Define weathering
is the process of breaking rocks, sand, and clay down into smaller pieces
Define Erosion
The process of moving sediment from one place to another
Define Deposition
The dropping off and layering of sediments in a new location or place
Name one type of fossil
Trace Fossil
Amber
Full body Fossil
 What does a physical map show?
What does a physical map show?
Elevation and other Physical Features
WEATHERING is the process of breaking rocks, sand, and clay down into smaller pieces called ________.
Sediment
Explain how weathering and erosion worked together to carve the Grand Canyon 
Weathering alone cannot carve a canyon. Erosion must also happen. As the Colorado River carried huge amounts of sediment from the canyon to the ocean, the water eroded the rock. Most scientists think it took about 6 million years for the river to weather and erode the whole Grand Canyon.
How can water cause deposition?
water carries sediment to a new place. As the water or current slows, the sediment is then deposited.
Define fossil
evidence of an animal or plant that lived a long time ago
What is an earthquake?
An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of rock underground.
Identify three causes of weathering.
water, wind, living things
Identify four causes of erosion.
water wind people animals
How can a beaver cause deposition?
A beaver is one animal that changes Earth's surface by depositing material. Beavers build dams. A dam is a wall of material that blocks the flow of a stream or river. Beavers use dams to get food and to protect themselves. The dams also allow them to access their homes. Beavers build their dams on a stream or river using rocks, mud, and pieces of trees. The dam stops water from flowing. Water builds up behind the dam, which causes a pond to form. Some of these ponds are larger than a football field!
How are fossils formed?
sediment covers dead creatures , eventually preserving them as fossils. As the layers of sediment accumulate and turn to sedimentary rock, the fossils are trapped and protected inside of them. Almost all fossils are found in sedimentary rocks.
Melted rock under Earth's surface is called _______.
Explain how weathering may have caused this landform.
How can humans prevent erosion?
Answers vary
How can a glacier cause deposition?
Glaciers deposit large amounts of rock, sand, and mud at their bases. The glacier carries its sediment down the valley to lower elevations, where it is warmer. This part of the glacier starts to break off and melt. Here, it deposits the soil and rocks that it carried. This is usually many kilometers from where the glacier started.
Most fossils are found in what type of rock?
Sedimentary
What is the pattern in location of earthquakes and volcanoes?
Most of the world’s earthquakes and volcanoes happen in an area around the Pacific Ocean.There are so many volcanoes here that it is called the Ring of Fire. A map can show that volcanoes and earthquakes happen in many of the same areas.
Explain how rainwater causes weathering and erosion.
After a storm, more water flows through rivers. As this larger amount of water flows, it erodes the river channel by loosening and transporting the soil downstream. If there is enough water, it may even carry rocks and boulders. These actions can also cause the break up of soil and rocks, weather material in the river channel.
 Explain how the process of ice wedging causes erosion
Explain how the process of ice wedging causes erosion
The ice wedging causes bits of rock to break off. These pieces that the ice breaks off do not always stay in the crack. Often the melted ice, rain, or other sources of water carry these bits of rock away from the crack. Gravity can make the pieces fall out too. In these ways, the weathered rock erodes.
How does the weight of sediment affect wind erosion and deposition?
The size of the pieces of eroded material affects their erosion and deposition. Large pieces such as large grains of sand are too heavy to be lifted high. Most winds can only carry them across the ground for a few centimeters or so at a time. Where the sand is carried and dropped by the wind, it can build up into hills called sand dunes. Some dunes are 400 meters (about 1,300 feet) tall!
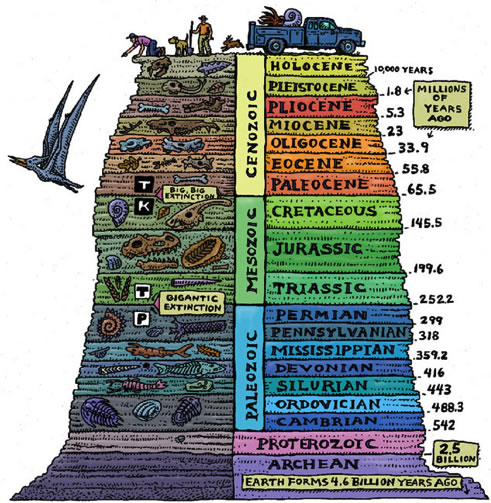 Name this image
Name this image
The Fossil Record
WHY do earthquakes and volcanoes happen mostly around the Pacific Ocean?
This is because they both occur at places where there are cracks in the Earth's crust.