What are the three levels of government?
Federal - taxation, defence forces, airports etc.; state - education, hospitals, emergency services etc.; local - libraries, rubbish, sewage etc.
Explain what parliamentary inquiries / royal commissions are.
Explain the role and function of the High Court.
The High Court of Australia serves as the highest court in the judicial system, interpreting the Constitution, hearing appeals, and safeguarding the rule of law.
Identify what case led to the recognition of native land rights and overrode the doctrine of terra nullius.
Mabo v Queensland (No. 2) (1992) 175 CLR 1
What are the separation of powers?
parliament (legislative), executive, judicature. The idea that the powers be separate was to avoid one arm or group from having all the power.
Explain what inquests are.
Inquests are when a coroner examines the circumstances of a person's death, partly in an effort to find ways to avoid similar deaths in the future (often including law reform).
Summarise the main functions of the Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia.
The Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 1) is a specialist family law court that continues the former Family Court of Australia. Established in 1975 under Chapter III of the Constitution, it is a superior court that hears the most complex family law trials and appeals.
The Federal Circuit and Family Court of Australia (Division 2) continues the former Federal Circuit Court of Australia. Established in 2000 under Chapter III of the Constitution, it is an intermediate court with broad federal jurisdiction across family law, migration, fair work, bankruptcy, intellectual property, consumer law, human rights, and administrative law.
When did the Australian Constitution take effect? What is the Australian Constitution?
1 January 1901. Australian colonies became an independent nation as the Commonwealth of Australia. Prior to the Constitution, Australia was made up of a number of separate British colonies with no federal government. The Constitution is the basic rules by which Australia is governed.
Explain how Queensland's unicameral system is different to the Federal bicameral system?
Queensland only has one house or chamber, without an upper house to review legislation and provide the checks and balances afforded by a bicameral system of governance. Queensland relies on the committee system to inquire into specified matters and report back to the parliament. Queensland only has a legislative assembly, whilst the federal system has a House of Representatives and a Senate.
Explain what specialist taskforces are.
Combined government and private sector groupings created to focus on very specific questions of law reform. In this context, we will also be looking at dedicated government law reform agencies, which exist specifically to consider proposals for law reform.
Summarise the role and function of the Queensland Civil Administrative Tribunal (QCAT).
The Queensland Civil and Administrative Tribunal (QCAT) provides a quick, affordable way to resolve disputes and review government decisions. It hears matters such as tenancy, consumer, and minor civil disputes, aiming for fair, accessible, and efficient justice.
What is the significance of Section 51 of the Australian Constitution?
It sets out the legislative powers of the Commonwealth Parliament - exclusive powers. The remaining powers were taken over by states and referred to as residual powers. Where both have the right to pass laws e.g., environment, health and education these powers are called concurrent powers. S109 allows Commonwealth to override State laws if there is an inconsistency.
Explain the principle of responsible government.
A responsible government is answerable to elected representatives of the people for its actions, especially a system where the ministry is drawn from within the parliament from members of the political party or parties with the support of a majority of a lower house and must maintain the confidence of the majority of that house.
Explain what lobbying or advocacy is.
Groups within society who see a need for something to change and make it their mission to bring those arguments to the parliament and to the broader community.
Describe the role of the Privy Council.
The Privy Council advises the British monarch and serves as the final court of appeal for some Commonwealth countries and UK overseas territories. Historically, it was Australia’s highest appeal court, but Australia ended appeals to the Privy Council in 1986, making the High Court of Australia the final court of appeal.
What is the significance of S128 of the Australian Constitution?
Section 128 of the Constitution provides the manner in which the Constitution can be altered, changed or modified. The Constitution can be changed by referendum according to rules set out in S128. For a referendum to pass, it requires a double majority - a majority of voters in a majority of states and a majority voters across the whole country.
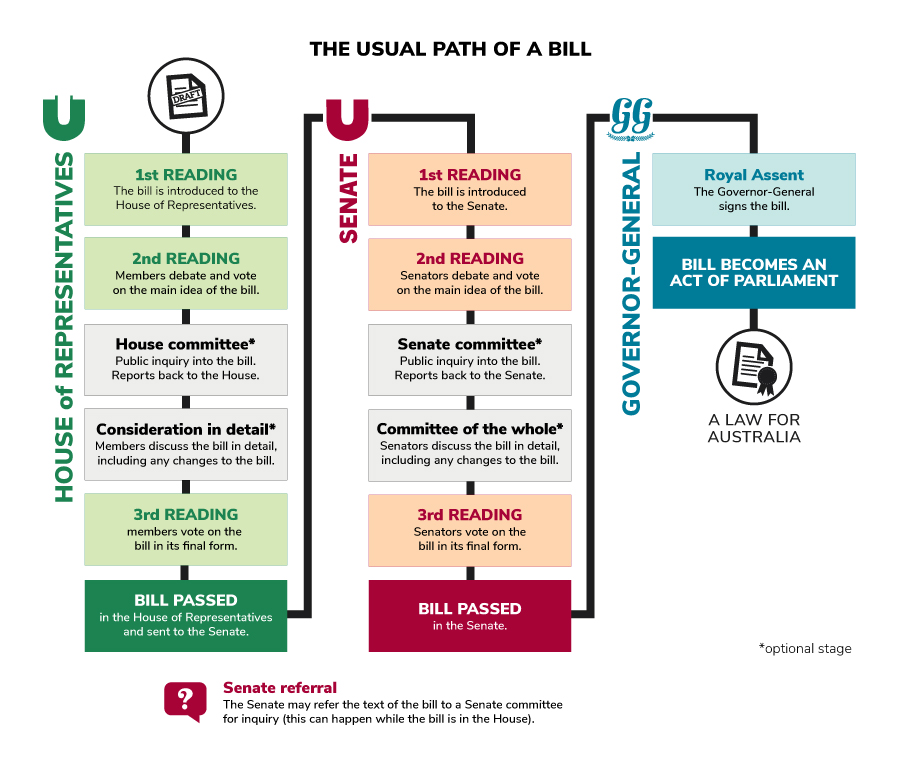
Explain how a Bill becomes law (legislative process)
Explain how the motivations for law reform between sectional lobby group and a promotional lobby group differ.
Sectional lobby groups represent the interests of a specific group within society, such as trade unions or professional associations. Their motivation for law reform is to protect or advance their members’ interests.
In contrast, promotional lobby groups advocate for broader social, moral, or environmental causes that benefit the wider community, such as human rights or environmental protection. Their motivation is to achieve law reform that promotes a particular public issue or value, rather than self-interest.
The High Court of Australia sets binding precedents for all lower courts in Australia. Its decisions must be followed by all other courts when dealing with similar legal issues.
Explain the significance of the Commonwealth v Tasmania (1983) 158 CLR 1 case.
The decision in this case was that the Commonwealth could validly override conflicting state laws in order to prevent a state from taking actions that would adversely affect areas of significance, such as a World Heritage site. The issue was pertaining to S51 and S109.