Heart arrhythmias are a complication of this electrolyte imbalance?
What is hyperkalemia
Living donor recipients are admitted on this day
When is Wednesdays
These are printed and interpreted every shift and PRN
What are ECG strips
This type of dialysis uses a machine and dialyzer to clean the blood outside of the body.
What is hemodialysis
These three immunosuppressants (antirejection) medications are given to help prevent graft failure
What are Tacrolimus, Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF), Prednisone
Correcting this electrolyte too quickly can cause Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome (ODS) which can cause permanent damage.
Vital signs are to be checked this frequently for the first 24 hours post transplant
What is every 4 hours
A common fast-paced irregular rhythm post renal transplant that affects the atrium
What is atrial fibrillation
This form of dialysis uses the patient’s peritoneal membrane as the filter to remove waste and excess fluid.
What is peritoneal dialysis
Signs and symptoms of rejection of kidney include
What is hypertension, swelling or puffiness (usually arms, legs, face), decreased urine output, fever, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, tenderness/redness/swelling of incision
This electrolyte imbalance can sometimes be caused by Tacrolimus.
What is hypomagnesemia
Patient charts must include this green form pre-operatively for deceased donor recipients
What is the Organ Allocation Kidney Recipient OR form
The automatic measurement and wireless transmission of cardiac data from remote sources
What is telemetry
For dry contamination in PD, this is left on the end for 15 minutes
These 4 professions must sign off on the renal transplant teaching checklist prior to discharge
Who are the renal dietician, transplant pharmacist, transplant nurse, and transplant social worker
This IV fluid is associated with a reduced risk of delayed graft function, hyperkalemia, and the need for post-transplant dialysis
What is Plasma-Lyte
A renal transplant recipient who is at high risk of rejection may get either of these medications pre-operatively
What are Basiliximab or Antithymocyte Globulin (ATG) (Thymoglobulin)
A supraventricular arrhythmia characterized by a "sawtooth" pattern, often causing fatigue, palpitations, and syncope
What is atrial flutter
For dialysate 1.5% dextrose and 4.25% dextrose, which would you expect to pull more fluids?
What is 4.25%
When assisting with self-meds, you observe patient having difficulty opening pill bottles, you take these steps to ensure a safe discharge
Consult homecare and/or arrange bubble packs
The new kidney may not fully regain its acid-base regulatory function, the patient presents with nausea/vomiting - based on the ABG results you might see this
What is metabolic acidosis
Call the Transplant Nephrologist if the urine output post transplant is?
What is Less than 30mL/hr OR decreased by 50% of previous hours output OR if urine output >300mL/hr
You have an order to give IV Metoprolol for a patient in this rhythm: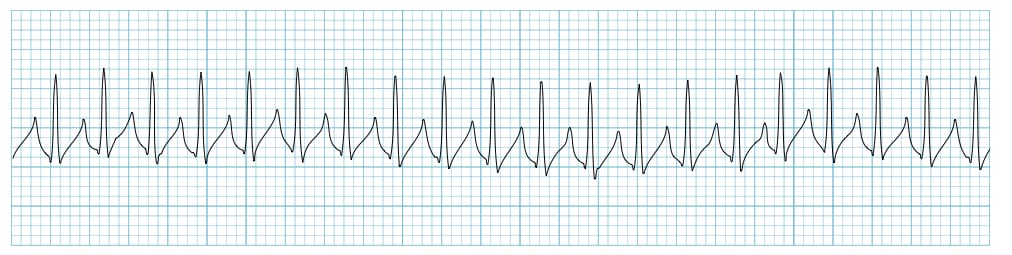
SVT or Atrial Tachycardia
This is one of the most common complications post-op in which the patient may need temporary dialysis until the new kidney “wakes up.”
What is acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
When teaching patients about self-administering medications, patients should be able to do what independently?
Calculate dosing for medications such as Tacrolimus, be able to open pill bottles, be able to track when they have taken their medications, tell time,