Ability of the brain to change its structure and patterns of activity in significant ways throughout life
What is neuroplasticity?
Our conscious or preconscious thinking (Mental activities of which we are aware or can become aware of with reflection)
What is cognition?
Provides clear descriptions of diagnostic categories so that practitioners of all disciplines can
–diagnose,
–communicate about, and
–treat people.
What is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V)?
A process of human life and development:
–Focusing on the search for a sense of meaning, purpose, morality, and well-being
–In relationship with oneself, other people, other beings, the universe, and ultimate reality, however understood
–Orienting around centrally significant priorities
–Engaging a sense of the transcendence
What is spirituality?
Basic working unit of all the nervous system
What is a neuron?
6 Interior Environment Systems
What are: nervous, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and reproductive systems?
A feeling state characterized by our appraisal of a stimulus
–By changes in bodily sensations
–By displays of expressive gestures
What is emotion?
Name the 4 theories of the self in relationships covered in Chapter 4 (and define 2)
What are:
–Relational Theory
–Attachment Theory
–Feminist Theories of Relationships
–Social Identity Theory
“An institutionalized (systematic & organized) pattern of values, beliefs, symbols, behaviors, and experiences that involves
•spirituality,
•a community of adherents,
•transmission of traditions over time, and
•community support functions that are directly or indirectly related to spirituality.”
What is religion?
provides the structure and processes for communicating sensory, perceptual, and autonomically generated information throughout the body.
What is the nervous system?
System that Supports and protects the body and provides motion
What is the Musculoskeletal system?
a major upset in our psychological equilibrium due to some harm, threat, or challenge with which we cannot cope.
What is crisis?
Name and explain the most influential theory of cognition in social work and psychology
What is Piaget's cognitive theory?
Based on transpersonal theories, specifically target the spiritual dimension. (focus on helping the person let go of ego attachments and transcend the self through various spiritually based practices)
What are fourth force therapies?
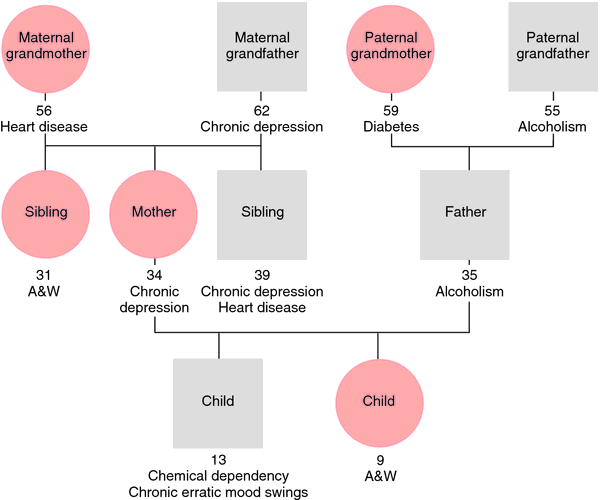
What is a genogram?
Called the silent killer and impacts this specific system
What is high blood pressure and cardiovascular system?
Any event in which environmental or internal demands tax the adaptive resources of an individual; it may be:
»Biological (disturbance in bodily systems)
»Psychological (cognitive and emotional factors involved in the evaluation of a threat)
»Social (disruption of a social unit)
What is stress?
Name the 3 categories of theories of emotion covered in Chapter 4 (and define 2 specific theories)
What are:
–Physiological Theories of Emotion
•Davidson’s Six Components of Emotional Style
–Psychological Theories of Emotion
•Psychoanalytic Theory
•Ego Psychology
•Attribution Theory
•Theory of Emotional Intelligence
–Social Theories of Emotion
•Social Constructionist Theory
•Symbolic Interaction Theory
Three factors that are significant in understanding religious conflict today (name & definition)
What are:
–Modernism (tension between science and religion)
–Multiculturalism (pluralistic reality versus unilateral belief systems)
–Modern technologies of warfare (arsenal now includes nuclear, biological, and chemical weapons of mass destruction versus primitive weapons)

What is an ecomap?
Three major subsystems that compose the nervous system (name and part(s) of the body)
What are:
1. Central nervous system (CNS): brain and the spinal cord
2. Peripheral nervous system (PNS): spinal and cranial nerves
3. Autonomic nervous system (ANS): nerves controlling cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and respiratory systems
unconscious, automatic responses that enable us to minimize perceived threats or keep them out of our awareness entirely (& name at least 2 common)
What are defense mechanisms? (examples on pg. 113)
Piaget's stages of cognitive operations
What are:
Sensorimotor stage (birth to 2 years)
Preoperational stage (2 to 7 years)
Concrete operations stage (7 to 11 years)
Formal operations stage (11 to adulthood)
The reasons that it is not enough for a social worker to know someone’s religious affiliation (name at least 2)
What are:
•Religious affiliation may or may not hold great significance for the person
•Beliefs and practices can be quite varied (even within families)
•Some feel connected to multiple spiritual perspectives (combining beliefs of different religions)
• Meaning of religious or spiritual affiliation may change across life course
•Meaning of person’s religious or spiritual affiliation must be understood within his or her broader historical, sociopolitical, an cultural context
Name at least 3 critical factors of our external socioeconomic environment that impact our interior health environment
What are:
•Differential access to health care
•Environmental exposures
•Health behaviors
•Exposures to stress
•Neighborhood and community