This type of graph is best for showing the proportion of different parts to a whole.
Circle Graph
If a slice in a circle graph takes up half of the circle, what percentage does it represent?
50%
A bar graph shows the heights of different plants, which plant is the tallest?
The tallest plant is the Tulip at 148 cm
What is one way a graph can be misleading?
By not having a clear title or labels, or by using an inappropriate type of graph
Which type of data can be counted in whole numbers (like the number of students in a class)?
Discrete data
This graph uses bars to show the frequency of data in different intervals.
Histogram
If a circle graph shows the favourite ice cream flavors, what does the size of each slice tell you?
the proportion (or percentage) of people who chose that flavour
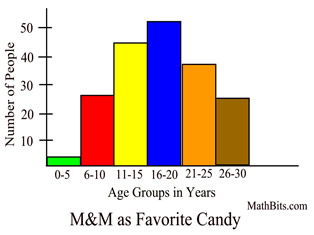
What information can you easily see by looking at the bars in a histogram?
What the ranges of values are and how many fall into each range
If the y-axis of a bar graph doesn't start at zero, how could this make the graph misleading?
It can make the differences between the bars look much larger than they actually are.
Which type of data can take on any value (including decimals) within a range (like a person's height)?
Continuous data
This graph uses points connected by lines to show how data changes over time.
Line Graph
What is the most and least popular mode of transportation?
Bus is the most
Other is the least
If a line graph shows a steady increase in temperature over several hours, what is happening to the temperature?
The temperature is increasing
How can changing the scale on the axes of a graph make it appear that there is a bigger or smaller difference between data points?
It can exaggerate or minimize the changes or differences in the data.
Give an example of discrete data.
The number of students in a class, the number of cars in a parking lot, or the number of pets a person owns
This graph uses separate rectangular bars to compare different categories of data.
Bar Graph
How can you estimate the actual number of people in a category if you know the percentage and the total number of people surveyed in a circle graph?
multiply the percentage (as a decimal) by the total number of people.
If a line graph shows a steep downward trend, what does that indicate about the data?
The data is a decreasing trend
What should you always check when looking at a graph to avoid being misled?
The title, labels on the axes, and the scale of the axis
Give an example of concrete data
The actual measurements or observations collected (e.g., the specific heights of plants, the exact test scores of students)?
This is a way of organizing data in columns and rows to show the frequency of each value or category.
Frequency Table
What is one advantage of using a circle graph to display data?
It clearly shows the proportion of each category in relation to the whole.
What is the main purpose of a frequency table before you create a graph?
To organize the data and see the frequency of each value before choosing the best type of graph to display it.
Give an example of how a graph might use pictures instead of bars to make comparisons misleading.
For example, if you use pictures of different sizes to represent quantities, the area of the pictures might be misleading instead of just the height.
What is one graph you would use to graph discrete data?
What is the graph you would use to graph continuous data?
Discrete: bar graph or pie chart
Continuous: line graph or histogram