True or False: Medicare Part A covers skilled nursing facilities and long-term care
False: Medicare part A does not cover long-term care, Medicaid does!
Medicare Part A covers the following: SNF, home health, hospice, inpatient care in hospitals
Dual-eligibles have both Medicaid and _____?
Medicare
What does CHIP stand for?
Children's Health Insurance Program
True or False: The ACA guarantees that everyone in America has a right to receive healthcare
False: it expanded access to health insurance through reforms like the individual mandate (now penalty-free), Medicaid expansion, and health insurance marketplaces
Remember: EMTALA is separate from the ACA, and also doesn't guarantee healthcare for all
Spending on Medicare Part ___ for outpatient prescription drugs is projected to keep growing rapidly, raising questions about long-term affordability
Medicare Part D
These two letters are used to describe Original/Traditional Medicare, which covers hospital and medical services but not routine dental, vision, or most drugs
Medicare Parts A and B
EPSDT (Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment services) is a ____ (federal or state) program mandated for what population?
Federal, children under 21 who are enrolled in Medicaid
CHIP offers low-cost health coverage for children in families that earn _____ (too much/too little) for Medicaid but _____ (not enough/more than enough) for private insurance
Too much, not enough
What did the "individual mandate" provision in the ACA do?
Individual mandate required Americans to have health insurance or pay a penalty. The goal was to help stabilize the insurance market and keeps premiums lower for everyone (by having a good mix of sick/healthy people)
*mandate still exists in law, but penalty was eliminated in 2019
True or False: In NFIB v. Sebellius, the Supreme Court ruled that the individual mandate was unconstitutional under the taxing power
False
Medicare covers what populations of people? (Name all 3)
People 65+ ( must be a U.S. citizen or permanent resident and have worked and paid Medicare taxes for at least 10 years)
People with disabilities
People with end stage renal disease or ALS
In states that have expanded Medicaid under the ACA, adults with incomes up to ___% of FPL are eligible to enroll
138% (or 133% FPL with a 5% income disregard if we want to be technical)
Children must be ___ years old or younger to be eligible for CHIP
19 years old or younger
Name 2 essential health benefits that plans in the ACA exchanges must cover
Ambulatory patient services (outpatient care)
Emergency services
Hospitalization
Maternity and newborn care
Mental health and substance use disorder services
Prescription drugs
Rehabilitative and habilitative services and devices
Laboratory services
Preventive and wellness services and chronic disease management
Pediatric services, including oral and vision care
What is one consequence on Medicare funding given the trends seen in this graph?

There are payments from fewer workers supporting medicare beneficiaries (# of beneficiaries are growing as our population ages while working class is declining)
How is Medicare financed?
Parts B and D: Primarily by general revenues from the federal government
Part A: Mostly payroll taxes (this is a smaller portion of total Medicare funding)
Premiums and co-payments (very small percentage)
How is traditional Medicaid financed? (Be specific!)
Traditional Medicaid is financed through a federal-state matching system, with the federal government paying a higher share in states with lower per capita incomes
Unlike Medicaid, CHIP is funded as a ____ _____ to states.
Block grant (fixed amount of money)
Name 2 reasons why tax credits are so important
They make marketplace premiums affordable for low- and middle-income people
They cap what people pay as a share of income
They help people in non–Medicaid expansion states, where marketplace subsidies are the only realistic option for many low‑income adults
By lowering premiums, they increase coverage and reduce the uninsured rate
In 2020, many ACA insurers spent less than the required 80% of premiums on enrollees’ medical care, leading them to return roughly $2 billion in _________ to about 9.8 million consumers?
Medical loss ratio rebates
Describe 2 reasons why someone would opt for a Medicare Advantage plan rather than a traditional Medicare plan?
Lower out of pocket costs, lower cost sharing, extra benefits (dental, vision, etc), out of pocket spending caps
Bonus Points: would being able to participate in part D coverage be an incentive for choosing Medicare Advantage?
Describe one change to Medicaid eligibility in the One Big Beautiful Bill Act and an impact of that change
Work requirements for Medicaid expansion adults: Able-bodied adults must work, attend school, or volunteer at least 80 hours per month to maintain eligibility.
Consequence: Many individuals, especially those with unstable jobs or caregiving responsibilities, may lose coverage if they cannot meet the requirement --> increased numbers of uninsured adults.
More frequent eligibility redeterminations: Expansion adults must renew eligibility every six months instead of annually, increasing administrative burden and risk of coverage loss.
Consequence: Higher risk of coverage lapses due to missed deadlines
Explain one reason why we might be seeing these trends: 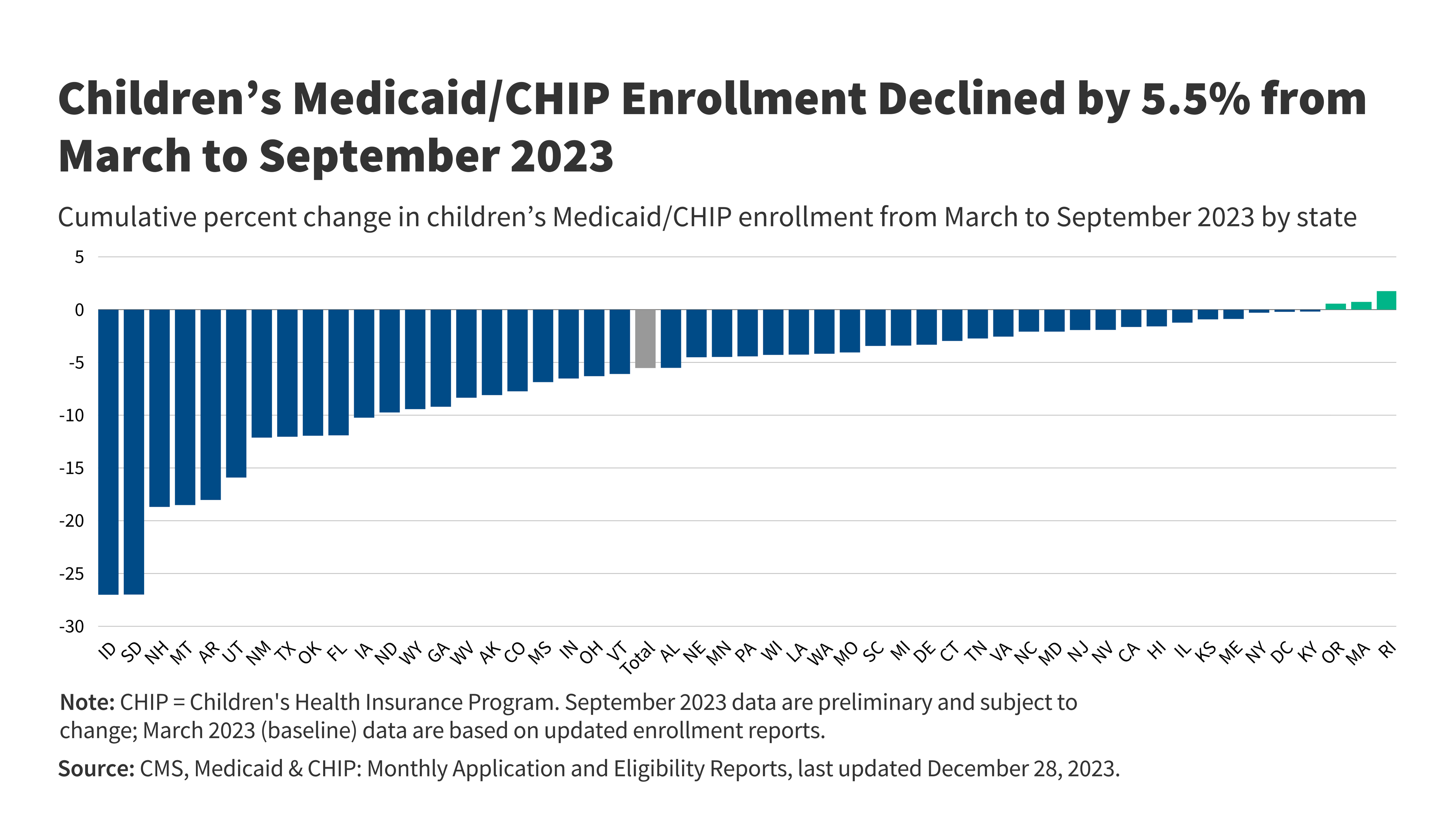
Eligibility checks restarted after COVID, many kids are losing coverage for procedural reasons (paperwork, missed deadlines, system errors)
This type of rule/regulation, which would put a hard dollar limit on how much insurers can charge in premiums, was NOT created by the ACA
Premium Cost Caps
As the population ages and health care costs rise, Medicare Part ___, which is financed mainly by payroll taxes through the Hospital Insurance Trust Fund, may not be able to pay full benefits after the early‑to‑mid 2030s.
Medicare Part A