The preserved remains of an organism.
What is a fossil?
The age of a rock compared to other rocks.
What is relative age?
This is the youngest layer and the law of relative dating that explains why.
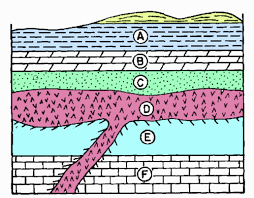
What is A and the Law of Superposition?
This is how we tell the age of trees.
What is count the rings?
This is what scientist use to determine the excat age of a rock layer.
What is absolute dating?
An example of this type of fossil would be footprints.
What is a trace fossil?
The law of relative dating that states rock layers at the bottom are always older than the rock layers on top.
What is the Law of Superposition?
This is the law of relative dating that explains why E is younger than D.
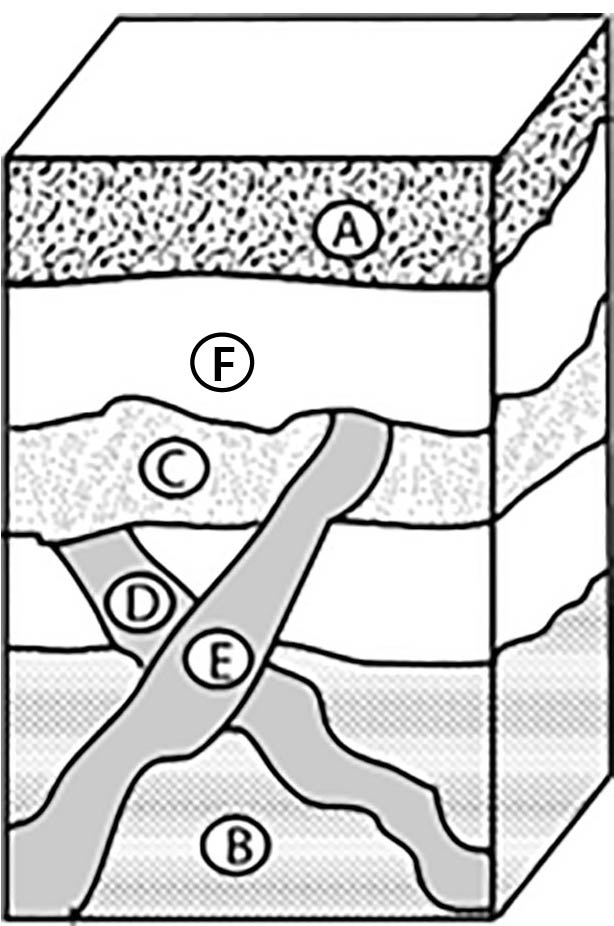
What is the Law of Cross Cutting?
When scientist observe this in a tree, they predict that there was a heavy rain season.
What is a thicker tree ring?
Scientist use this principle to help them “reverse time” and study the past.
What is the Principle of Uniformitarianism?
The term for fossilized animal dung.
What is a coprolite?
This law of relative dating states that the intrusion is always younger than the rock layers it goes through.
What is the Law of Crosscutting?
These are the TWO laws of relative dating that explain why B is older than C.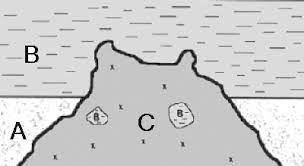
What are the Laws of Cross Cutting and Inclusions?
These can form when fine grained sediments at the bottom of a shallow body of water dry out.
What are mud cracks?
The difference between an intrusion and inclusion.
What is an intrusion is a cut across a rock layer and an inclusion is a rock inside of another rock?
Three main things that fossils can tell scientist.
1) Display when and where organisms lived. 2) Show how the environment has changed over time. 3) Show how life forms have changed over time.
This law of relative dating states that the small pieces of rock inside a bigger rock are always older than the bigger rock.
What is the Law of Inclusions?
This is the order of rock layers from YOUNGEST to OLDEST.
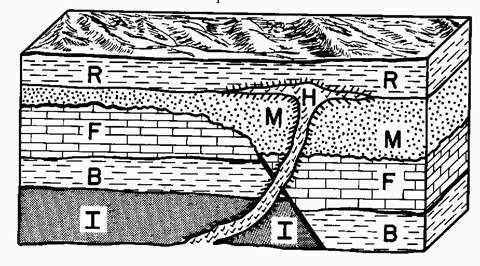
What is H, R, M, F, B, I ?
Fossils of similar animals and plants found on several continents across oceans is solid evidence for the existence of this structure.
What is Pangea?
The fossil below was found at the top of the Himalayan Mountains. What can you conclude about this discovery?
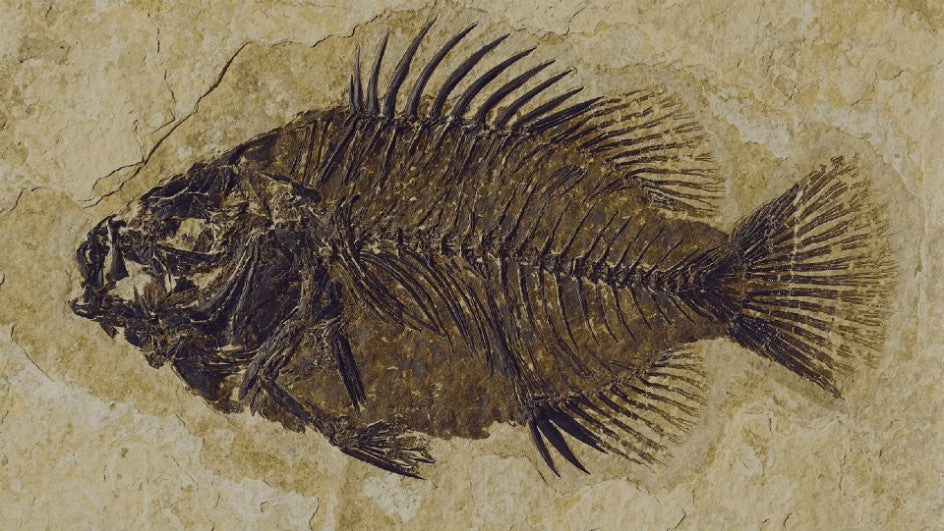

What is the Himalayan Mountains must have been under water at some point?
Useful fossils that help to tell the relative ages of the rocks around them.
What are index fossils?
What does it mean when fossils are not present in the next rock layer?
That species went extinct during that time period.
This is the order of rock layers from OLDEST to YOUNGEST.
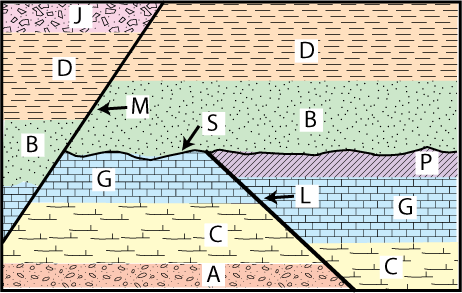
What is A, C, G, P, L, S, B, D, J, M ?
This is why it is extremely hard to determine the exact age of the Earth.
What is the Earth is constantly recycling itself due to the rock cycle and plate tectonics?
The "father" of geology.
Who is James Hutton?