Diagnosis of SBP is established by (name both)
1- positive ascitic fluid bacterial culture.
2- elevated ascitic fluid absolute PMN count (≥250 cells/mm3)
Wernicke's syndrome, characterized by nystagmus, opthalmoplegia, ataxia, and confusion, is almost exclusively described in chronic alcoholics with this deficiency.
Thiamine
Name 4 extraintestinal manifestations of IBD.
- Oral aphthous ulcers
- Arthritis including spondylitis and sacroiliitis
- Episcleritis or uveitis
- Erythema nodosum
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
This esophageal motor disorder is associated with failure of the LES & aperistalsis, what is the gold standard for diagnosis?
Esophageal manometry
This is a premalignant condition caused by longstanding GERD.
Barrett esophagus
This is given to patients after a large volume paracentesis. List when it is indicated and what the dose is.
25% Albumin.
Large volume paracentesis: Typically defined as the removal of more than 5 liters of ascitic fluid. The recommended dose is 6-8 grams of albumin per liter of ascitic fluid removed.
Most likely diagnosis in this patient with abdominall pain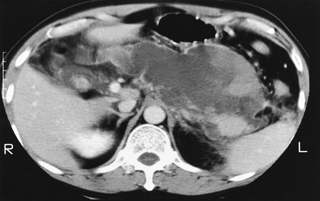
Necrotizing pancreatitis
Chronic senna use can lead to this benign finding.
Melanosis coli
Cyclical vomiting syndrome in young men relieved with hot shower
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome
Treatment for H. Pylori
Triple therapy: amoxicillin/metronidazole, clarithromycin, and PPI
This coagulation factor can help distinguish DIC from acute liver disease
Factor VIII
Pancreatic disease associated with parotid gland enlargement and mediastinal lymphadenopathy
Autoimmune pancreatitis (IgG4 disease)
Patients with celiac disease have an increased prevalence of this colitis
Microscopic colitis
A young adult presenting with extreme dysphagia and food impaction might have... and what is required to meet the diagnostic criteria
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophil-predominant inflammation on esophageal biopsy, characteristically consisting of a peak value of ≥15 eosinophils per high power field (HPF)
Two substances that may result in melena - like stool
bismuth & iron
Diet: spinach, charcoal, licorice, beetroot, aluminum hydroxide
Define 3 of 4 criteria needed to meet the definition for acute liver failure
1. INR > 1.5
2. Neurologic dysfunction with any degree of hepatic encephalopathy
3. No prior evidence of chronic liver disease or cirrhosis
4. Disease course of < 26 weeks (6 months)
Based on the "WATERFALL trial" what was the recommended rate of fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis?
-Bolus 10 ml/kg (only if hypovolemia present).
-infusion 1.5 ml/kg/h.
-Additional boluses if UOP <0.5 ml/kg/hr or SBP less than 90
-If normovolemic infusion will stop after 20 h if pt tolerated oral intake for>8 h
- Suspicious for volume overload: decrease or stop infusion
Postprandial abdominal pain, fear of eating, and weight loss should prompt what study to look for what problem?
CTA to look for chronic mesenteric ischemia
Definition of refractory GERD?
Persistent bothersome heartburn (>2 times/week for 3 months) despite BID PPI therapy.
Gastric disorder associated with 'watermelon stomach' appearance on endoscopy
Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE)
Name the type of syndrome that is associated with cirrhosis and is characterized by pulmonary hypertension with portal hypertension and how it is diagnosed.
Portopulmonary. Diagnosed by echocardiography.
The Tokyo 2018 guidelines diagnostic criteria for acute cholangitis
A- Systematic inflammation (fever>38/chills, leukocytosis >10k, leukopenia<4, increased CRP)
B- Cholestasis: Jaundice (TBili > or equal 2), elevated ALP, GGT, AST, or ALT>1.5 upper limit)
C- Imagining:- Biliary dilation, evidence of etiology (stricture, stone, stent)
Suspected cholangitis?: one item from A and one from B or C.
Definitive: one item from A one item from B and one item from C
Criteria for severe C. diff infection and what is the treatment
WBC>15k, Creatinine>1.5
Vancomycin PO 125 mg qid for 10 days OR fidaxomicin 200 mg bid for 10 days
This medication is FDA-approved for erosive esophagitis treatment (class c/d) and as part of the H. Pylori treatment regimen, what is the mechanism of action?
Vonoprazan is a potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) that inhibits the H +, K + -ATPase enzyme system in a potassium-competitive manner.
The most sensitive and specific test for diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
secretin stimulation test
The King's College criteria for liver transplantation in acetaminophen-induced ALF?
>> Arterial lactate >3 mmol/L after fluid resuscitation.
OR
>> PH <7.3
OR
>> Grade 3 or 4 encephalopathy with INR >6.5 and Creatinine > 3.4