: wispy clouds at high altitudes, formed of ice crystals
Cumulus: puffy clouds, form when rising air pushes past the LCL.
Stratus: Thin cloud layers, exist on overcast days
During the day islands will get hotter than the ocean because water requires more energy to heat up. Where would you expect there to be high pressure, over the land or the sea?
Over the sea
This is the rate of cooling for a saturated air parcel, which is variable and depends on the air parcel's temperature and moisture content.
Moist Adiabatic Rate
These long ridges of unsorted till can be found at the edge or end of a glacier, marking its maximum advance.
Moraines
The process by which softer rocks erode away more quickly than harder, more resistant rocks, leading to unique formations like arches and rock pedestals.
Differential Weathering
Mass movement can be distinguished in two ways, what are they?
(hint: rockfall, solifluction)
Water content and speed of movement
Pressure Gradient Force, Coriolis, Friction
What is a rainshadow?
a dry region on the leeward (downwind) side of a mountain range that receives very little precipitation.
Found where orographic lifting occurs
What are two examples of positive feedbacks that relate to the glacial and interglacial cycles?
Ice-albedo feedback and Greenhouse gas feedback
Denudation is largely accomplished by a series of processes related to climate. What are these processes and briefly define them.
Weathering: breaking down of rocks
Erosion: removal of weathered material by running water, wind, etc.
Transportation: movement of eroded sediments from their original location
Deposition: final settling of material in a new location
What is an example of physical and chemical weathering?
Physical: wind, frost wedging (water freezes and expands rocks)
Chemical: acid rain and oxidation
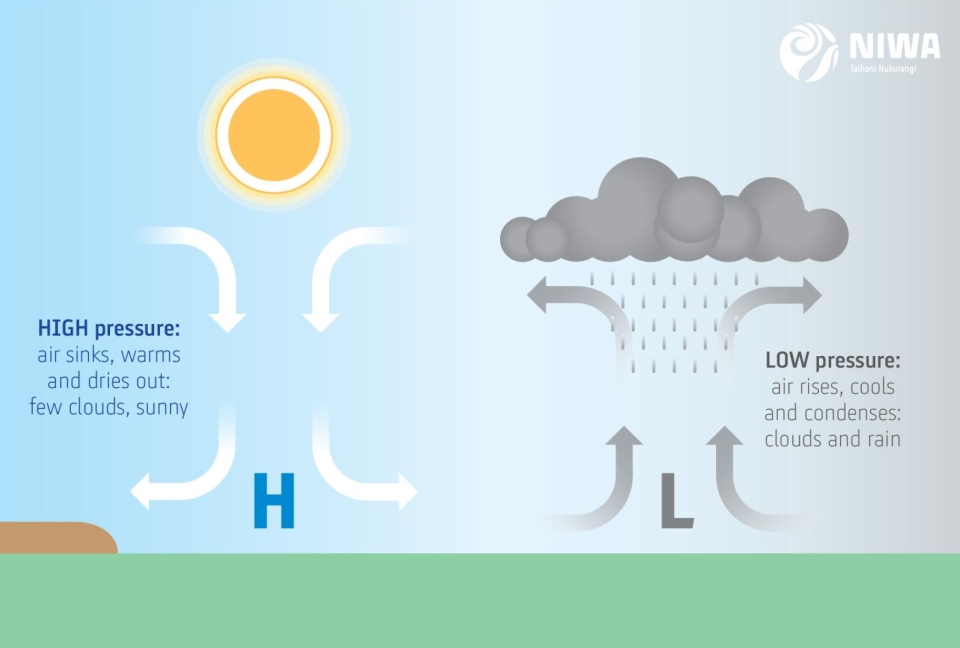
Draw how air will converge and diverge over a surface and in the air aloft in a Low Pressure system.
Describe Collision Coalescence
This is where water droplets will fall and collide with smaller droplets, until they form into larger droplets, and fall as rain.
They will fall as rain once the cloud/wind can no longer sustain them.
Melting of glacial ice has led to this phenomenon?
Rise in sea level
Unlike normal soil creep, which is a near-constant process, this movement is primarily driven by the repeated freeze-thaw cycles that characterize cold-climate environments.
solifluction
What would happen if earths axial tilt was 0 degrees instead of 23.5 degrees?
The suns radiation would always strike at the equator, and daylength would equal 12 hours at every latitude all year round.
What force does each arrow represent?
Orange: PGF
Blue: Coriolis
Red: Actual Wind Direction
Green: Friction
This type of front is stalled with warm and cold air masses pressing against each other, while this other type forms when a cold front overtakes a warm front and forces it skyward.
There are several hypotheses that account for the glacial-interglacial oscillations in climate, and they are as follows: Variations in solar output, Release of Aerosols, Position of the landmasses, changes in earths orbital parameters, and climate feedbacks.
Describe 2 of these hypotheses
Variations in solar output: abundance of hotspots which go through cycles
Release of Aerosols: released by major volcanic eruptions, increase earths albedo and reduce the amount of insolation absorbed
Position of the landmasses: continental glaciation must have continents at high latitudes.
Changes in earths orbital parameters: involve three main changes: the shape of Earth's orbit (eccentricity), the wobble of Earth's axis (precession), and the tilt of the axis (obliquity)
Climate feedbacks:Ice Albedo feedbacks, greenhousegas feedbacks
This is a landscape formed by the dissolution of soluble bedrock, featuring features like sinkholes, caves, and disappearing streams.
Karst Terrain
What are the major belts of pressure around earth in order?
