Name the 3 states of matter.
Solid, liquid, gas.
What does a plant cell have that an animal cell doesn't?
Cell wall.
Name the six types of simple machines.
Wheel and Axle, Pulley, Screw, Inclined Plane, Wedge, Lever
What is light?
A form of energy.
Define potable.
Safe to drink
What are the 5 changes of state?
Sublimation, Condensation, Vaporization, Melting, Freezing.
What leads your food to your stomach?
Hint: Digestive system
Esophagus
What is the formula for work? Specify the measurements.
Work (Jules) = force (Newtons) x distance (Meters)
Provide an example of phosphorescence light.
Glow-in-the-dark stickers.
Which wastes less water: a shower or bath?
Shower.
On a chart, where would you place saturated, unsaturated, and supersaturated?

Name the Levels of Organization (multicellular organisms).
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
Provide an example of gravitational energy.
A swing.
Define refraction.
The bending of a ray as it passes at an angle from one medium to another in different speeds.
What percentage of water is saltwater? Freshwater?
97% saltwater, 3% freshwater.
What are the two types of pure substances? Name an example of each.
Types: Elements and compounds. Examples: water (compound), hydrogen (element)
Define the function of the epiglottis. What system is it located in?
In the Respiratory System, the epiglottis serves as the "gate" between your esophagus and trachea. It closes in the process of consumption, and opens when you inhale/exhale.
Where is the force in and out located on this diagram?
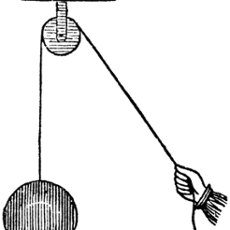
Right side, pointing down = force in
Left side, pointing up = force out
How do our eyes see the image through a flat mirror?
Plane mirrors work because the light rays create a virtual image behind the mirror. Light rays are emitted in all directions. The light rays bounce off of mirrors into your eye.
Where is the majority of Earth's freshwater located?
Glaciers and icecaps.
How can viscosity affect the flow rate of a substance? Provide an example.
The thickness of a substance defines the resistance to flow. Example: honey is a thick substance, resulting in its slow flow rate.
What are the 5 main structures in the Circulatory System?
Heart, Arteries, veins, capillaries, blood.
Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy. Provide an example.
Potential energy is stored, kinetic energy is moving.
Ex: A roller coaster moving upward = potential, roller coaster moving downward = kinetic
Define Bioluminescence light. Provide an example.
Chemical energy in living organisms that produce light. Ex: Firefly
What forms can water be in?
Gas water vapor, liquid water, and solid ice cubes.