What causes atoms to dance faster?
increased heat/energy
What is the name of the model we currently use for atomic structure?
quantum/electron cloud
What is the name for the rows and columns in the periodic table?
Rows = periods
columns = groups or families
What sub-atomic particles live in the nucleus and what is their charge?
Proton (+)
Neutron(0)
If an atom gains an electron what charge will the ion be?
negative (more - charges than +)
If an atom is a letter, what is a molecule?
word
What bond transfers electrons and what bond shares electrons?
Transfer = ionic
Sharing = Covalent
Give three physical properties of maple syrup
- high viscosity
- brown colour
- sweet smell
- translucent
What are 2 errors in Thompson's cookie model?
- no nucleus, stationary electrons,
The metaloids divide what two classes of element on the periodic table
metal, non-metal
What subatomic particles are not located in the nucleus and what is their charge?
Electrons (-)
If an atom loses an electron what charge will the ion be?
Positive (more + charges than -)
How many atoms:
H2O
3
How many shared bonds can carbon create?
4
If a substance can be compressed, what state MUST it be in?
gas
Why is Heisenberg's model known as a probability cloud?
shows where electrons are most likely to be rather than drawing them in definitive locations
What are two things that atomic families tend to have in common
# of outer electrons, chemical properties etc
What element?
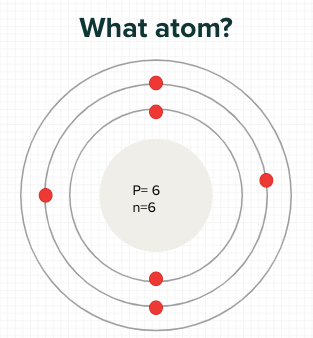
Carbon
Why do ions form?
Atoms want to have a full outer shell of electrons
How many atoms:
3C2H5OH
27
What classes of elements are involved in an ionic bond?
Metal + non-metal?
What is the main difference between a physical and chemical change
chemical change results in new particles
Which of Dalton's following observations do we now know are incorrect?
a) all matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms
b) all atoms of an element are identical
c) atoms of different elements are unique
none, maybe (a) if they can justify
What pattern determines the length of the first three periods?
# of valence (outer shell) electrons
What element am I?
Protons = 16
Neutrons = 16
Sulfur
Are non-metals more likely to gain or lose electrons? Why?
Gain, it's easier to fill a few empty spots than lose more electrons
What determines where the atoms in a molecule go (aka the structure of a molecule)
The number of bonds each atom can create.
What determines how many bonds an atom can make?
number of electrons in the outer shell
Name the type of matter for each:
1) coca-cola
2) beach sand
3) table salt
1) solution
2) mechanical mixture
3) compound
Explain how Rutherford's foil experiment gave proof of the nucleus
most +'ve particles passed through but some deflected. Showed small, + charged core of atom surrounded by empty space
Give the family name, an example and 2 notable characteristics of family 18
non-reactive, odourless, colourless gasses
Give me the Protons, electrons and neutrons of element He
2, 2, 2
If an alkali metal forms an ion, what will the charge be and why?
Positive, they are more likely to lose their outer electron
Why do some atoms have 1 line and some atoms have 2? What do the lines represent?
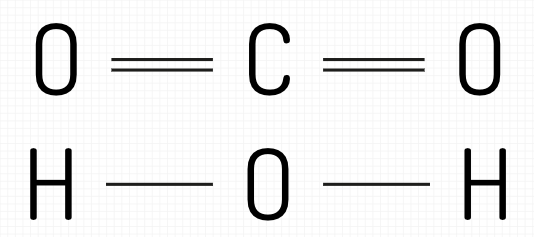
Lines = shared electron pairs
double line = 2 pairs
Why does a metal + non-metal create ionic bonds while two non-metals create a covalent bond?
metals want to lose ions and non-metals want to gain which makes the transfer of electrons easy. 2 non-metals both want to gain so which results in shared electron pairs