The state of matter where particles are moving the slowest and are tightly packed. Has a fixed volume and fixed shape.
What is solid?
In this type of reaction, heat energy is released by the system.
What is exothermic reaction?
This remains constant during a phase change, even though heat is being added or removed.
What is temperature?
When temperature is changing but phase is not, this equation is used to solve for heat.
What is q = mCΔT?
A 25.0 g sample of water is heated from 20.0°C to 45.0°C. Use the specific heat of water, 4.18 J/g·°C, to calculate how much heat energy is absorbed.
What is q = 2926 J?
When a liquid evaporates into a gas this happens to the spacing between the particles.
What is particles get further apart?
In this type of reaction, heat energy is absorbed by the system.
What is an endothermic reaction?
While temperature is changing, this type of energy, associated with particle motion, is also changing.
What is kinetic energy?
This equation is used when a substance is melting or freezing.
What is q = mHf?
A 15.0 g ice cube at 0.0°C melts completely into liquid water at 0.0°C. Using Hf = 334 J/g, calculate the heat absorbed during this process.
What is q = 5010 J?
In this process, water vapor cools into liquid water.
What is condensation?
Melting and sublimation can be identified as this type of reaction.
What is an endothermic reaction?
On a heating curve with plateaus at 20°C and 100°C, ____________ and ___________ are occurring at each plateau (flat segment).
What is melting and evaporation?
This equation is used when a substance is boiling or condensing.
What is q = mHv?
A 10.0 g sample of steam at 100.0°C condenses into liquid water at 100.0°C. Using Hv = 2260 J/g, calculate the heat released. Be sure to include the correct sign for q.
What is q = -22600 J?
In this process, the potential energy of the particles increases.
What is melting or evaporation?
The following reaction shows that energy was ____________.
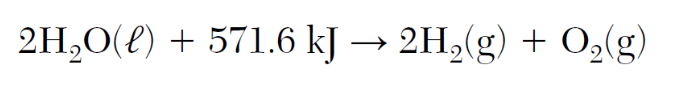
What is absorbed?
From time interval _____ min to _____ min on the following cooling curve, the substance exists as both a liquid and solid. 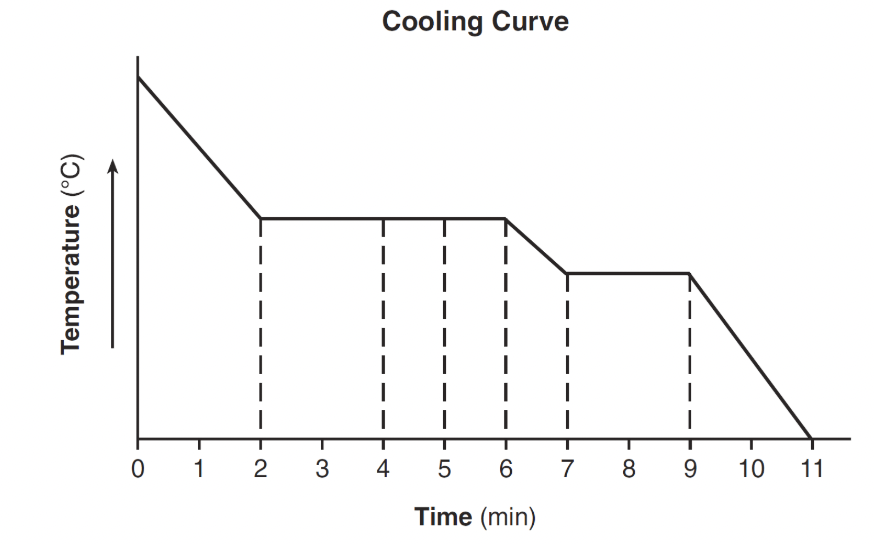
What is 7 min to 9 min?
The amount of heat energy required to vaporize 10.00 g of water at its boiling point.
What is 22600 J?
A 30.0 g sample of water at 20.0°C is warmed to vapor at 100.0°C. Calculate the total heat absorbed, using C (water) = 4.18 J/g·°C for warming and Hv = 2260 J/g for vaporization.
What is 77800 J?
These two processes release energy as particles come closer together and slow down.
What is condensation and freezing?
When a 100°C piece of copper is placed into 20°C water, _____________ energy transfers from the _________ to the ___________.
What is thermal, copper, and water?
The following substances melts at this temperature.
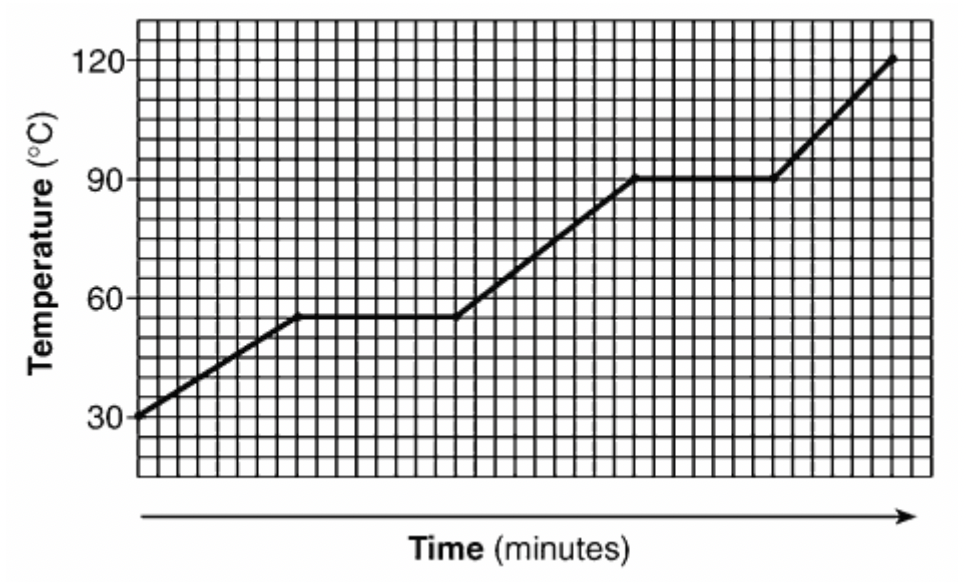
What is 55°C?
The total number of joules of energy released when a 5.00-gram sample of water changes from liquid to solid at 0°C.
What is 1670 J?
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 24.0 grams of aluminum from 300. K to 350. K. (Solid aluminum has a specific heat capacity of 0.90 J/g•K)
What is 1080 J?