Identify and describe the characteristics of the four climate zones
Tropical - warm and wet year-round
Temperate - moderate & seasonal temp and precipitation
Arid and semi-arid - hot and dry
Continental and polar - cold and seasonal rain

Temperate (moderate temperatures; moderate, seasonal precipitation)
Identify three activities that humans alter environments for
Mining
Urbanisation
Agriculture
Availability - the physical supply of food
Access - being able to obtain food
Utilisation - absorbing nutrients
Stability - the reliability of food supply and access
Identify three reasons pristine forests are important for the environment.
1. Barrier against erosion
2. Provide fresh air
3. Provide clean water
4. Attract rain
5. Supports habitats and ecosystems
6. Absorbs and retains rain water
Identify three factors that influence climate.
1. Latitude
2. Elevation
3. Rain shadow effect
Identify the climate zone for this climate graph.
Arid and semi-arid
- Low precipitation
- Temperatures (too high to be polar/continental - likely a hot desert during the day, but averages out as moderate due to cool nights in the desert)
Identify three physical changes that may occur to the environment as a result of human activities
Land clearing
New species of plants or animals introduced
Removing vegetation, replacing with concrete
Increased traffic in the area
Increased demand for water and other resources
Which climate zone/s are most likely to have the best food security in terms of availability? Briefly, why?
Tropical and temperate zones due to their climate that is suitable for agriculture (higher rate of moderate temperature and rainfall; has higher rates of fertile soil due to this climate)
Pests may damage crops, reducing the yield, thus reducing the availability of food. 
How do biomes and climate zones affect food security?
Temperates must be moderate for conditions to be ideal for agriculture - harsh conditions affect the growth of crops and livestock
Soil should be nutrient-rich and fertile in order to be agriculturally productive
Write a PEE(EE)L paragraph, identifying which climate zone Figure 1 represents.
Points allocated based on depth -
100 points: accurate, but not thorough
200 points: accurate, reasonable depth
300 points: accurate, thorough
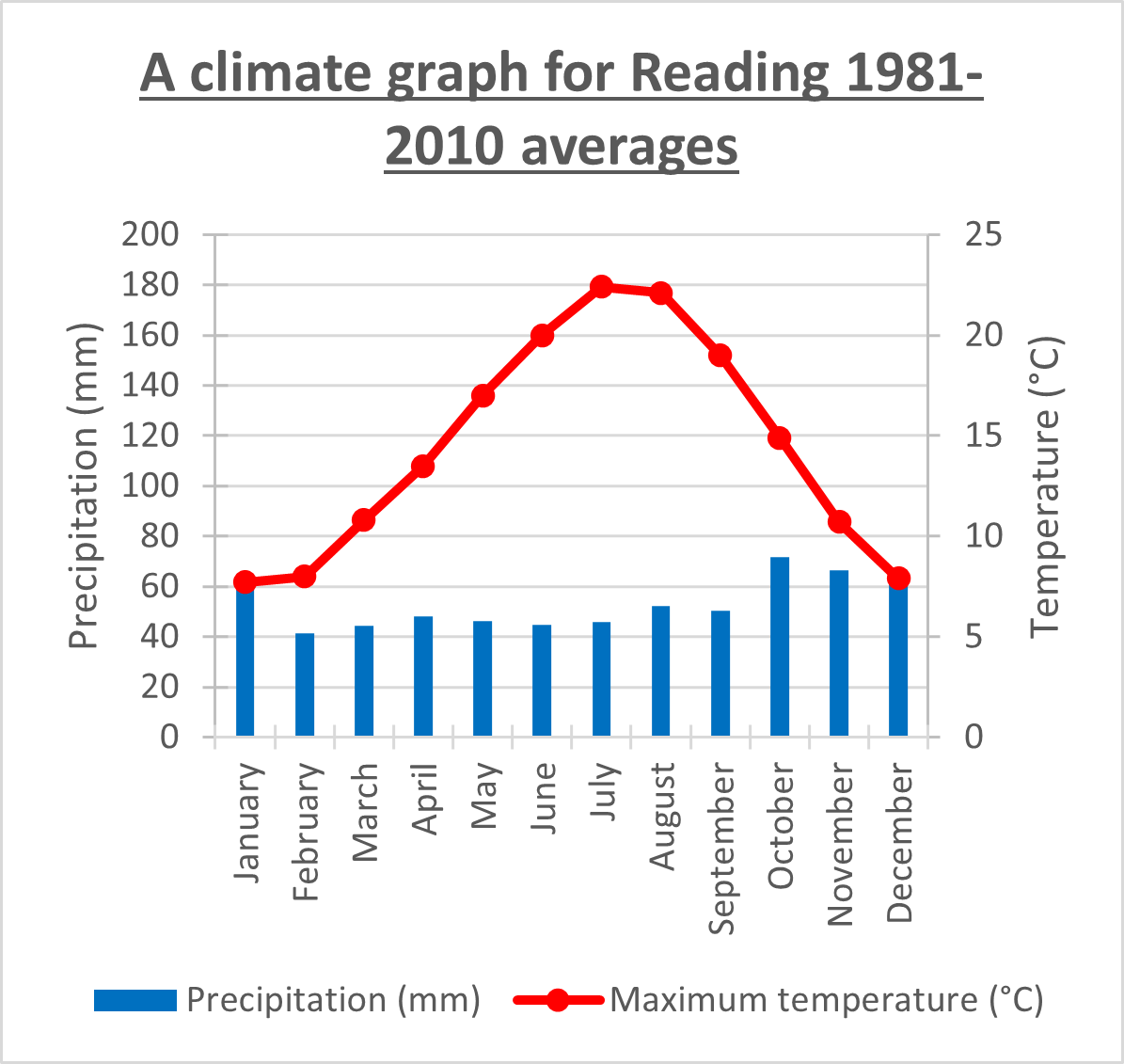
Figure 1 represents a temperate climate, evident by its moderate and seasonal temperatures, and moderate precipitation. The temperature in Figure 1 is moderate, with a range of 7°C during the cooler months December and January) to 23°C during the warmer months (July), consistent with the moderate and seasonal characteristics of a temperate climate zone. Additionally, the precipitation is moderate year-round, with a range of 40mm to 70mm, consistent with precipitation expected in a temperate forest, typically found in the temperate climate zones. Therefore, Figure 1 represents a temperate climate zone due to its moderate and seasonal climate patterns.

Numerous changes have occurred to the land in Source 1. Land has been cleared, as depicted by the green fields beside the forest, in order to make room for monoculture.
2. Native vegetation has been replaced with a single specie of plant that is not native, for monoculture.
3. Monoculture will increase the demand for water.
4. Chemicals will likely be used in the soil.
Consider Source 1 below. Describe one POSITIVE and one NEGATIVE impact of Europe's land use on people and/or the environment.
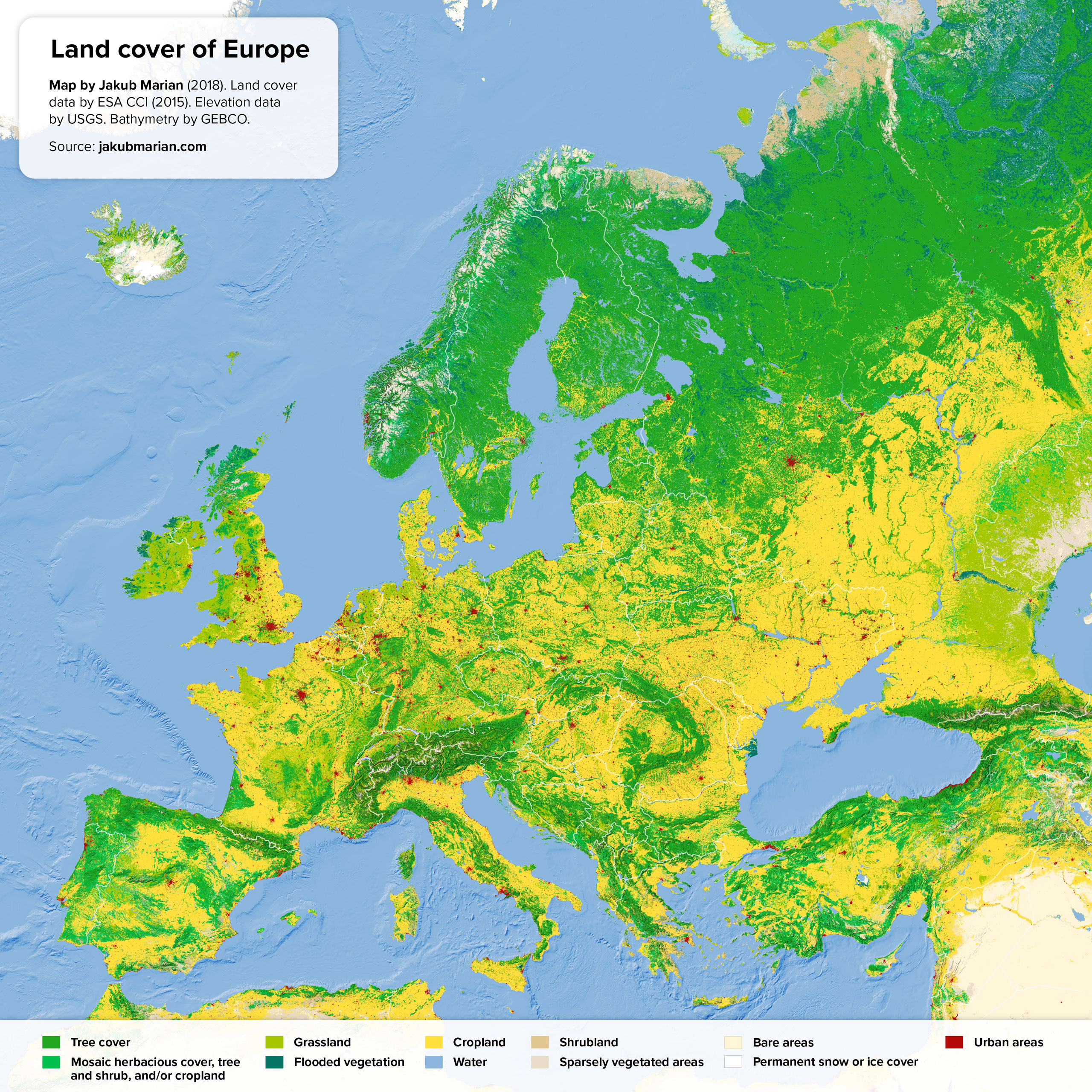
+ Vast amounts of cropland supports immediate food security (availability)
- Monoculture practices may damage the environment due to land degradation (nutrient depletion; use of chemicals...)
- Land would have been cleared or changed --> habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity; reduced carbon sequestering, leading to climate change...
Write a PEE(EE)L paragraph identifying which climate zone Figure 1 likely represents.
Points allocated based on depth -
100 points: accurate, but not thorough
200 points: accurate, reasonable depth
300 points: accurate, thorough

- Tropical rainforest
- High precipitation
- Consistently warm temperatures
There is a tundra located in northern India and western South America.
a) Why is this an anomaly to the pattern of global biome distribution?
b) Explain why these anomalies likely occur.
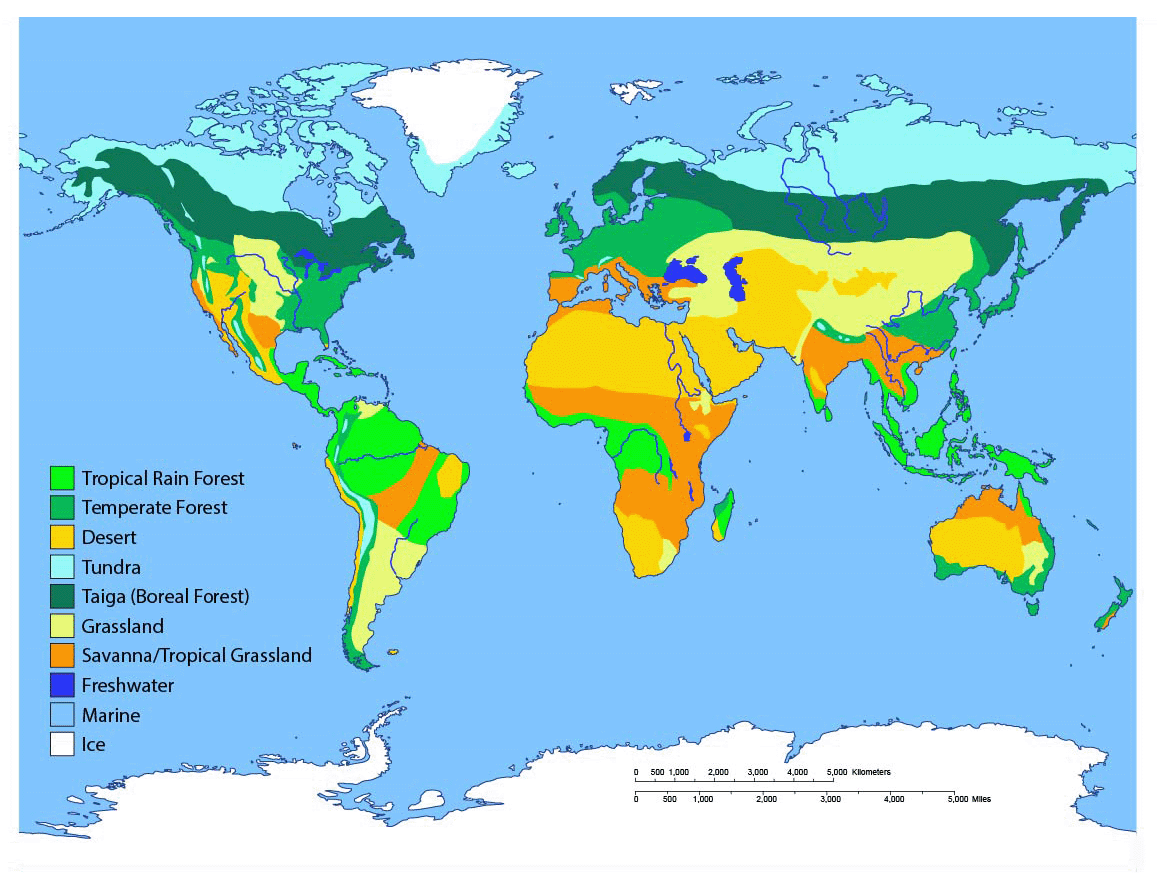
Tundras are cold biomes that exist mostly in polar regions. It is an anomaly as India and South America are located in the subtropical regions with temperate climates, which have more moderate temperatures.
These regions may have mountain ranges, with higher elevation than surrounding areas. Places of high evolution are typically cooler due to the air being colder higher up.
Write a PEE(EE)L paragraph, identifying which climate zone this climate graph represents.
Points allocated based on depth.

- Continental and polar
- Cold most of the year
- Seasonal precipitation
Explain how land clearing causes topsoil erosion, and how this impacts the environment.
Bonus points for A standard.
Natural vegetation prevents soil erosion by protecting the land from wind and rain through its roots giving soil structure, and the canopy of vegetation shielding the land from wind and rain. When vegetation is cleared, the soil is now more loose without the root support, and it is now exposed to wind and rain without the shield of vegetation. Wind and rain are now able to transport the top layer of soil elsewhere. Over time, the topsoil is eroded away.
This impacts the environment by degrading the soil. Soil becomes less fertile over time as the topsoil is the most nutrient-rich layer. When it is eroded, less vegetation will thrive, affecting the ecosystems and future growth of plants. Furthermore, as this place will now not support plant life, this will contribute to climate change as there are no longer plants absorbing carbon from the atmosphere.
Evaluate the likely food security status of north Russia.
Points awarded based on depth. Bonus points awarded for A-standard response.
North Russia is likely to experience challenges with food security due to its harsh climate, affecting agriculture. Tundra biomes are characterised by freezing cold temperatures, often leading to permafrost. This thick layer of ice in the soil impacts the growth of crops as roots cannot grow through the ice, thus affecting the production of food.
While traditional livestock, such as cattle, chickens, and sheep, would not thrive in harsh conditions, more local animals may be more suitable for agriculture. However, food security requires a diet that is nutritious, so this alone would not attain food security.
North Russia may rely on imports in order to achieve food security, however the cost of food may fluctuate based on the global economy and be expensive; and may be disrupted by weather events and conflicts.
Evaluate the likely food security status of western Europe.
Points awarded based on depth. Bonus points awarded for A-standard response.

Western Europe is likely a highly food secure region due to its ideal climate for agriculture.
Western Europe is mostly comprised of a temperate forest biome, characterised by moderate temperatures, that are not too harsh for crops and livestock; moderate precipitation, ensuring enough water resources for the cultivation of crops; and nutrient-rich soil, meaning the soil is highly fertile and suitable for crops.
These conditions make food likely highly available in Western Europe, which is one pillar of food security. Food security would also depend on the ability of the population to physically and economically access the nutritious foods.
Write a PQE paragraph, describing the pattern of global soil degradation.
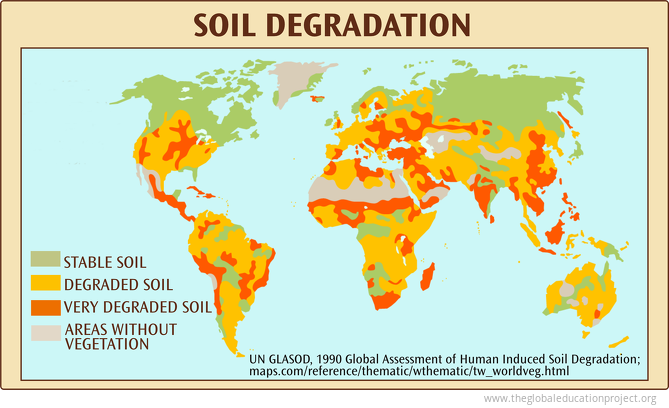
Most of the world's soil is degraded in the subtropical and tropical regions. This is evident as approximately a third to half of the land is classified as "degraded soil", as can be seen in approximately 85% of Australia; most of central and Eastern Africa; and approximately 85% of South America. Most of the Northern region has maintained is stable soil, as can be seen in most of Russia, Canada, and the northern-most tip of Europe. "Very degraded soil" can be found throughout the tropical and sub-tropical regions too, evident in central, southern and eastern Europe, eastern and western Asia and particularly India, central and southern Africa, and central North and South America. An exception to this pattern is that some stable soil remains in a few tropical and subtropical regions, such as central Australia, Papua New Guinea, and a few areas within Africa and South America, while most land surrounding it has been degraded.
Write a PEE(EE)L paragraph, identifying which climate zone this climate graph represents.
Points allocated based on depth.
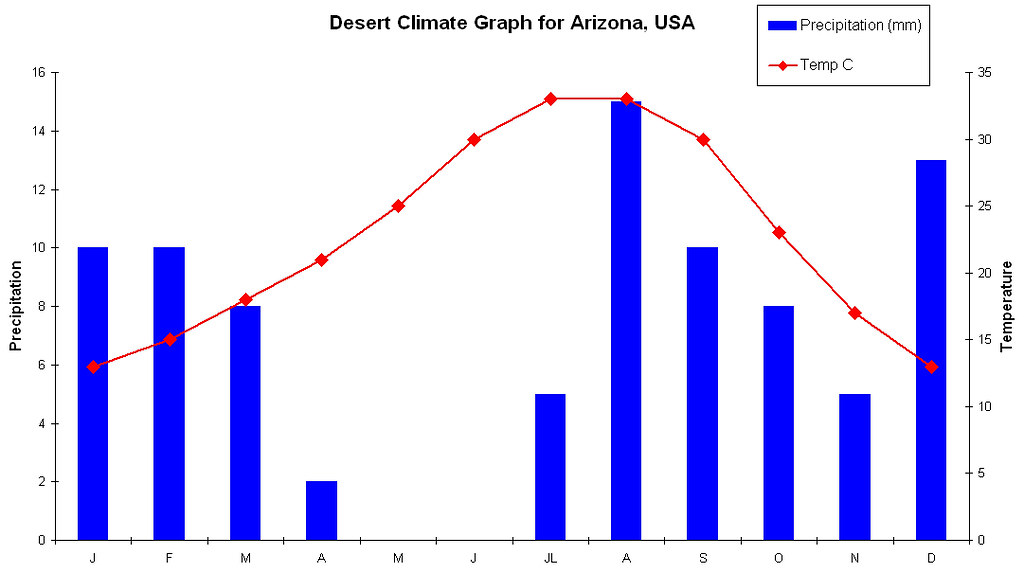
- Arid and semi-arid
- Low precipitation
- Warm temperatures (likely cold due to cool nights)
Consider the image below. Explain the possible impacts of this land change on people and environments.
Points allocated based on answer accuracy and depth.
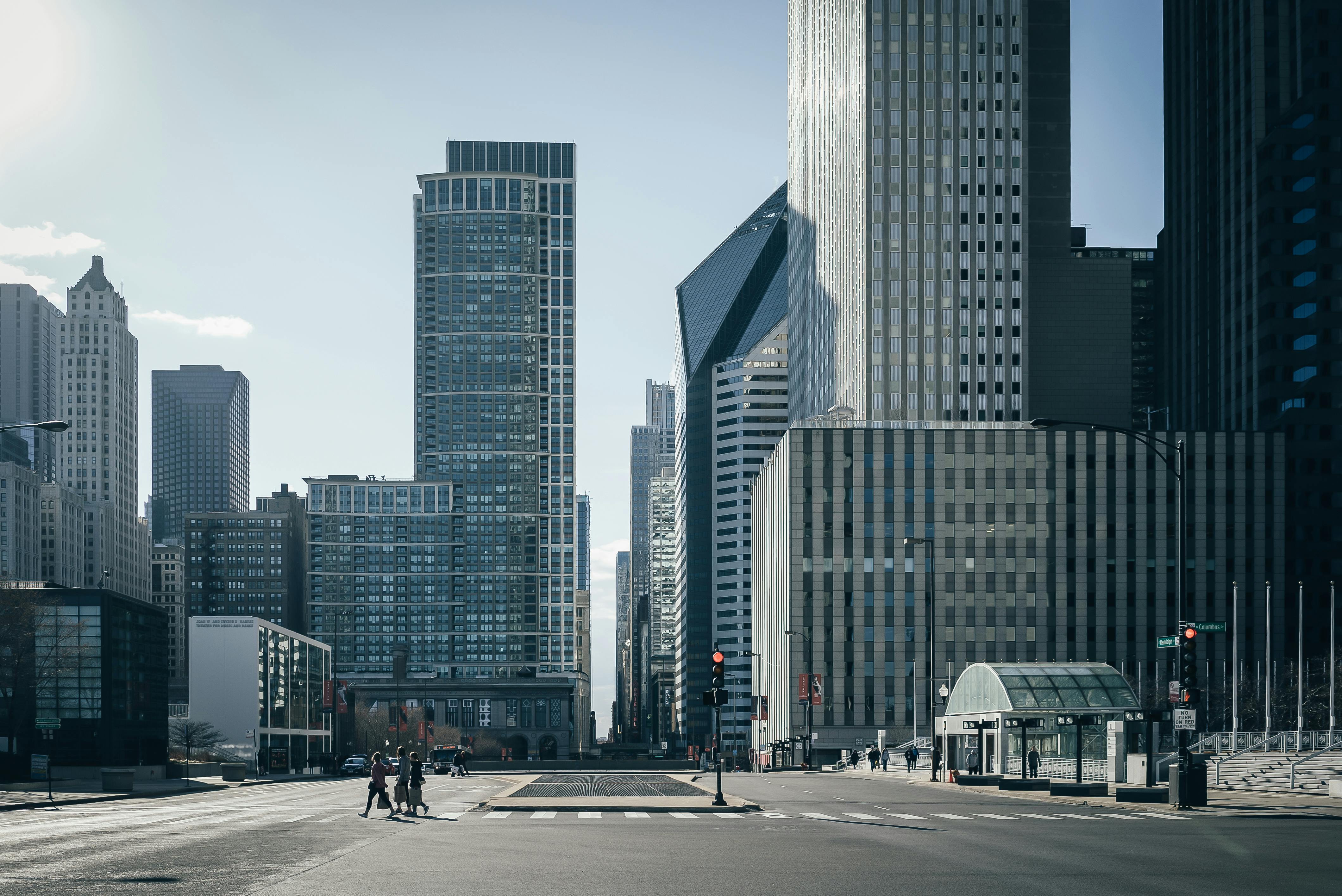

Urban heat island effect - One possible impact of urbanisation is an increase in temperature of the region, due to the urban heat island effect. When trees and vegetation are removed and replaced with surfaces such as asphalt and concrete, this increases the ground temperature as these surfaces absorb and retain heat, while greenery reflects heat and cools the place through transpiration. An increase of temperature can add to climate change, and can make the temperature more uncomfortable for people living in the area.
Run off/flooding - Additionally, unlike natural soil and vegetation which absorbs water, roads and cement are impermeable surfaces. This means rain is unable to be absorbed into the ground, and instead it either floods the area, causing damage to property, livelihoods, and the economy; or runs off into nearby waterways, carrying pollutants with it and affecting water quality, and flooding other areas.
Loss of biodiversity/increased traffic - The land change that would have occurred in order to develop urban areas would lead a loss of biodiversity, as natural habitats are replaced. Wildlife that once inhabited the area would now be forced to migrate elsewhere; and plants would have been removed. This would have an impact on the local ecosystem, creating an imbalance in the environment. The addition of human traffic would effect the environment by disturbing wildlife, or endangering wildlife with vehicles.
Explain two ways climate change will impact future food security.
1. Changes to climate (temperature and precipitation patterns) - may result in harsher conditions; less rain will lead to drought; intensified rain may lead to flooding - reduces supply of food, and increases the cost.
2. More frequent and intense hazards will damage agricultural industries, reducing supply of food and increasing the cost.
3. Rising sea levels bring salt into coastal soil --> affects growth of crops
Consider the image below. Explain the possible impacts of this extent of soil degradation on people and environments.
Points allocated based on answer accuracy and depth.

Vast amounts of soil degradation will have significant impacts on people and the environment. Degraded soil will affect the growth of natural vegetation and therefore the local ecosystems. When soil is degraded, vegetation will not thrive as the soil will lack nutrients. This may be due to nutrients being depleted from the soil due to monoculture; and the nutrient-rich layer of soil being lost to topsoil erosion as a result of land clearing. Additionally, agricultural practices may affect soil fertility through soil compaction, with machinery and livestock compacting the soil so that there is no longer space for water, air, or roots to grow.
The lack of plant growth will impact food security, as crops will not thrive or grow in these areas. Crops require nutrient-rich soil to grow and to be nourishing. As so much soil is degraded, this means there is significantly less land to produce food for a growing population, thus affecting global food security.