What are the 5 characteristics all minerals must have?
Occur naturally, inorganic, solid, definite chemical composition, repeating crystal structure
Compare and contrast land won ore and marine won ore.
Both are types of mining. Land-won is under open ground, marine-won is under the ocean
What is uniformitarianism?
When looking at a striated rock, are newer layers on the top or bottom?
Uniformitarianism is the principle that states today’s landforms were created over a very long time by the same slow, gradual processes that we see at work today. Newer layers are deposited on the top.
Compare & contrast physical weathering and chemical weathering.
Both break rocks down into smaller pieces. Physical weathering does not change the composition of the rock, but chemical weathering does.
Name and describe 4 types of farming methods that can be used to conserve soil.
Conservation tillage: disturb soil and plant cover as little as possible
crop rotation: planting different crops in one field each year
contour plowing: planting fields along curves of a slope
conservation buffers: waterways and riparian buffers promote biodiversity
windbreaks: rows of trees or shrubs prevent wind erosion
terracing: stair step planting to prevent water runoff
wetlands: catch and hold water to slow soil erosion
Which mineral property is:
Least reliable?
Found by scratching with a fingernail?
Found by rubbing on a ceramic plate?
How light reflects off it?
1. Color
2. Hardness
3. Streak
4. Luster
Name 2 items extracted from quarries and 2 items extracted from mines.
Quarries- sand, gravel, rocks; Mines- gold, copper, iron, etc.
Name the 4 compositions of igneous rocks.
What is Felsic, mafic, ultra mafic, intermediate?
Name these soil horizons from top to bottom (letters are fine).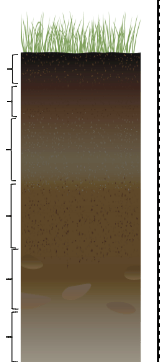
O, A, E, B, C, R
What are geosmins and how do they form?
Geosmins are metabolites that give soil its smell. They form from the bacteria Streptomyces.
What scale is used to determine a mineral’s hardness? What are the softest and hardest minerals?
Moh’s hardness scale, talc, diamond
What problems can we expect in the future regarding mineral supply and cost of mining?
Mineral supply will diminish and be harder to extract, which will lead to increased mining costs.
List the 4 textures igneous rocks can have.
What is fine grained, coarse grained, glassy, porphyritic?
Rank the following from largest to smallest:
Silt, clay, sand
What is Sand, silt, clay?
Describe the difference between permeability and porosity of soil.
Porosity is the rock’s ability to hold fluid, while permeability is how easily the fluid can flow from space to space within the soil.
Match the following:
Large Crystals - Formed slowly
Small Crystals - Formed quickly
No Crystals - Formed very quickly
What are the benefits & drawbacks to surface and subsurface mining?
Surface mining is safer and less expensive but has large impacts on the environment because it drastically alters the landscape. Subsurface mining has less impacts on the surface landscape, but is more expensive, less safe, and can still cause acid mine drainage.
What are the 4 types of metamorphism?
What are the 2 categories of metamorphic rocks?
What is Contact, dynamic, regional, hydrothermal; foliated and nonfoliated?
Name & describe the 3 ways wind can erode soil.
Creep- rolling or sliding across ground
Saltation- bouncing
Suspension- moving in air
A soil sample has 5 inches of sand, 2 inches of silt & 3 inches of clay. What type is it?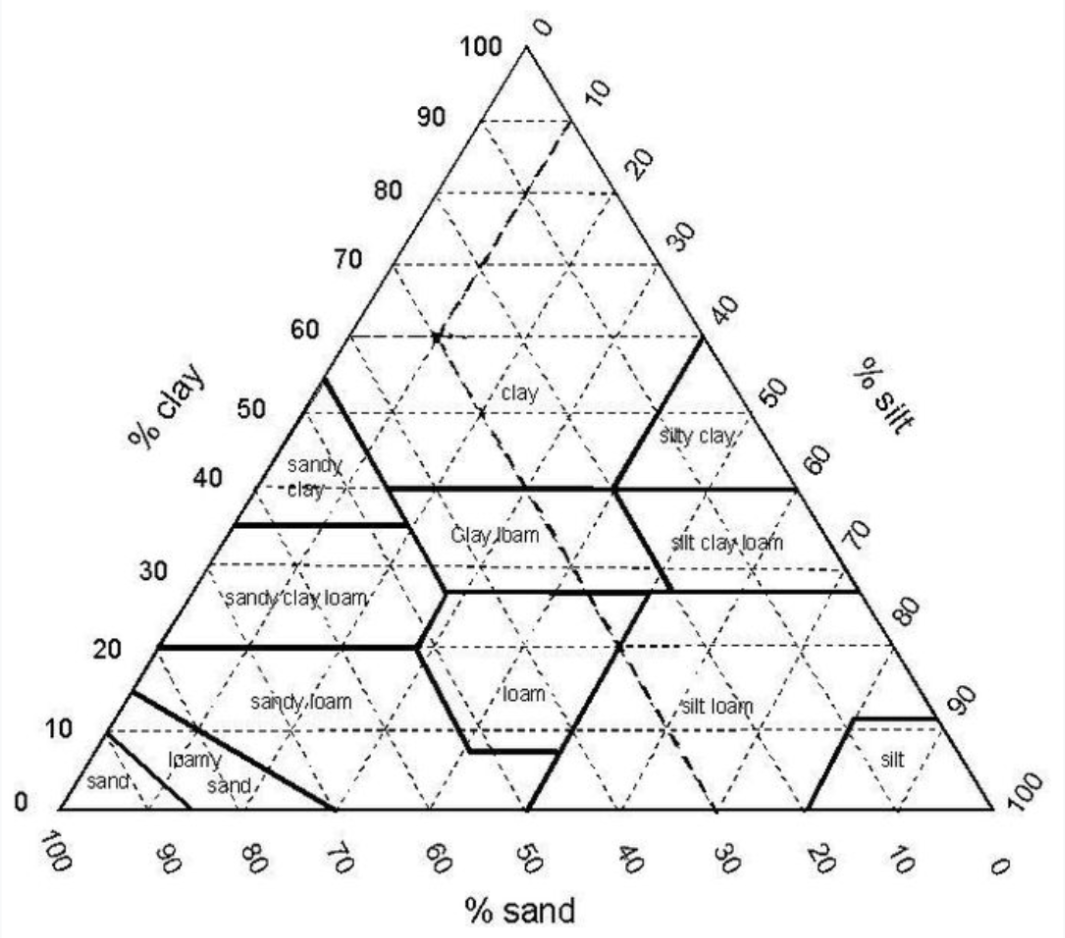
Sandy clay loam
Name 2 “special” properties of minerals.
What is Magnetic, bubble in acid, salty taste?
How do reclamation and restoration differ in terms of mining?
Reclamation is the rehabilitation of a disturbed site for a useful or desirable purpose, while restoration is a legal term that involves returning a disturbed mining sit to a nearly natural state.
What are the 3 types of sedimentary rocks and how do they form?
Clastic- weathering & erosion of preexisting rocks, chemical- mineral deposits from solution, organic- remains of plants & animals
Name the 5 types of water erosion.
Sheet, rill, ephemeral, gully, streambank
What biome might this soil sample be from?
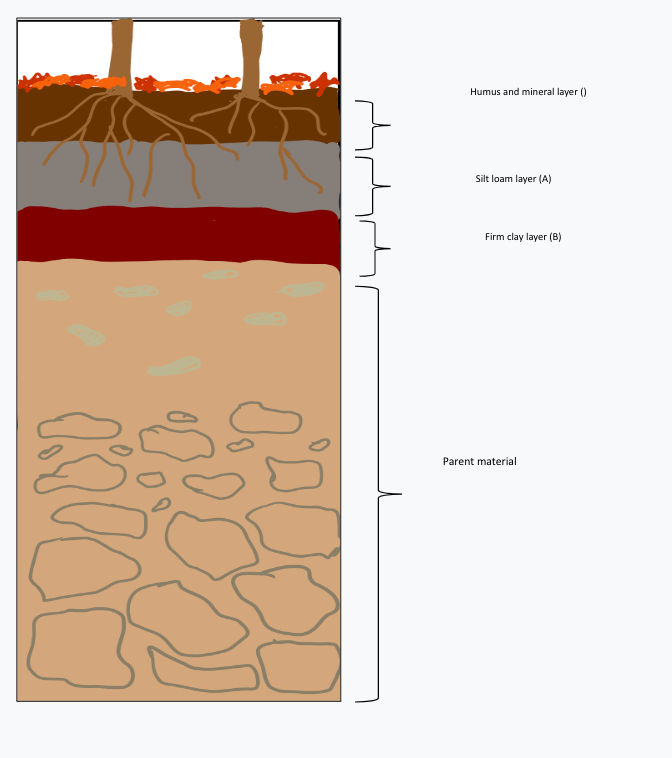
Temperate deciduous forest (it has a significant amount of leaf litter and organic matter on top)