Which Assessment finding may be present in children with a migraine headache?
A)Abdominal pain
B) Sharp pain in cheek
C) Bandlike pain
D) Ice-pick pain
A) Abdominal Pain. Children with a migraine headache may present with abdominal pain and also have anorexia, nausea, vomiting, or pallor. Sharp, stabbing pain in 1 cheek- trigeminal neuralgia is more common in older adults and elderly.
Medication overuse headache is suspected if:
Use of prescription medication on at least ___ days/month, or use of acetaminophen or NSAIDs on at least ___days/month
10
15
Name a Triptan and Ergot that comes in the formulation of a nasal spray.
Sumatriptan (Imitrex) 5mg or 20mg in 1 nostril
Zolmitriptan (Zomig) 2.5-5mg in 1 nostril
Dihydroergotamine (Migranal) 1 spray (0.5mg) into each nostril
An elderly female pt is diagnosed w/ trigeminal neuralgia. Which assessment finding would the nurse practitioner expect?
Shock-like facial pain. Trigeminal neuralgia presents with extreme, shock-like facial pain that lasts from a few seconds to 2 minutes per event.
A 22 year old male athlete presents w/ knee pain for which the NP performs a Mc Murray test. A positive sign indicates which condition?
 Meniscal tear
Meniscal tear
The NP is educating a pt newly diagnosed with migraines about potential triggers. What statement by the patient suggests that more teaching is required?
A)"Cigarette smoke could precipitate a migraine"
B)"I should avoid foods that are high in potassium"
C)"My sleep patterns should be as consistent as possible"
D)"Stress reduction techniques could be helpful"
B)"I should avoid foods that are high in potassium". Nitrates can precipitate migraines, so patients should avoid consuming them.
Name 2 characteristics of Tension Type Headaches
Bilateral, non-pulsating pain, mild-moderate intensity, headache NOT worsened by activity
A 40 y.o complains to the NP of severe stabbing pains behind his left eye for the past 2 days. They are accompanied by some nasal congestion and rhinorrhea, which is clear in colour. The patient denies pharyngitis and fever. Which of the following conditions is most likely?
A) Migraine headache w/ aura
B) Cluster headache
C) Tic douloureux
D) Cranial neuralgia
B) Cluster headache. Cluster headaches' cardinal symptoms are excruciating, unilateral, orbital, supraorbital, and/or temporal pain. The attack ranges from 15 min - 3 hours or more. Autonomic sx include ptosis (drooping eyelid), miosis (pupil constriction), lacrimination (tearing), and rhinorrhea in the nostril on the affected side of the face.
Migraine headaches w/ aura include visual changes, such as blind spots or flashing lights, that appear before the onset of the headache.
Trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux) is a unilateral headache from compression or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
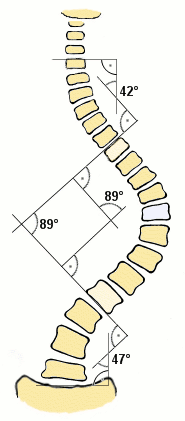
In an adult with scoliosis, what degree of spinal curvature requires a referral for surgical correction?
A)10-20 degrees
B)20-30 degrees
C)30-40 degrees
D) >40 degrees
D) >40 degrees- requires surgical intervention with a Harrington rod.
Curvature btw 5 and 20 degrees should be monitored for changes. Bracing is necessary for curvature between 20 and 40 degrees.
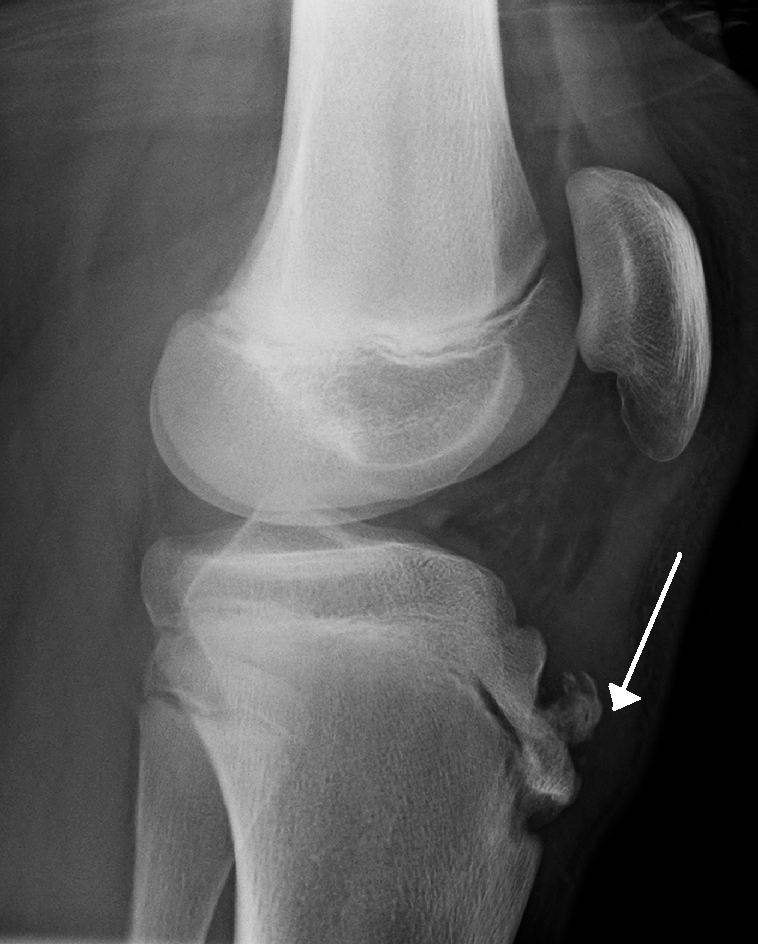
15 y.o male pt who is 6 ft. tall and a basketball player is seen for c/o of painful lumps on his anterior knees. The NP notes a bonelike growth on the upper tibia midline below the kneecap on both knees. He has full ROM, with no joint tenderness, redness, or swelling. What condition does he most likely have?
Osgood-Schlatter disease, is characterized by pain over the tibial tuberosity w/ palpation of a bony mass over the anterior tubercle of one or both knees. Exercise worsens the pain. Disease resolves on it's own once growth stops.
When would you consider preventive medications?
if >4-6 migraines per month, w/ significant severity and impact on quality of life
MIDAS- Migraine Disability Asessment is a 7 item validated self-administered questionnaire.
Name a medication for prophylactic treatment of tension-type headache
1st line- amitriptyline 10-100mg daily or nortriptyline 10-100mg daily
2nd line- venlafaxine 150mg daily or mirtazapine 30mg daily
Which of the following is a contraindication for prescribing the "triptan" drug class?
A)Peptic Ulcer Disease
B)Ischemic Heart Disease
C)Acute Kidney Injury
D)Hepatic Impairment
B)Ischemic Heart Disease. Due to limited evidence, it is recommended that triptans be avoided in pt's w/ hemiplegic or basilar migraine, ischemic stroke, ischemic heart disease. prinzmental angina, uncontrolled HTN, and pregnancy. Triptans should be limited to <10 days of use per month to avoid MOH.
A 60 y.o. female pt who works as a truck driver presents to the outpatient urgent care clinic of a hospital complaining of worsening of her low back pain in the past few days. Pain is accompanied by numbness in the perineal area. She describes the pain as "sharp and burning" and points to the left buttock. She reports that the pain started on the mid-buttock of the left leg and recently started to go down the lateral aspect of the leg toward the top of the foot. During the physical exam, the ankle jerk and the knee jerk reflex are 1+ on the affected leg and 2+ on the other leg. The pedal, posterior tibialis and popliteal pulses are the same on both legs. Which should the NP consider first for this pt?
Order an MRI scan of the lumbosacral spine ASAP! You want to r/o cauda equina syndrome as this is an emergent condition.
What type of imaging is MOST sensitive for detecting a meniscal tear?
MRI - detects the extent and type of meniscal tear. However, unless sx is being considered, plain radiographs can be appropriate for some pts w/ suspected meniscal tear. US can be used but not specific and depends on examiner. CT can be considered in some pts.
Name 2 of the characteristics that are required in diagnostic criteria for migraine without aura.
- Bilateral or Unilateral location, Pulsating, Moderate-severe pain, Aggravation by physical activity
- Migraine also needs at least 1 associated symptom of nausea/vomiting, photophobia/phonophobia
Cluster headaches are more common in females
F
These headaches are MOST prevalent in middle aged men between 30 and 40 years of age
A middle aged adult reports rhinitis and an ice-pick headache behind the left eye. The patient has a BMI of 20.1, FEV 1 of 63%, and CRP level of 3.7mg/L. Which of the following interventions is appropriate for this patient?
A)Administer 100% oxygen at 12L/min by mask
B)Administer a dose of sumatriptan (Imitrex) by injection.
C)Administer a dose of verapamil (Calan) orally
D)Advise patient to engage in stress-relieving activities
B)Administer a dose of sumatriptan (Imitrex) by injection. The pt likely has a cluster headache. The best intervention to treat this pt is to administer sumatriptan (Imitrex) by injection or nasally. Provides the fastest relief 10-15 min.
According to the BODE (BMI, oximetry, dyspnea, exercise) index score, the pt has COPD and should not receive O2 at high doses bc it will shut down the breathing center in the brain. The patient's CRP level is slightly elevated at 3.7 mg/L (normal is <3mg/L), indicating an inflammatory process. Verapamil (Calan) orally daily is prescribed for maintenance therapy. Stress relieving activities are important for the treatment of muscle tension headaches.
A highschool football player suffered a decleration pivoting injury of his left knee during a game.He states that he felt a sudden "pop" w/ subsequent swelling, and the knee seemed to buckle. Which action by the NP is appropriate when examining this patient?
A)Conduct Lachman's test
B)Apply ice to the joint
C)Perform isometric exercises
D)Support the joint with a compression wrap
E)Refer to an orthopedic specialist
A,B,D,E. Lachman's test should be used to test for ACL damage. An ACL injury is classically associated w/ a sudden "pop" and swelling. RICE protocol. Referral should be made to an orthopedic specialist for repair and f/u. Avoid isometric exercises during the early phase of recovery from a MSK injury.
1)The Lachman's maneuver is used to detect______. To perform this test, the knee is placed at ____degrees.
2)The anterior and posterior drawer test is used to detect______. To perform this test, the knee is placed at ____degrees.

 1) Instability of the knee. E.g. damage to ACL or tear of the ACL. The maneuver should be tested on both knees, comparing the injured knee and the opposite knee. Perform the test by bending the knee 30 degrees. The laxity is graded on a 0 (normal) to 3 scale (1.0-1.5cm of translation).
1) Instability of the knee. E.g. damage to ACL or tear of the ACL. The maneuver should be tested on both knees, comparing the injured knee and the opposite knee. Perform the test by bending the knee 30 degrees. The laxity is graded on a 0 (normal) to 3 scale (1.0-1.5cm of translation).
2)Instability of the knee-90 degrees.
The NP sees an adult who reports frequent headaches over the past few months. The patient has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen without relief. The patient has a hx of a MI, bradycardia, and kidney stones. Which medication is most appropriate for this patient?
A) Topiramate (Topamax)
B) Sumatriptan (Imitrex)
C) Imipramine (Elavil)
D) Atenolol (Tenormin)
C) Imipramine (Elavil). Based on the patient's medical history, imipramine at half strength is an appropriate medication to prescribe. Topiramate is NOT appropriate b/c of the pt's hx of kidney stones. Atenolol and propranolol are NOT appropriate b/c of a hx of bradycardia. Sumatriptan is not safe b/c of her history of MI.
What would be considered a Chronic Tension-Type Headache?
A) ≥ 10 days/month for a duration >3 months
B) 15 days/month
C) ≥15 days/month for a duration >3 months
D) 10 days/month
C) ≥15 days/month for a duration >3 months.
A middle-aged male patient with a history of cluster headaches arrives at the primary care clinic for treatment. Which of the following interventions is included in the acute treatment plan?
A)Ice pack on forehead
B)Acetaminophen
C)Intranasal 4% lidocaine
D)Phenytoin (Dilantin)
C)Intranasal 4% lidocaine. A patient with a cluster headache should be initially treated with 100% oxygen at 12L/min via mask and intranasal 4% lidocaine. These headaches are MOST prevalent in middle aged men between 30 and 40 years of age. An ice pack to the forehead and a dark room are effective for a migraine headache. Dilantin would be administered for trigeminal neuralgia. Acetaminophen or nonsteroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are helpful for muscle tension headaches.
A 74 y.o male patient presents with an acute-onset unilateral headache with a reddened and indurated temple. The patient is at risk for:
A)Vertigo
B)Amaurosis fugax
C)Ptosis
D)CN VII paralysis
B)Amaurosis fugax. The pt is experiencing temporal arteritis (giant cell arteritis), which causes an acute headache in one temple area w/ an indurated, reddened temporal artery and scalp tenderness. A major complication of this condition is transient blindness (amaurosis fugax) of the affected eye.
Vertigo is not a common complication of temporal arteritis but often occurs w/multiple sclerosis. Ptosis is seen frequently with cluster headaches rather than temporal arteritis. CN VII paralysis is often observed with Bell's palsy or injury to the specific nerve.
A 36 y.o male presents complaining of a hx of cervical and upper back pain for many months. On examination, the ROM of his spine is limited, especially with lateral flexion. The other joints in the patient's body are normal. Only the spine seems to be affected. The patient's reports that a laboratory test from a previous clinician showed increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), (-) antinuclear antigen (ANA), and (-)rheumatoid factor (RF). Which of the following is best described?
A)Rheumatoid arthritis
B)Lupus erythematosus
C)Degenerative disc disease of the spine
D)Ankylosing spondylitis
D)Ankylosing spondylitis is a lifelong autoimmune disease and a form of arthritis that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness, mainly in the spinal joints. The typical pt is a young adult. In early stages of AS, the pain and stiffness often start in the lower back, but overtime may move up to the spine and into the neck. Most people with AS experience episodes of acute pain, known as flares, followed by periods when symptoms temporarily subside. The ESR is increased by the inflammation, and often the ANA level is elevated for these patients. HLA-B27 gene may be completed to support the dx of AS.While, the ESR may also be elevated in RA and SLE, pts with RA commonly have elevated RF and more commonly experience pain in joints of extremities rather than spine. Pts with RA , lupus erythematosus, and DDD of the spine do not have abnormal HLA-B27 gene testing