It is the presence of Goblet cells in a background of squamous cells
What is Barrett's esophagus
For parastomal hernias, the Keyhole mesh repair has higher recurrence rate than this technique (21% vs 12%)
What is Sugarbaker repair?
Fusiform dilation of the CBD is the most common type of this condition
What are Choledochal Cysts?
Gastrin and acid are produced in these parts of the stomach, respectively
What are Antrum and Body?
Pyloric Antrum is distal, and produces Gastrin that makes the proximal Body secrete Acid
Presence of this is a contraindication to non-operative management of acute uncomplicated appendicitis
What is an appendicolith (or fecalith)?
The risk of occult carcinoma in this premalignant condition is 40%
Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia
This common complication after inguinal hernia repair, is more common with laparoscopic approach than with the open approach
What is urinary retention?
A cholecystectomy alone is adequate for treating this malignancy stage
What is Stage 1A gallbladder cancer? (1A: invasion into lamina propria)
These two kinds of peptic ulcers are associated with acid hypersecretion
What are Peptic Ulcer types 2 and 3?
It is classically described as the presence of abdominal pain, fever, and jaundice
What is Charcot's triad?
It is an anterior 180º wrap of the stomach
What is Dor fundoplication?
This open hernia repair technique fixes both inguinal and femoral hernias
What is McVay repair
Rigler's triad is a sign of this condition
What is gallstone ileus?
Rigler's Triad:a) Pneumobilia
b) Small bowel obstruction
c) Ectopic calcified gallstone
This complication after inguinal hernia repair, is more common with laparoscopic approach
What is urinary retention?
Laparoscopy and general anesthesia + paralysis --> higher IV fluid support --> more urine produced --> bladder distended during surgery
This is the sufficient operation for a 0.5 cm adenocarcinoma found at the tip of the appendix
What is a Right colectomy?
Intervals for surveillance endoscopy are 2 years, 1 year, and 6 months, respectively
What is Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia, with low-grade dysplasia, and high-grade dysplasia
In this operation, the mesh is placed in the pre-peritoneal space, along with separation of the rectus muscle-IO/TA complex from the EO, and from the posterior rectus sheath
What is Rives-Stoppa repair?
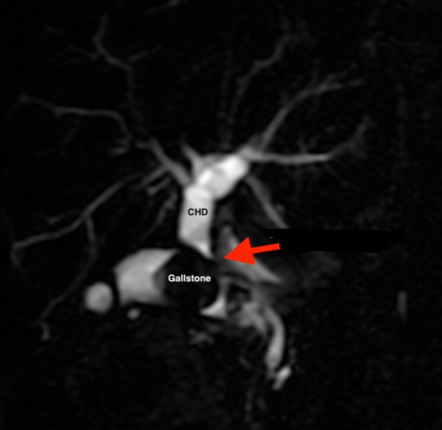
What is Mirizzi's syndrome?
This is the most common sarcoma of the GI tract, with the most common location being the stomach
What is a GIST?
These are the second common cause of death in FAP (after adenocarcinoma), and usually develop after surgery
What are Desmoid tumors?
Esophageal motility in this problem shows high pressures (>180 mm Hg), that last a long time (>6 seconds)
What is Diffuse Esophageal Spasm?
This operation involves suturing the conjoint tendon to a ligament than extends from the pubis medially to behind the Femoral V. laterally
What is the Bassini repair
A Bismuth Type B injury involves division of this structure
What is an accessory right hepatic duct?

This is the most appropriate operation for a Siewert 1 tumor
The anastomosis could be in the thorax (Ivor-Lewis), or in the neck (McKeown)
High metabolic activity in these tumors can lead to deficiency of vitamins B3 and B7
What are carcinoid (neuroendocrine) tumors?