Study the diagram. What part of Earth’s structure is Layer 2 on the diagram?
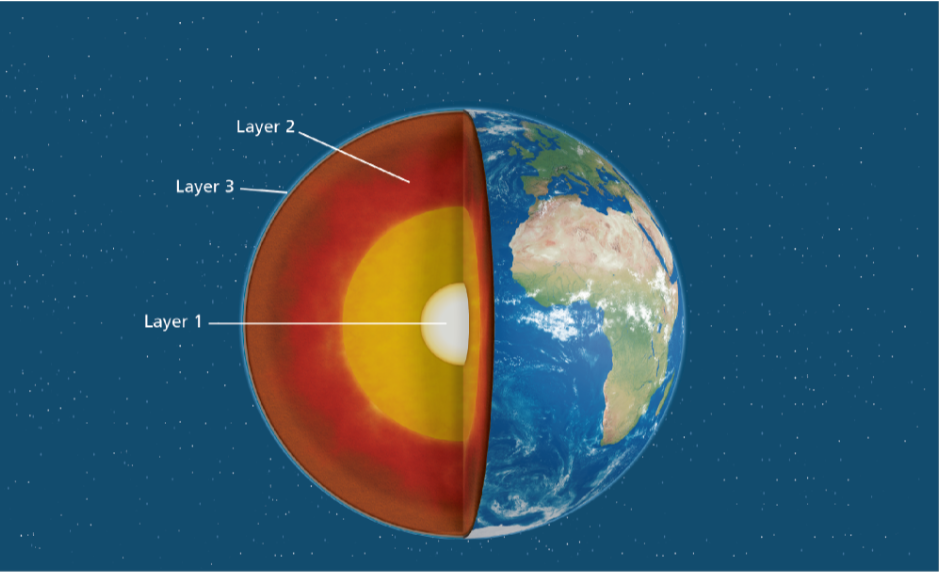
mantle
Look at the map. What kind of map is this?
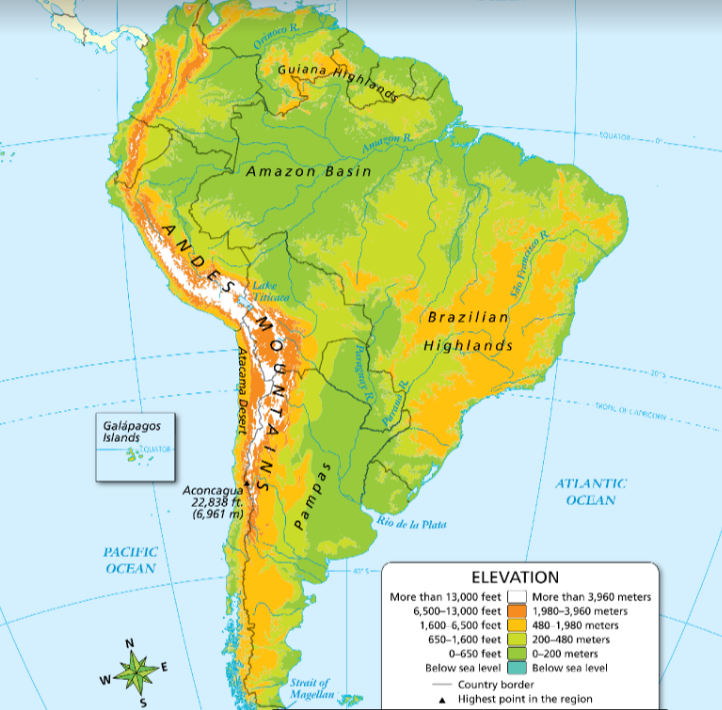
physical map
Which imaginary lines allow geographers to pinpoint any location?
latitude and longitude
When a geographer studies the migration patterns of humans over many centuries and how that has
affected the geography of North America, which theme of geography is he or she using?
movement
What is "precipitation"?
things that fall out of clouds. Precipation is greatest near the equator.
What are the names of each phase of the water cycle?
evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Look at the map. What kind of map is this?
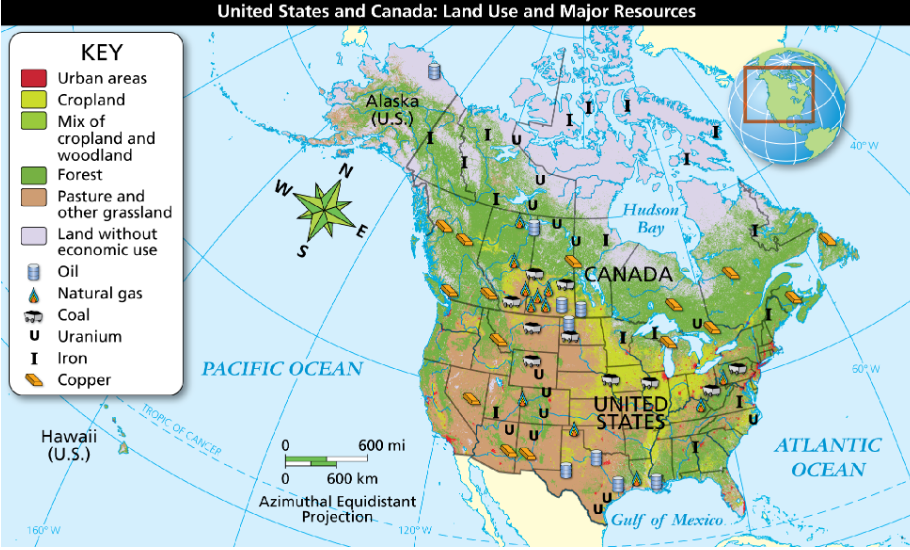
special-purpose
Which part of a map would you look at to find directions on a physical map?
compass rose
What are the five themes of geography?
location, place, region, movement, and human- environment interaction
What is "The Water Cycle?"
the movement of water from Earth’s surface into the atmosphere and back again
What causes earthquakes?
Blocks of crust slide against one another, often at plate boundaries.
How are equal-area projections of Earth inaccurate?
Directions and the shapes of the landmasses are distorted.
What are examples of "intermediate directions"?
Northwest, Northeast, Southwest, and Southeast. Intermediate directions lie at the midpoint between two cardinal directions.
Places that are near each other and have something in common with each other are called _____.
Regions
What are "plate tectonics?"
a process involving huge blocks of Earth’s crust and upper mantle that are called tectonic plates
What is weather? How is it defined?
It refers to the conditions of the air and sky at a certain time and place. Example: It determines whether you should take an umbrella on Monday if the precipitation of rain, for instance, is high.
What type of information does a physical map always show?
natural features
What are cardinal directions?
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, south, east, and west.
People, ideas, goods, etc that are transported from one location to another describe the theme of _____.
Movement
What is "magma"?
molten rock
***Liquid rock at extremely high temperature under the surface of the earth. When molten rock cools down, it solidifies and forms rocks and minerals.***
What is climate?
Climate is the average weather of a place over many years.
On which type of map would you be mostly likely to be able to identify the capital of the state of Montana?
a political map
Absolute and relative are words that describe...
Location
Human-environment interaction is the relationship between _____ and _____.
People, the world.
What is "erosion"?
a process in which water, ice, or wind remove small pieces of rock and move them somewhere else