Mouth/Neck
These compose of the Integumentary system and contribute to an individual's own unique appearance.
(hint 5 items)
What are skin, hair, nails, glands, and mucous membranes.
This simple bedside diagnostic test can be performed without a physician order and completed by observation with foods or fluids.
What is a swallowing evaluation?
This may be inherited, caused by maternal rubella or complications at birth, certain infectious diseases such as meningitis, chronic ear infections, use of ototoxic drugs, exposure to excessive noise, and aging..
What is hearing loss?
This is a buildup of intraocular pressure that damages the eyes optic nerve causing loss of peripheral vision.
What is Glaucoma?
Changes in this can be related to nutrition, stress, systemic disease, vitamin or iron deficiency, infection, and biting or picking..
What are changes in the nails?
It is imperative to assess this........ especially for someone at risk for impaired skin integrity.
What is nutritional status?
This lesion: is raised, round, or oval and filled with serous blood or clear fluid. (example: herpes simplex)
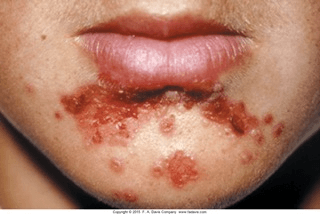
What is a vesicle?
These cancer risk factors refer to: Genetics, occurs three times more often in women, diets low in iodine, exposure to radiation.
This organ of hearing serves as the microphone in the ear, converting sound impulses and vibrations from the outer ear into electric impulses that are sent to the brain via the acoustic nerve (cranial nerve VIII)..
What is the cochlea?
This is a device to measure intraocular pressure (IOP); the device measures the outflow of the aqueous humor from the eye (screening test for glaucoma).
What is tonometry?
Changes in this can be related to diet, stress, genetics, infections, and endocrine disorders..
What are changes in hair?
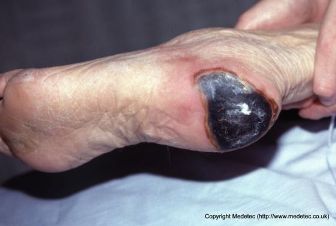 Name this tissue in the wound base.
Name this tissue in the wound base.
What is Eschar?
The best location to assess this is the clavicle area, but may also be done on the lower arm or abdomen. Pinch the skin between two fingers and let go.
What is assessing skin turgor?
(In a well-hydrated person, the skin returns to flat position immediately. In a dehydrated person or someone w/ extreme weight loss the skin remains tented and slowly returns to flat position. Skin turgor greater than 3 sec may be related to fluid loss.)
This is a common side effect from the following drugs:
Anticholinergics, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antihistamines, antihypertensives, antineoplastics
What is xerostomia? (dry mouth)
Otoscope and tuning fork
What are equipment needed to assess the ears?
This refers to the inability to see from side to side or up and down without moving the eyes or turning the head.
What is loss of visual field?
Tension, cluster, sinus, and migraine are all included in assessing this body part..
What is the head?
Stage this pressure injury..

A= Asymmetry
B= Border
C= Color
D= Diameter
E= Evolving
This ABCDE mnemonic is used to assess:
What are moles?
This is considered a medical emergency if is last longer than 30 minutes, interferes with breathing, or is following an injury..
What is epistaxis? (nosebleed)
These are what kind of signs of hearing loss; leaning forward, tilting the head and ear toward you and looking at your mouth (reading lips)
What is nonverbal body language?
This is a quantitative measurement to assess visual acuity.
What is the Snellen Eye Chart?
This is the perception of sound when no actual external noise is present; it is commonly referred to as "ringing in the ears"
What is tinnitus?
Name this staging.
What is DTI (deep tissue injury)?
These two vascular lesions: one are tiny, pinpoint hemorrhages caused by superficial bleeding from the capillaries of the skin; measure less than 3mm may be related to platelet deficiencies. The other is a hemorrhagic red or purple spot or rash that is flat and does not blanch; measures 3-10mm, may be associated with platelet disorders.
What are petechiae and purpura?
This cranial nerve assess symmetry of the face.
What is cranial nerve VII? (facial)
(nasolabial folds: the distance from the corner of each nostril to the corner of the lip bilaterally should be equal. & Palperbral fissures; distance between the upper and lower eyelids)
This test is used to assess for impaired or high-frequency hearing loss.
What is the whispered voice test?
Distant objects appear blurred because the visual image becomes focused in front of the retinal instead of on the retina.
What is Nearsightedness (myopia)?
According to American Diabetes Association; patients who have genetic disposition of diabetes are at greater risk for developing these eye disorders.. (4 disorders)
What are retinopathy, blindness, glaucoma, and cataracts?
Stage this wound..

What is stage 1?
You would best assess color change in the conjunctiva, palm of hands, and mucous membranes for this person...
What is dark pigmented skin tone?
Lips inverted, swelling, erythema, lesions, cracking of skin are what kind of findings?
What are abnormal assessment findings of the lips?
(angioedema is edema of the lips usually related to an allergic reaction)
These are the two most common complaints in which someone would seek medical care..
What are otalgia (ear pain) and otorrhea (ear drainage)?
This chart is used to determine if a patient has difficulty reading.
What is the tumbling "E" chart?
This diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens), and eating fish high in omega-3 fatty acids are important for which organ.
This force is a sliding movement of skin and subcutaneous tissue while the underlying muscle and bone are stationary.
What is shearing?
This is excessive growth of thick, dark hair in women where normally the hair does not grow, including areas as face, chest, abdomen, arms, and legs. Usually caused by abnormality of androgen production (testosterone), metabolism, medications, or hormonal therapies..
What is Hirsutism?
This cranial nerve assesses position of the tongue.
What is the hypoglossal nerve or cranial nerve XII?
If you answer "yes" to how many questions on the "Do you need a hearing test?" should you seek a consult from an otolaryngologist or and audiologist for hearing evaluation..
What are 3 or more "yes" answers?
This is a sign of elevated bilirubin in the blood; occurs with patients who have liver disease.
What is scleral jaundice (icterus)?
This is one of the largest and heaviest organs of the body.
What is the skin?
Stage this pressure ulcer..

The following are all examples of :
Macule (freckle), Patch (Mongolian spot), Papule (mole), plaque (psoriasis), vesicle (herpes simplex), nodule, tumor, wheal (hives), cyst...
What are primary skin lesions?
Fall prevention, car safety, and recreational safety are patient education topics to prevent this...
This test is used to assess unilateral hearing loss and functioning of the cochlear nerve (CN VIII).
What is the Weber Test?
Inspect the eye, Assess: Visual acuity, color blindness, central vision, peripheral vision, ocular motility, accommodation, pupil size/consensual response, and internal structures.
What is the sequence of an Eye Assessment?
This is the ideal recommendation from American Academy of Dermatology to prevent sun damage.
What is sunblock with SPF 30 and water resistant?
Stage this pressure injury.
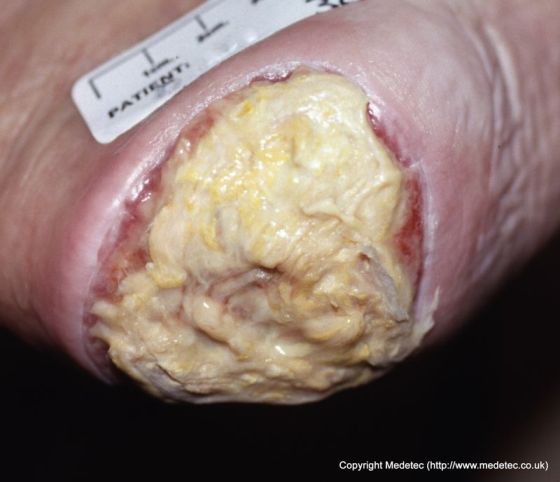
What is unstageable?