What is meant by voluntary migration?
when the individual has a free choice about wether to migrate or not
Name all 3 types of coral reefs
1)Fringing reef
2)Barrier reef
3)Attol reef
Danleone wants to travell to London but he does not want to order all his tours one by once so he deicides to tell his secretary to place a package tour for him . What is meant by a package tour ?
A package tour, package vacation, or package holiday comprises transport and accommodation advertised and sold together by a vendor known as a tour operator.
What are the main factors that influence the rate of soil erosion?
The rate of soil erosion is influenced by several factors, including:
Slope: Steep slopes increase the rate of erosion as water flows more quickly and with more force.
Soil type: Some soil types are more susceptible to erosion than others. For example, soils with high clay content may be more resistant to erosion, while sandy soils are more easily eroded.
Vegetation cover: Vegetation cover helps to hold soil in place by reducing the force of raindrops and providing roots that bind the soil together. The removal of vegetation cover can lead to increased erosion rates.
Rainfall intensity: High-intensity rainfall can cause erosion by dislodging soil particles and increasing the flow of water over the soil surface.
What is a scale
a ratio between paperwork: real life
What are some 4 advantages of out-of-town shopping centre?(200 points)
-plenty of free parking
- there is lots of space, so shops are not cramped
-easily accesible by car
- Bringing on the edge of the town, means the land price is lower, so the cost of developement is kept down
Draw a well labelled instument used to maeasure rainfall(200 points)
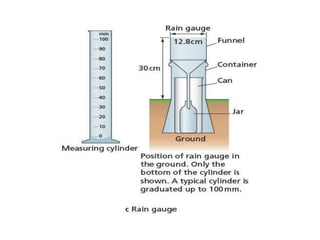
What does a TNC (transnational corporations)mean and give 3 examples of TNC'S
transnational corporations are large businesses that operate in a number of countries.
examples include:-
apple
microsoft
amazon
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to the short-term, day-to-day atmospheric conditions in a particular location.
Climate, on the other hand, refers to the long-term average weather conditions in a particular region or location. It is the statistical description of the weather patterns over a period of at least 30 years.
5,4,7,8,4,7,2,8,5,7,4,7,4,9,4
calculate the following
a) mean
b)mode
c) median
d) range
a)5.6666666666667
b)4
c)5
d)7
Study the picture below , which is a photography showing homes in a squatter settlement in Accra , Ghana (an LEDC IN Africa)
i) Describe three features of the buildings shown in the image below (300 points)
Made of wood;
With some sacking/plastic sheeting/tarpaulins;
Metal/zinc/corrugated/tin/flat iron roofs;
Small/single storey;
Close together/cramped;
Weak/not stable/easily destroyed;
Boards/shutters over window space, etc
Sort these following into high, low and medium clouds.
i)cirrus
ii)stratocumulus
iii)altostratus
iv)cirrostataus
(300 points)
i)high cloud
ii)low cloud
iii)meduim cloud
iv)high cloud
Qatar, Israel and Lebanon are some of the countries that suffer physcial water scarcity and . Pakistan and Afghanistan are some of the countries that suffer economic scarcity, What is the meaning of economic and physcial scarcity?
physcial scarcity is when physcial access to water is limited
economic scarcity is when a population does not have the necessary monetary means to utlize an adequate source of water
Explain how the water cycle works
The water cycle is a natural process through which water continuously circulates between the earth's surface, the atmosphere, and back again. It is also known as the hydrological cycle. The following are the steps of the water cycle:
Evaporation: This is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas or vapor form, driven by heat energy from the sun. Water is evaporated from the surface of oceans, lakes, rivers, and plants.
Condensation: As water vapor rises into the atmosphere, it cools and condenses into small droplets, forming clouds.
Precipitation: The water droplets in the clouds combine and grow larger until they become heavy enough to fall back to the earth's surface as precipitation, which can be in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Infiltration: Some of the precipitation infiltrates the soil and becomes groundwater, which can later seep into rivers and other water bodies.
Runoff: The remaining precipitation runs off the land and into rivers, lakes, and oceans, completing the water cycle.
1) There has been alot of traffic jam in the Los Angeles ,United States Of America. Some students from the Penn State Department of Geography were sent out to carry out a survey.
i)Come up with the most appropriate topic of study they should have come up with? {1}
ii)Formulate two objectives for their study{1}
iii) Give two appropriate methods to collect data for this investigation{1}
(ONE CAN SAY)
i) TRAFFIC JAM IN LOS ANGELES
ii)TO INVESTIGATE the transport of mean that causes the most traffic jam
TO INVESTIGATE if the pedestrians are also the main cause for traffic
iii)
- Surveys and Questionnaires.
- Interviews.
- Observations.
- Records and Documents.
- Focus Groups
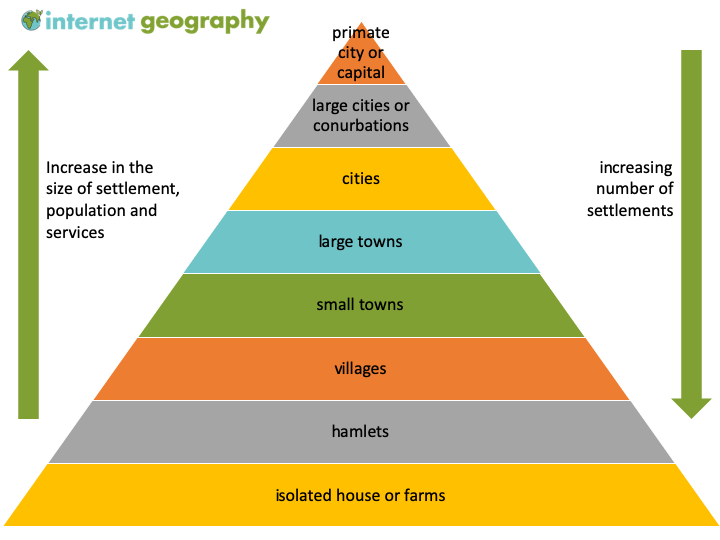
Draw a well-labelled diagram of the settlement heirchary showing the increasing in population and number of settlements
Name and describe two factors affecting the climate (400 points)
-latitude
-proximity to the sea
-ocean currents
-altitude
-winds
-cloudcover
-pressure
How is acid rain formed? and how does acid rain affect the environment negatively?
Acid rain results when sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOX) are emitted into the atmosphere and transported by wind and air currents. The SO2 and NOX react with water, oxygen and other chemicals to form sulfuric and nitric acids. These then mix with water and other materials before falling to the ground.
freshwaters and soils,
destroys insects and aquatic life-forms,
causes paint to peel,
corrosion of steel structures such as bridges, and weathering of stone buildings and sculptures,
-as well as impacts on human health.
How do plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions?
Plate boundaries: Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur at plate boundaries. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent, and transform. At divergent boundaries, plates move away from each other, creating rifts and fissures in the crust that can lead to volcanic activity. At convergent boundaries, plates collide and one plate is forced under the other, causing earthquakes and volcanic activity. At transform boundaries, plates slide past each other, causing earthquakes.
Subduction zones: At convergent boundaries where one plate is forced under another, the sinking plate melts and forms magma, which rises to the surface and causes volcanic eruptions.
Hotspots: Hotspots are areas of the earth's crust where magma rises to the surface, regardless of plate boundaries. These areas can cause volcanic activity even in the middle of a tectonic plate.
Fault zones: Fault zones are areas where the earth's crust is cracked or broken, creating areas of weakness that can cause earthquakes.
Name and desribe fully 3 types of sampling
stratified, random, systematic
Name 6 features of a Central Business District
-multistorey developemnet
-vertical zoning
-low residential population
-high pedestrain flows
-alot of offices
-functional grouping (shops which are similar locate and increase their threshold
What are some of the adaptations that allows the fennec fox to live in such hot desert environments 
-light coloured coat to reflect heat
- large ears with blood vessels close to the surface to easily loose heat
- gets most of its misture from its prey
-soles of feet protected by thick fur ro run across hot sand
-lives in burrow during the day to avoid heat
define the following terms
a)quaternary sector
b)primary sector
c)secondary sector
d)tertiatry sector
and give an example of each sector
quaternary sector is defined as the industry based on human knowledge which involves technology
The primary sector includes all those activities the end purpose of which consists in exploiting natural resources: agriculture, fishing,
The secondary sector covers all those activities consisting in varying degrees of processing of raw materials e.g manufacturing,
The tertiary sector involves the provision of services to other businesses as well as to final consumers. Services may involve the transport
How do humans impact the carbon cycle, and what are the consequences of these impacts on the environment?
Humans impact the carbon cycle in several ways, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use changes. These activities release large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, which is a greenhouse gas that traps heat and contributes to global warming. The following are the main ways in which humans impact the carbon cycle:
Burning of fossil fuels: The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. This is the main source of human-caused carbon emissions.
Deforestation: Deforestation involves the clearing of forests for agriculture, development, or other human activities. Forests are important carbon sinks that absorb and store large amounts of carbon. When forests are destroyed, this carbon is released into the atmosphere.
Land-use changes: Changes in land use, such as the conversion of grasslands or wetlands to agriculture or urban areas, can alter the amount of carbon stored in soil and vegetation. This can lead to increased carbon emissions.
The consequences of these impacts on the environment are significant. The buildup of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere contributes to global warming and climate change. This has led to rising temperatures, more frequent and intense heatwaves, changes in rainfall patterns, sea-level rise, and ocean acidification
THE QUESTION WILL BE PRESENTED
1