What is the definition of a conductor?
Something that conducts (transfers) heat well
Why do hot fluids rise and cool fluids sink?
Hot fluids rise because they become less dense and cool fluids sink because they become denser.
Heat moves from the _____ object to the ______ object.
hotter ; cooler
Feeling warmth from a campfire.
Radiation
Warm clothes prevent you from losing heat through radiation. Are they insulators or conductors?
insulators
The transfer of heat energy from the sun to Earth.
Radiation
The current of hot magma rising and cool magma sinking.
Convection
Accidently burning your hand on a hot metal pan.
Conduction.
Are styrofoam coffee cups insulators or conductors?
Insulators. They don't conduct heat.
Do the molecules in a cube of ice move or are they completely still?
They still move a little. Cool things still have heat energy that moves the molecules.
What method of heat transfer is this?

Conduction (energy transfer via contact)
Radiation is when _____________ waves travel through space, without direct contact.
electromagnetic
What is the definition of an insulator? Provide one example of an insulator.
What method of energy transfer is this?
(Description: Heat flows from the hotter cup into the cooler hands. )

Conduction (energy transfer via contact)
What method of heat transfer is shown in the photo?
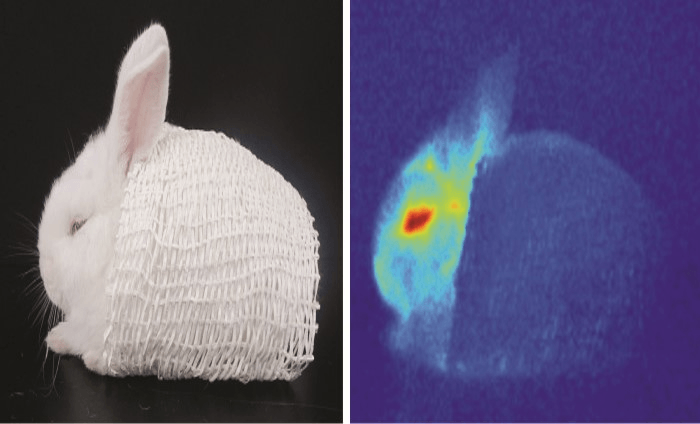
It is showing heat radiation and how the mesh over the rabbit is an insulator blocking the transfer of heat from the rabbit.
According to our Gizmo lab, which type of heat transfer works better? Conduction or convection? Explain.
Convection works best when there is heat on the bottom that will rise up naturally due to density. Conduction works best when the heat is on top to transfer the down. Conduction works equally as well when the hot fluid is on top or bottom.
Explain why a metal spoon feels warmer than a plastic one in the same cup of hot tea. Use the terms insulator and conductor.
The plastic spoon is an insulator, so does not conduct heat from the tea. The metal spoon is a conductor and it will absorb the heat from the tea, making it feel warmer.
What method of heat transfer is shown here?
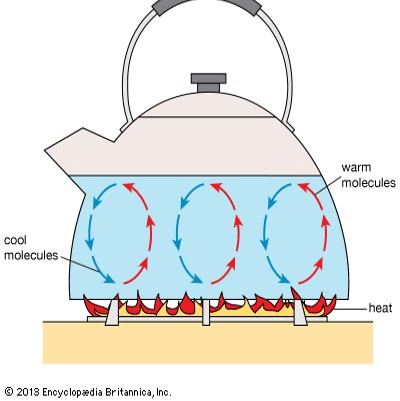
Convection heating (hot fluid rises, cool fluid sinks)
Describe an example of radiation.
Answers will vary. The warmth we feel from a fire.
Explain why it’s much colder at the bottom of a pool than at the top. Also, describe what heat transfer processes are taking place.
Convection makes the cool water sink and hot water rise. Radiation heats the surface of the water and may not penetrate down to the bottom.
Explain one example of a conductor and one example of an insulator you use while cooking.
An oven mitt, rubber-coated handles on pans and pots, and rubber and plastic utensils are all examples of insulators. Pots, pans, and metal baking sheets are all examples of conductors.
There are two types of Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, UVA and UVB. After a lot of exposure, how might each of these affect your body?
UVA causes aging and wrinkling. UVB causes burns. Both can cause skin cancer.
Describe an example of convection.
Answers will vary. The convection currents in the ocean and atmosphere.
Describe an example of conduction.
Answers will vary and must involve direct contact.