What are glacial and interglacial periods?
Glacial periods is when there are extensive ice sheets presents. Whereas, interglacial periods are warmer periods with less ice sheets present.
Define Population Density
How many people live per measured land (e.g. km2).
What is climate change?
Climate is the average temperature and precipitation patterns on Earth over time.
Formula for calculating gradient?
Rise over Run
Define Biodiversity
The variability of life on Earth. The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat.
What is albedo and how does it impact the enviornment?
Albedo is the reflectivity of a surface - how much sunlight is reflected vs absorbed. It helps control how much solar energy is retained in the atmosphere, regulates glaciers and ice formation, affects ocrean currents and influences weathering and erosion rates.
What is the DTM Theory? (Demographic transition model)
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) is a theory that explains how a country’s population structure changes over time as it develops economically and socially.
Desertification is the process by which fertile land becomes desert, primarily caused by climate change, deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable agricultural practices.
Calculate the gradient:
Rise 120m
Run 1.2kms
120 divided by 1200 = 0.1
1:10
Define Glaciers
A system of flowing ice that forms through accumulation and recrystalisation of snow. It alters landforms through erosion.
What is a secondary consumer?
Animals that eat primary consumers (herbivores). Examples: Small fish, frogs.
Japan’s fertility rate is below replacement level. What is one reason why many Japanese families are having fewer children?
What are high living costs, long working hours, and cultural expectations that women prioritise childcare over careers
what are the three things required for a fire?
oxygen, fuel and heat
What is the formular for vertical exaggeration?
Vertical Scale divided by horizontal scale
Define albedo
The proportion of sunlight reflected by a surface, with ice and snow having a high albedo and absorbing less heat
This circulation cell is found near the Equator and features warm air rising, creating low pressure and heavy rainfaill in tropical regions.
Hadley Cells
What is one major challenge Japan’s ageing population creates for its workforce, and how does this affect the economy?
Labour shortages that reduce the size of the workforce, increase wage pressure, and discourage manufacturing and business investment
How does topography influence the speed of a bushfire?
Fire move faster uphill, doubling in speed for every 10° increase in slope
Calculate the vertical exaggeration: A cross section has a horizontal scale of 1cm = 1 km and a vertical scale of 1cm = 100m. What is the VE?
1km = 1000m, so the horzontal scale is 1cm = 1000m
VE = Horizontal scale divided by vertical scale
1000 divided by 100 = 10
In population geography, what is the dependency ratio and why is it important?
The ratio of dependents (young and elderly) to the working-age population, showing the economic pressure on workers to support non-workers
What is the key difference between biocentrism and ecocentrism?
Biocentrism is centred on all living organisms, whereas ecocentrism nature/ ecosystems are the centre.
What were some of the social implications of Uganda? due to rapid population growth?
High levels of teen prganancy, limited education for women, unequal access to family planning (3 in 10 women unable to access contraception), strain on social services from refugees, widespread child malnutrition leading to stuning 29% of children under 5) and high dependency ration, pressure on working age population
To what extent have humans contributed to the increased frequency and intensity of bushfires? Give two examples.
Through climate change, which creates hotter, drier conditions and longer fire seasons, and land-use changes like deforestation and agricultural clearing, which leave behind flammable debris
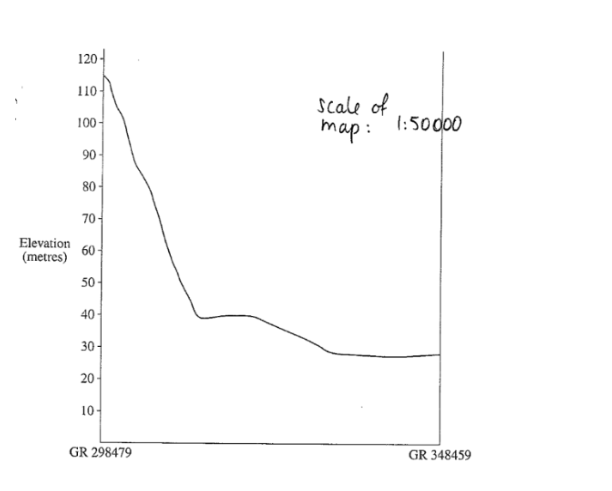
Calculate the VE
HS: 1cm: 50000 --> 1:500m
VS: 1cm = 10m
500/10 = 50
50 times
Explain the difference between a positive feedback loop and a negative feedback loop in environmental systems, giving one example of each.
What is a positive feedback loop amplifies change (e.g., melting ice reduces albedo, causing further warming), while a negative feedback loop counteracts change (e.g., more CO₂ increases plant growth, which absorbs CO₂ and slows warming)?