What are the three types of rocks?
Sedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
convergent, divergent, transform
What is a volcano?
opening in Earth's crust that allows molten rock from beneath the crust to reach the surface
What is an earthquake?
shaking and vibration of the Earth's crust due to movement of the Earth's plates
What particles make up the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and Neutrons
What forms of energy drive the rock cycle?
Heat and Mechanical
What drives the plate movement and where does this movement happen?
convection currents in the mantle (asthenosphere)
What molten rock is called on the surface of the Earth.
What is Lava?
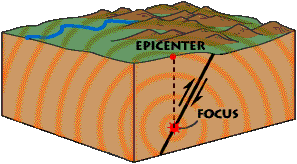
Where is the epicenter located in relation to the focus?
When an element loses a proton, its ___________ changes.
Atomic Number....Element
What is happening at #3 and 4?
heat and pressure
The hypothesis that continents have slowly moved to other locations.
What is continental drift?
What molten rock is called inside of the earth.
What is Magma?
What are the earth's layers starting from the inside? (4)
Inner Core...Outer Core...Mantle...Crust
The difference between Nitrogen-14 and Nitrogen-15.
One Neutron!
Explain how this could be both chemical and physical weathering.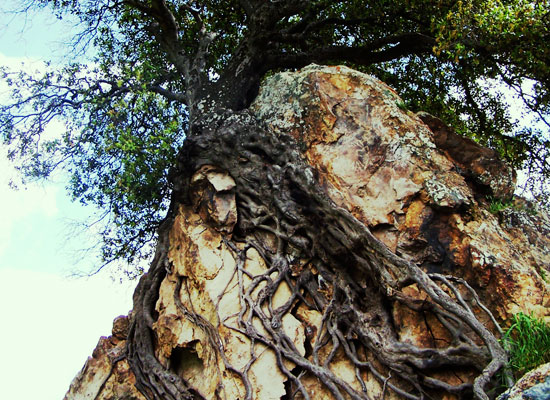
Chemical-plant secretes chemicals that alter rock
physical- roots grow and break rock apart
The youngest rocks on the ocean floor are located....
At mid-ocean ridges.
Do all volcanoes occur at plate boundaries? Explain.
No, Hawaii is formed from a hot spot underneath the Pacific Plate.
What types of plate boundaries are earthquakes likely to occur near? Describe what happens.
Transform. When the force of the moving blocks finally overcomes the friction of the jagged edges of the fault and it unsticks, all that stored up energy is released.
What powers the Inner Core?
Radioactive Isotopes
Explain the process from magma to a sedimentary rock.
Magma-->cooling and solidification-->igneous rock-->weathering and deposition-->sediment-->compaction and cementation-->sedimentary rock
The German meteorologist that first introduced the theory of continental drift.
Who is Alfred Wegener?
Where on the Earth do you find the most volcanoes? What is this place called? Why do volcanoes occur here?
The Ring of Fire on the Pacific Plate; convergent-subduction zone between two plates
What does magnitude measure? What is the difference between P and S waves?
Magnitude measures size or intensity of the earthquake. P waves are primary waves, arrive to seismic station first, and vibrate along the same direction as the direction of travel. S waves are secondary waves, arrive to the seismic station second, and vibrate at right angle to the direction of travel
How is earth's magnetic Field Generated?
Convection currents in the mantle and outer core Surround a solid Iron Inner Core. This together creates an electromagnet within the Earth.