This principle states that in undisturbed rock sequences, the oldest rocks are at the bottom and the youngest at the top.
What is the Law of Superposition?
True or False: The youngest rock layers are located at the bottom of a rock formation.
What is false?
These fossils are preserved remains of plants, animals, and microorganisms preserved in rock.
What are body fossils?
This process is responsible for wearing away the Earth’s surface?
What is erosion?
The Earth's geologic history is thought to span this many years.
4.6 Billion Years
This principle states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity and only move after force is applied?
Law of Original Horizontality
True or False: The oldest rock layers are located at the bottom of a rock formation.
What is true?
These types of fossils represent evidence of animal activity rather than the preserved remains of the organism itself?
What are trace fossils?
This process is responsible for adding layers to Earth's surface by the laying down of sediment.
What is deposition?
These types of fossils are used by geologists to determine the geologic time period that other organisms are from.
What are index fossils?
This law states that rock structures that cut across existing rock structures such as intrusions are younger than the existing rocks.
What is the Law of Cross Cutting Relationships?
This process involving sedimentary rocks causes the youngest layers to be on the top of a rock formation.
What is sedimentation?
Ancient Shark vertebra is an example of this type of fossil.
What are body fossils?
This type of dating is used when geologists determine the vertical position of two rock layers.
What is relative dating?
This is like a timeline that geologists use to help organize Earth's History. This timeline is organized into Eons, Eras, Epochs, Periods, and Ages
What is the Geologic Time Scale?
This Steno's law explains how two rock formations separated by a river can have the same pattern of rock layers due to the sediment extending laterally in all directions.
What is the law of lateral continuity?
This rock layer depicted below is the oldest.
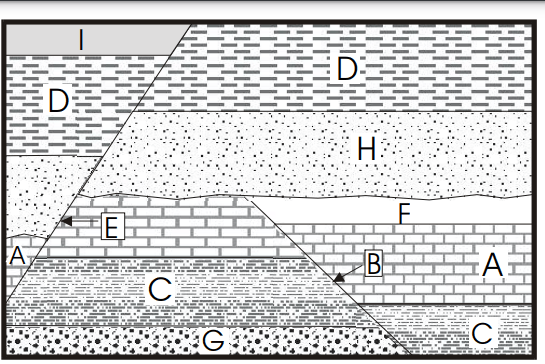
What is layer G?
This type of fossil can be used to identify specific time periods or if two rock layers were deposited at the same time.
What are index fossils?
If geologist use radioactive dating to determine the age of rocks, this type of dating is being used.
What is absolute dating?
Why can the geologic record be analyzed by looking at different rock layers?
The layers have different ages with the youngest being on top.
This principle states that organisms succeeded one another in a definite and recognizable order through geologic time.
What is faunal succession?
The rock layers in the picture below were formed in this order. List the oldest to youngest layers.
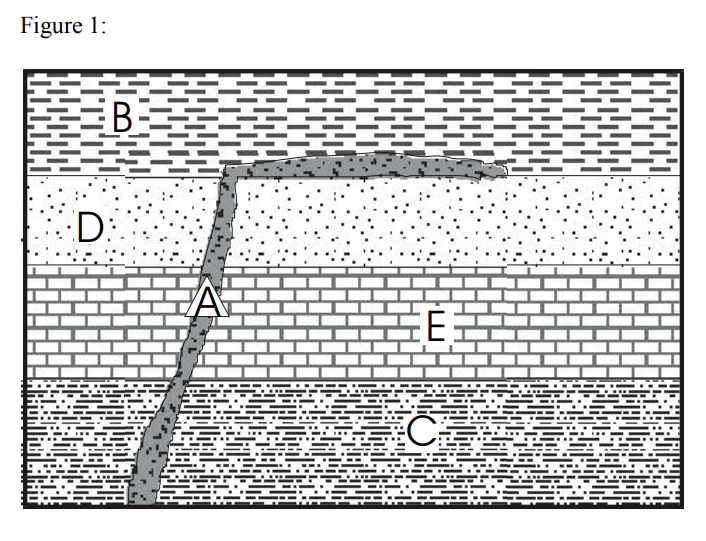
What is C, E, D, B, A?
If you find a trilobite fossil in one rock layer at the bottom and a dinosaur fossil in another layer on top, what can you conclude based on the principle of faunal succession?
The trilobite layer is older than the dinosaur layer.
What do the lines labeled B and E represent?
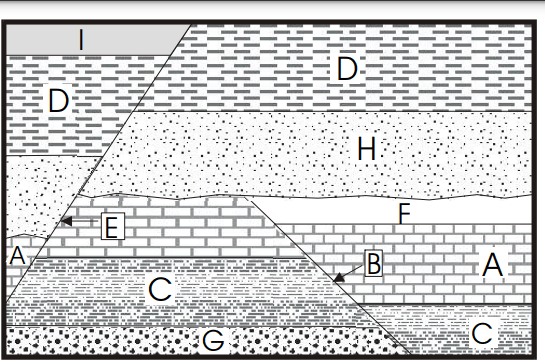
What are faults or fault lines?
This principle proposed by James Hutton states that geological processes are cyclical meaning that current geological events can explain geological events of the past.
What is Uniformitarianism?