This is the term for any form of water that falls from clouds
Precipitation
Name the state change and what is happening to the particles when a substance changes from a liquid to a solid.
Freezing (solidification); the particles are losing energy until the cannot pass each other
What is labelled at B?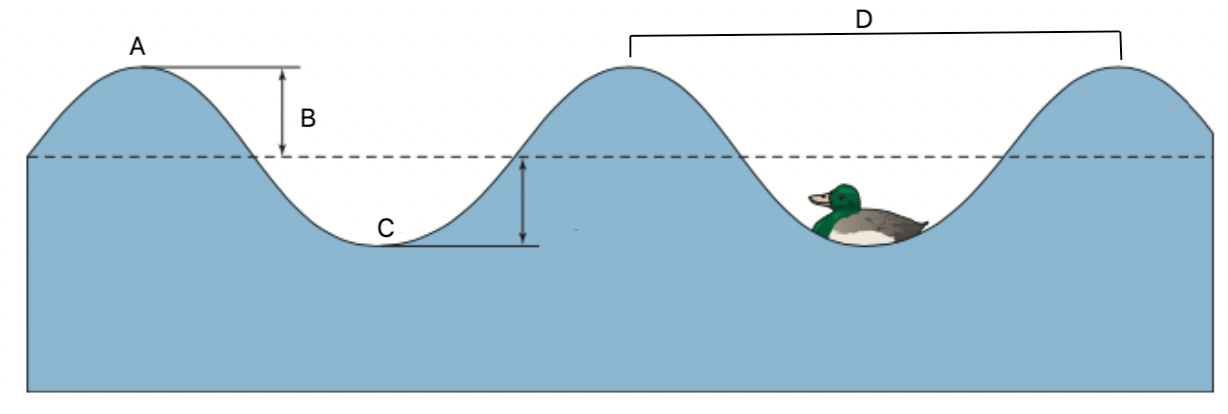
Amplitude
Name a section of the electromagnetic spectrum that has a higher frequency that visible light.
UV, x-rays, gamma rays
What is the difference between transparent, translucent, and opaque?
Translucent: nearly all light goes through, no refraction.
Transparent: some light goes through with refraction
Opaque: no light goes through
Name 2 things that increase your carbon footprint.
Driving a car, heating your house, flying, eating meat, etc...
What is the change of state that occurs when a substance changes from solid straight to gas?
Sublimation
If the time between beginning of point A to end of point D is 4 seconds, what is the frequency in Hz?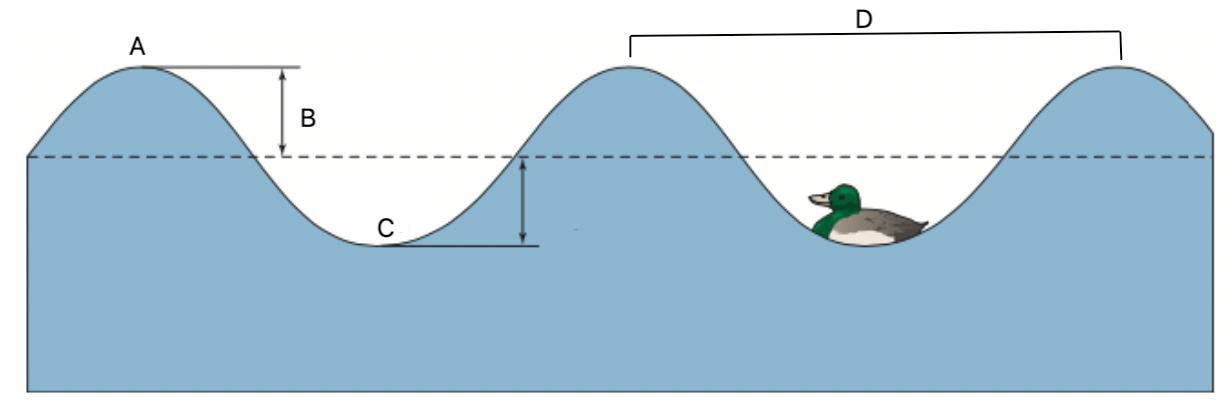
0.5 Hz
Name a section of the electromagnetic spectrum that has a longer wavelength than visible light.
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared
Name the colour order that light refracts through a prism, and why it is in that order
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet. They are in order of wavelength from longest to shortest.
What is the greenhouse effect and name one greenhouse gas.
When a layer of insulation (glass, gas, etc.) traps and reflects heat radiation, heating the environment. Carbon dioxide.
If a hot pan is left on a counter, what will happen to the pan? What is this called?
The pan will cool to room temperature because the energy from its particles will even out with the energy of the particles in the air. Thermal equilibrium
How is the movement of energy different in a transverse waves vs a compression wave?
Transverse waves the energy moves up and down (perpendicular to the wave movement)
Compression waves the energy moves side to side (parallel to the wave movement)
Which section of the electromagnetic spectrum is most harmful to human cells?
Gamma rays
In a plane mirror if the angle between the incidence ray and the normal is 38º, what will the angle of reflection be?
38º
2 terms: one that means water turning from liquid to gas from the ground, and one that means water turning from liquid to gas from plants.
Give any 3 points of the particle theory of matter
1. Everything is made of particles
2. Particles are always moving
3. Particles never touch
4. Particles in a pure substance are all the same
5. Particles are attracted to one another
What is the amplitude of this wave? 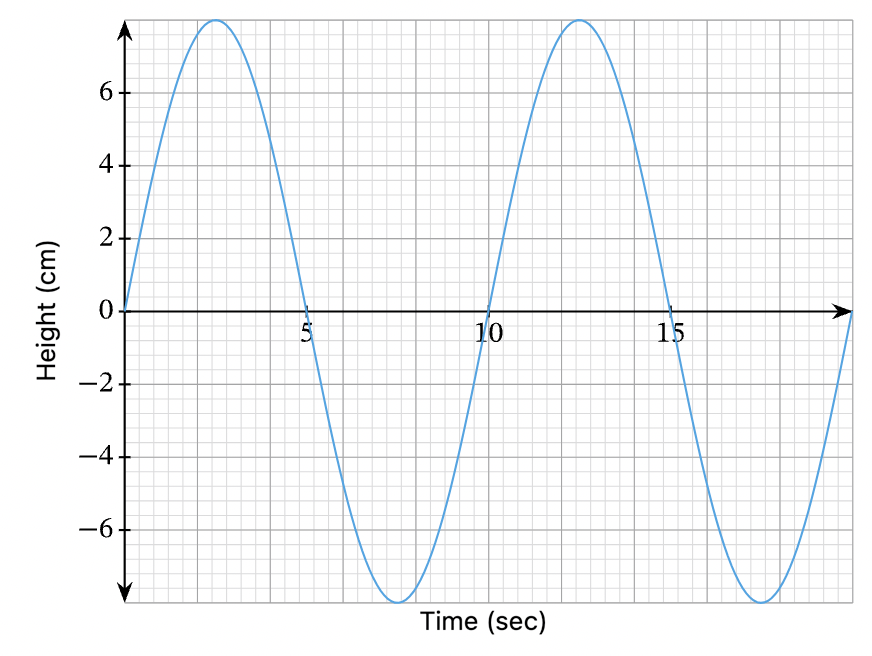
8cm
Red
What is the S.A.L.T of an image reflected in a plane mirror?
S: same
A: upright
L: same
T: virtual
Name the 3 'spheres' in the water cycle, and where they are.
Atmosphere: air
Hydrosphere: surface water
Lithosphere: underground
Define specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise 1mL of a substance 1ºC.
What is the frequency of this wave in Hz?
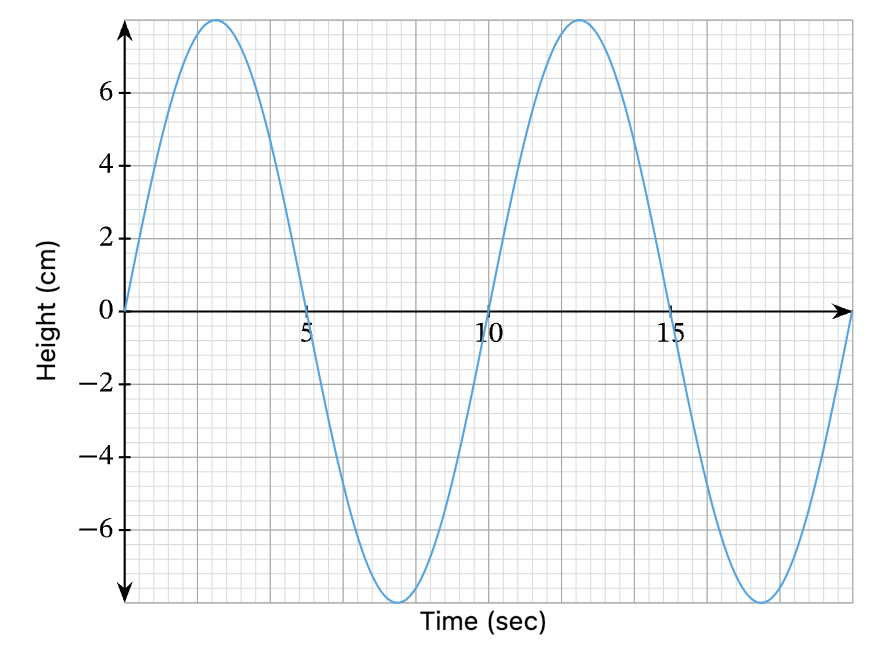
0.1 Hz
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
They are inversely related (one gets larger the other gets smaller)
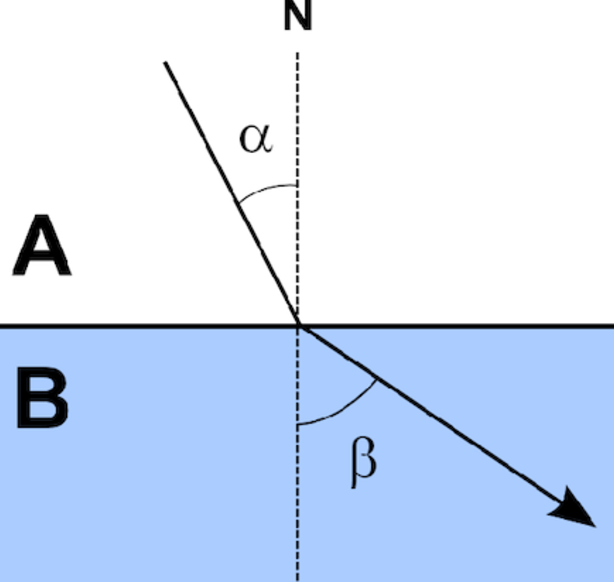
Using what you know about angle of refraction, compare the densities of substance A and B.