They are the four transformations in Geometry.
What are translation, reflection, rotation and dilation?
Angles 1 & 5 and angles 2 & 6 are examples of these congruent angles:
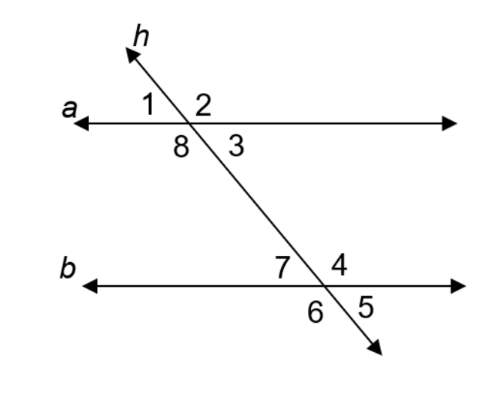
Alternate exterior angles.
The transformation rule of (x,y) ---> (x+5, y).
Translation to the right 5 units.
During our intro game today, who said that they liked skiing?
Lana and ...
This is the only non-rigid transformation.
What is dilation?
Angles 3 & 4 and angles 8 & 7 are examples of these supplementary angles:

Consecutive (same side) interior angles
The transformation rule (x,y) ---> (y,x)?
Reflection across the line y = x.
The transformation rule of (x,y) ---> (-x,-y).
180 degree counterclockwise or 180 degree clockwise rotation.
These transformations preserve distance.
What are translation, reflection and rotation?
The value of x in this diagram:
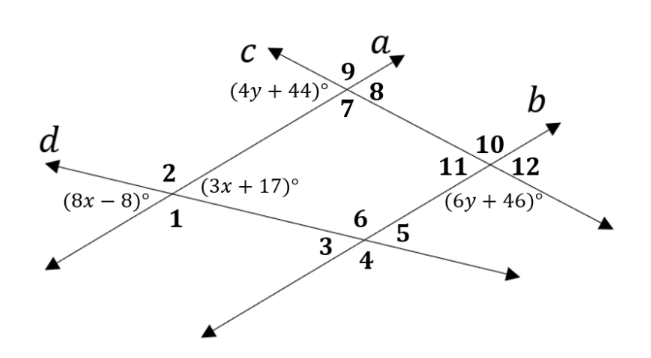
x = 5.
*vertical angles are congruent
* 8x-8 = 3x +17
5x = 25
x =5
The coordinates of Z′′ if ∆XYZ is rotated 90° counterclockwise about the origin, then translated by the rule (x, y) → (x−5, y−2)?
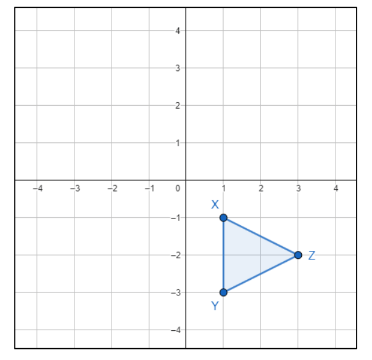
What is (-3,1)?
The triangle congruence or similarity theorem/postulate that corresponds with the diagram:
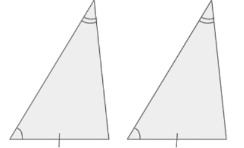
Angle-Angle-Side
This transformation does not preserve distance.
What is dilation?
The value of y in this diagram:

y=9.
*consecutive (same side) exterior angles are supplementary
* 4y+44 + 6y + 46 = 180
10y = 180 - 90
10y = 90
y=9
The four main lines of reflections and their transformation rules.
What are x-axis (x, -y),
y-axis (-x,y),
y=x (y,x)
and y=-x (-y, -x)?
The transformations that will create an image that are similar to the preimage?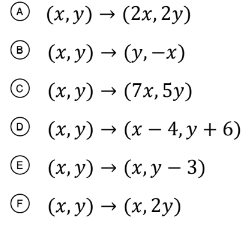
What are A, B, D, and E?
This is a common geometric construction illustrated in the image below.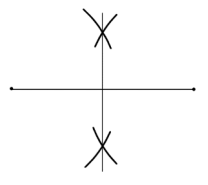
A perpendicular bisector.
What is the value of y in the diagram:
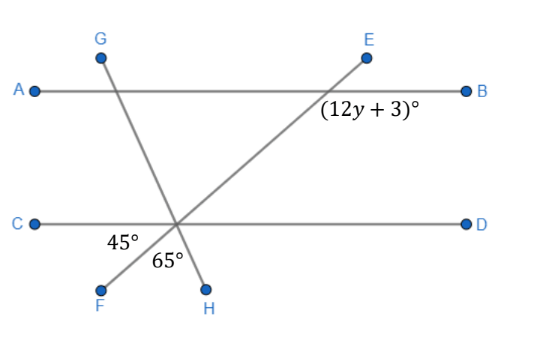
11
Rectangle ABCD is reflected over the line y = 1 and then translated by this rule to map to A"B"C"D"
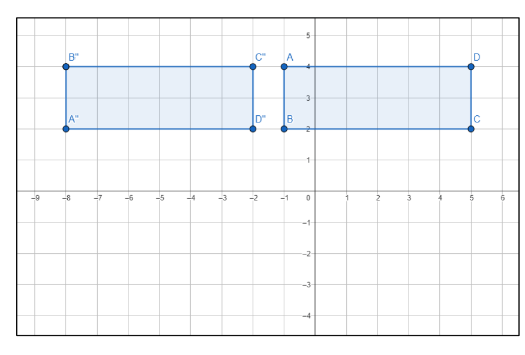
Translation (x-7, y+4).
Measure of each interior angle in a pentagon (in degrees)
108 degree.