Find BC. 
4
What is the complement of 69 degrees?
21 degrees
What transformation occurred?
Reflection
Classify the triangle by its sides and angles. 
Acute isosceles
In a proof, you ALWAYS start with the.....
GIVEN
Name the angle.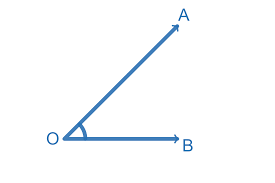
Find the value of x if L is the bisector of segment XZ. 
7.5
Using words, where does the coordinate notation tell you to translate the figure? (x,y)-->(x-1, y+5)
Left 1, Up 5
By which theorem or postulate are the two triangles congruent? 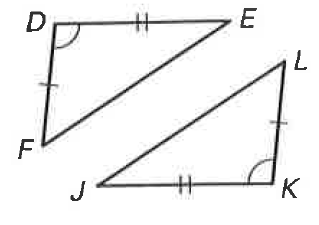
SAS
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its diagonals....
bisect each other.
Find the measure of <ABD.
110
Ray BD bisects <ABC. Find the value of x. 
x = 25
What transformation occurred?
180 degree rotation
Find m<E. 
44 degrees
If a parallelogram is a rhombus, then the diagonals... (two criteria)
are perpendicular and congruent.
IF KM is perpendicular to JL, find the value of y. 
y = 6
Find the value of x. 
x = 49
Using words, describe where the vector directs you to move the figure. <2, -8>
Right 2, down 8
By which theorem or postulate are the two triangles congruent? 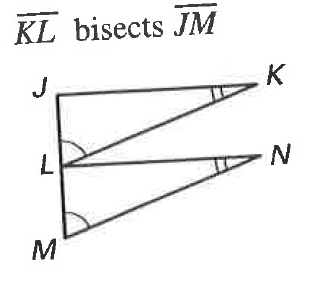
AAS
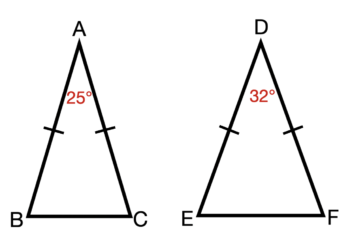 In the following image, use the hinge theorem to compare BC and EF.
In the following image, use the hinge theorem to compare BC and EF.
BC<EF
Find the distance between the points (-2,4) and (3,-1). Leave answer in exact radical form.
sqrt50
Find the value of x. 
x = 55
Give the coordinates of the point (-3,5) if it was reflected over the x-axis.
(-3,-5)
Fill in missing reason in the following proof. 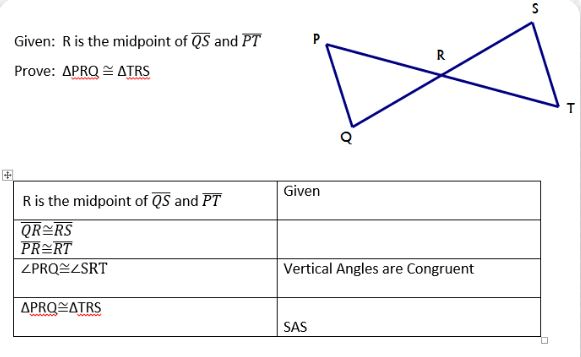
Definition of midpoint
Find the missing side. 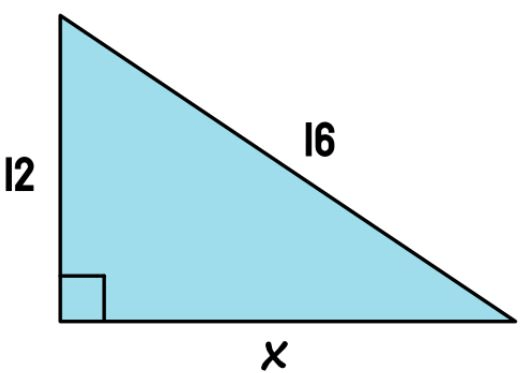
sqrt(112)~~10.58