Explain what comparative advantage means in trade theory.
Comparative advantage means a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another.
Define globalisation
Globalisation is the process of increasing interconnectedness among countries.
What is the main goal of external stability?
External stability means keeping the balance of payments sustainable without large fluctuations.
Define exchange rate.
An exchange rate is the price of one country’s currency in terms of another’s.
Define terms of trade.
Terms of trade measure export prices relative to import prices.
What is absolute advantage?
Absolute advantage is the ability of a country to produce more of a good with the same resources than another country.
List three major drivers of globalisation
Three drivers: technology, trade liberalisation, and multinational corporations
Define sustainable economic growth.
Sustainable economic growth is growth that meets current needs without compromising future resources.
Differentiate between a fixed and floating exchange rate system.
A fixed system is government-controlled; a floating system fluctuates based on market forces.
Explain the balance of payments.
The BOP records a country's economic transactions with the rest of the world.
Explain the concept of competitive advantage and how it differs from comparative advantage.
Competitive advantage refers to the ability of a country or business to produce goods or services more efficiently, with higher quality, or at a lower cost than its competitors. Michael Porter argues that competitive advantage can be created rather than being solely based on natural endowments or resources. This view emphasises that countries or businesses develop competitive advantage through deliberate strategies and investments in unique capabilities, resources, and innovations.
What are two positive economic effects of globalisation?
E.g. Economic growth and access to global markets are two positive effects.
Describe internal stability
Internal stability is maintaining full employment, low inflation, and stable economic growth.
What factors can cause an appreciation of a country’s currency?
Appreciation occurs due to higher interest rates, increased foreign investment, or rising export demand.
How does an increase in export prices relative to import prices affect terms of trade?
Terms of trade improves, as higher export prices increase purchasing power.
Calculate the opportunity cost of producing 10 units of wheat if a country could produce 5 units of textiles instead.
Opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of wheat = 0.5 units of textiles (Producing wheat means giving up the production of textiles.)
Explain how globalisation can lead to cultural homogenisation
Cultural homogenisation means that local cultures adopt similar customs, influenced by global culture.
Explain how maintaining low inflation is related to internal stability.
Low inflation prevents the erosion of purchasing power, aiding economic stability.
Draw a supply and demand diagram to show the effect of increased demand for exports on the exchange rate.
Draw a diagram showing an increase in demand for domestic currency as exports rise, shifting the demand curve right.
Calculate the terms of trade index if a country’s export prices increased by 10% and import prices by 5%. Assuming this happens in the year following the base year (which has TOT index of 100)
Terms of trade index = (110 / 105) * 100 = 104.8.
If Country A can produce 50 units of Product X or 30 units of Product Y, while Country B can produce 60 units of Product X or 40 units of Product Y, which country has a comparative advantage in Product Y?
Country B has a comparative advantage in Product Y, as it gives up less Product X than Country B does when producing Y.
OC of Y (Country A) = 50/30=1.67 units of X
OC of Y (Country B) = 60/40= 1.5 units of X
Describe how multinational corporations (MNCs) impact economic growth in developing countries
MNCs create jobs and infrastructure but may also exploit resources and provide low wages in developing countries.
Explain why achieving full employment can sometimes lead to higher inflation in an economy.
When an economy is close to full employment, most available workers are employed, and businesses may struggle to find enough workers to meet demand. As a result, businesses may raise wages to attract more workers. Higher wages increase workers' spending power, which can drive up demand for goods and services.
Explain, with a diagram, how interest rate changes can lead to currency depreciation.
Draw a currency depreciation due to falling demand when interest rates decrease, shifting the demand curve left.
If a country’s terms of trade index moves from 120 to 130, what does this indicate about its trade position?
An increase to 130 indicates the country can afford more imports per unit of export.
Draw a production possibility curve modelling both country A and Country B's production possibilities.
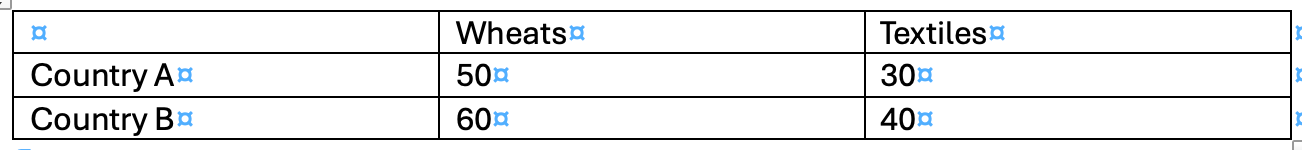
Draw production possibility curve
Explain how globalisation can affect a country's terms of trade
Global demand for exports can raise prices, benefiting terms of trade.
How does government policy support sustainable growth in an open economy?
Government policy supports growth through infrastructure, innovation, and trade incentives in an open economy.
If Country X’s currency depreciates due to increased imports, illustrate the impact on the demand and/or supply curves in the foreign exchange market.
Increased imports shift the supply of the domestic currency right, leading to currency depreciation.
What could be the effect on the current account if Country A has an increase in imports worth $2 billion while its exports remain constant?
The current account balance worsens by $2 billion.
Explain how a country can transition from having a comparative advantage to building a competitive advantage in a particular industry. Discuss how government policies and private sector initiatives could support this transition.
Government Policies: The government can support this transition by investing in infrastructure, providing subsidies or tax incentives for research and development, and enhancing education and training to build a skilled workforce.
Private Sector Initiatives: Private companies can invest in technology, adopt advanced production techniques, and focus on brand-building to differentiate their products. By improving quality, innovating, and reducing costs, they create a unique position in the global market.
Using a real-world example, discuss the impact of globalisation on domestic employment in a particular industry
Example:offshoring in the manufacturing sector led to domestic job losses but increased efficiency and lower prices.
Evaluate the challenges of simultaneously achieving internal and external stability in an economy.
Managing inflation, trade balance, and employment can conflict, making simultaneous stability challenging.
e.g. Trade Balance vs. Employment: High employment can lead to higher domestic consumption, including demand for imported goods. This can worsen the trade balance as imports exceed exports. To improve the trade balance, a country may implement policies to reduce domestic spending on imports or devalue its currency to make exports more competitive. However, these actions can reduce consumer purchasing power or lead to job losses in sectors reliant on imported materials.
Inflation vs. Trade Balance: To manage inflation, a government may increase interest rates, which can strengthen the domestic currency. While this helps curb inflation by reducing demand, a stronger currency makes exports more expensive on the global market, potentially worsening the trade balance. Additionally, reduced export competitiveness can lead to lower production in export sectors, potentially increasing unemployment.
Using a supply-demand model, show the effect of inflation in Country Y on its currency's exchange rate, including shifts in the demand and/or supply curves.
Inflation increases the domestic price level, decreasing demand for exports and shifting the demand curve left.
Use the terms of trade model to illustrate how changes in world prices for a country's main export can affect its economic growth.
As world prices fall/rise for the export, terms of trade worsen/improved, decreasing/increasing export revenue and economic growth.