This painful eye condition presents with a “steamy” cornea and a mid-dilated pupil.
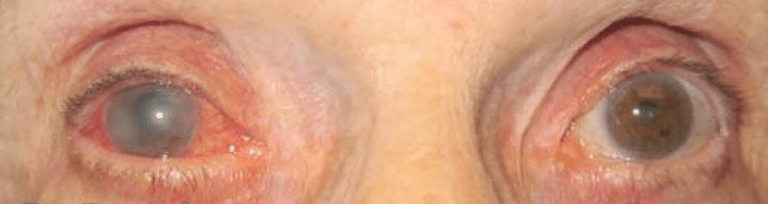
What is acute angle-closure glaucoma?
This most common location of anterior nosebleeds.
What is Kiesselbach’s plexus?
A patient presents with ear pain, vesicles in the external auditory canal, and facial paralysis. You diagnose this syndrome.
What is Ramsay Hunt syndrome?
A completely avulsed permanent tooth should be stored in this solution if immediate reimplantation is not possible.
What is Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (or milk if unavailable)?
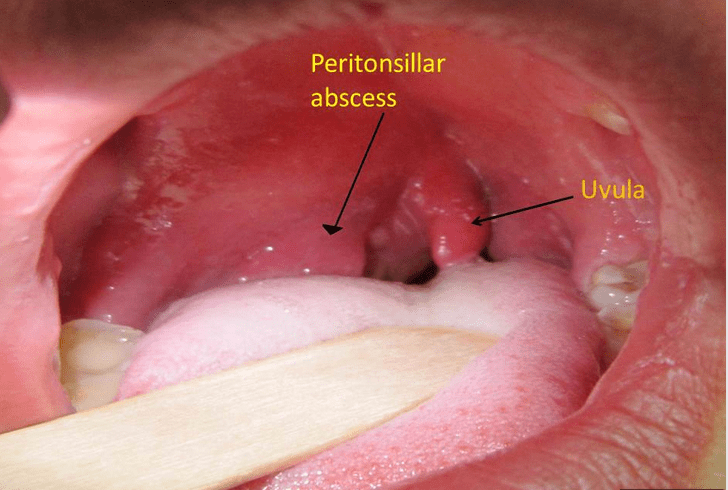
A patient with a “hot potato voice” and uvular deviation likely has this condition.
What is a peritonsillar abscess?
Muffled "hot potato" voice, trismus, and uvula deviation.
Diagnosis?
What is a peritonsillar abscess?
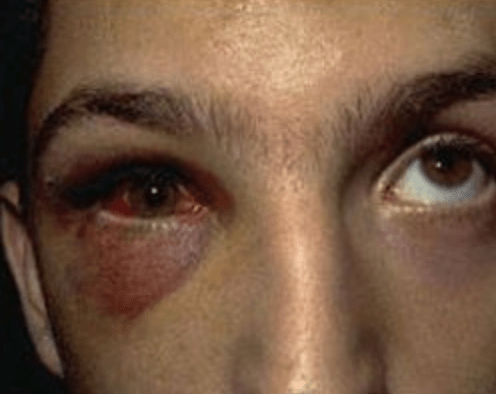
A patient who got hit in the eye with a tennis ball has diplopia and cannot look up. You suspect this type of injury.
What is a orbital floor blowout fracture?
A nasal fracture with a “blue boggy” swelling needs immediate drainage to prevent this deformity.
What is a saddle-nose deformity (from septal hematoma)?
The classic triad of vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss suggests this inner ear disorder.
What is Meniere’s disease?
Suspect this infection in a patient who presents with submental fullness and brawny edema following a dental extraction.
What is Ludwig’s angina?
A fishbone stuck in the throat is most likely to lodge in this anatomic space.
What is the vallecula?
Barking cough, inspiratory stridor, and steeple sign
Diagnosis?
What is laryngotracheobronchitis (croup)?
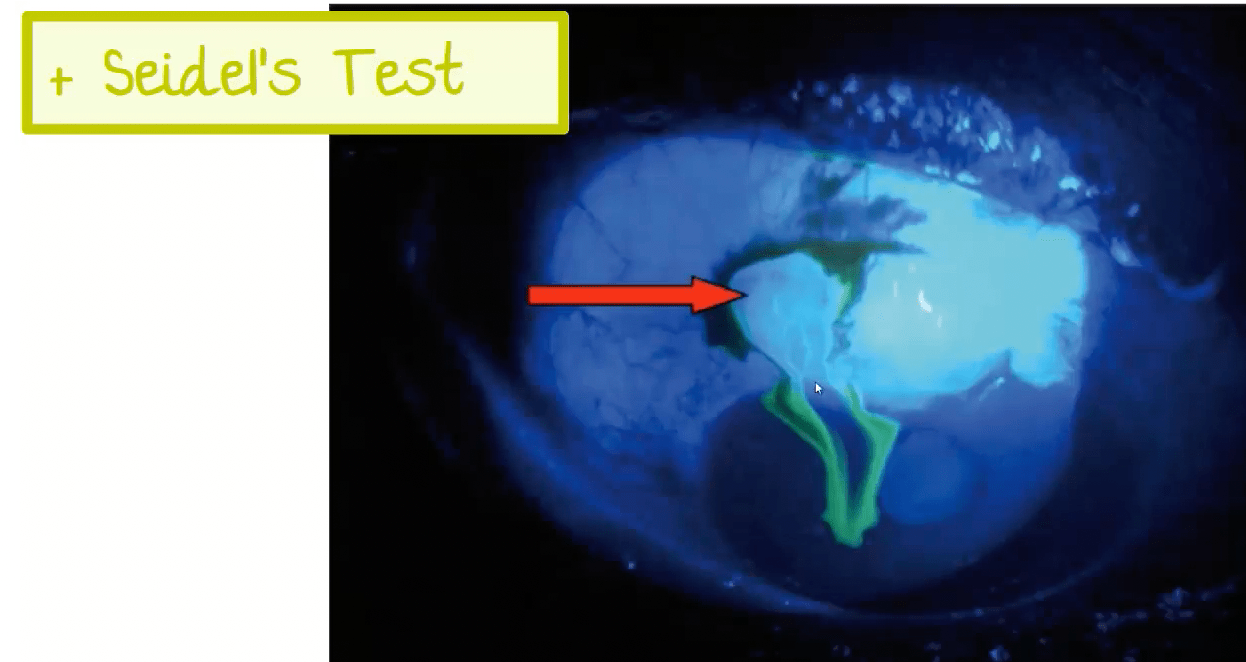
A high-speed drill user presents with a painless red eye and a teardrop-shaped pupil. You grab a Wood’s lamp to check for this sign.
What is Seidel’s sign (for a globe rupture)?
This life-threatening complication of posterior nasal packing occurs due to bacterial superantigen release, leading to fever, hypotension, rash, and multi-organ dysfunction.
What is toxic shock syndrome?
A patient with fever, posterior ear displacement, and posterior ear tenderness needs IV antibiotics for this condition.
What is mastoiditis?
This painful oral condition, commonly seen in immunocompromised patients, presents with punched-out gingival ulcers and foul-smelling breath.
What diagnosis is shown here?
What is acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG, or trench mouth)?
For the diagnosis shown in this photo, name 3 common infectious causes?
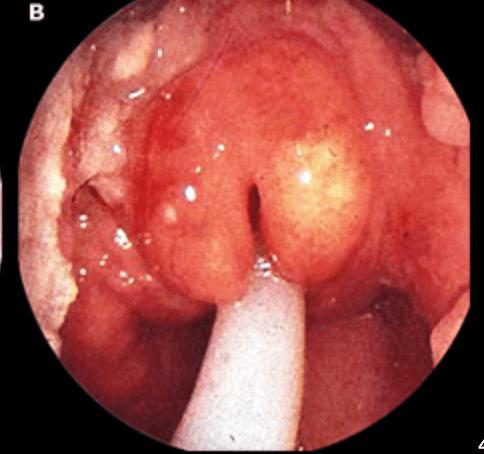
Diagnosis: Epiglottitis
Causes: Haemophilus Influenzae type b, streptococcus spp, staphyloccocus aureus, moraxella catarrhalis
Head/neck infection, ophthalmoplegia, and venous obstruction.
Diagnosis?
What is cavernous sinus thrombosis?
This bacterial infection, commonly caused by Staph or Strep, causes pain with eye movement, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia and decreased vision
What is orbital cellulitis?
A child is brought in with foul-smelling, unilateral rhinorrhea. This common pediatric diagnosis should be on your radar.
What is a nasal foreign body?
This rare but deadly necrotizing otitis externa is most commonly seen in diabetics and is caused by this bacteria.
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
This is the most common location of a mandibular dislocation.
What is anterior?
This bacterial infection, caused a Corynebacterium, presents with sore throat, low-grade fever, and the formation of a grayish pseudomembrane in the pharynx, which can lead to airway obstruction.
What is diphtheria?
Elderly, temporal artery tenderness, jaw claudication, and polymyalgia.
Diagnosis?
What is giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis)?
This eye emergency presents with painless, sudden vision loss and a “cherry-red spot” on fundoscopic exam.
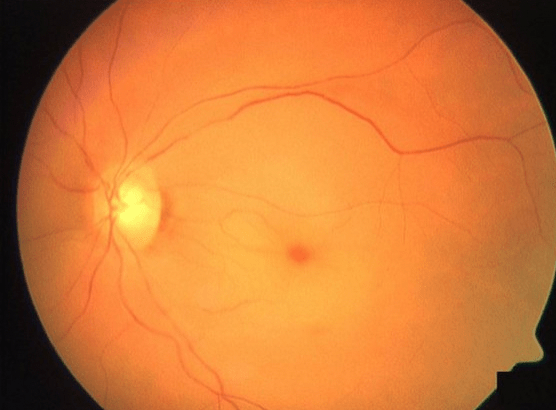
What is central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO)?
This zoonotic infection, caused by a mold with right-angle branching, is an aggressive cause of necrotizing nasal and sinus disease in diabetics and immunocompromised patients.
What is mucormycosis?
This painful middle ear condition, often caused by viral or bacterial infections like Streptococcus pneumoniae or Mycoplasma pneumoniae, is characterized by vesicular lesions on the tympanic membrane and can present with otalgia and conductive hearing loss.
What is bullous myringitis?
This type of Le Fort fracture is characterized by a floating maxilla, extending through the pterygoid plates.
What is a Le Fort I fracture?
This rare but serious complication of tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess, or pharyngitis can cause septic thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein, often associated with Fusobacterium necrophorum.
What is Lemierre’s syndrome?
A post-operative complication, sudden vision loss, pain, hypopyon, and severe intraocular inflammation.
What is endophthalmitis?
This diagnosis is classically described as having a retina seen below on fundoscopic exam
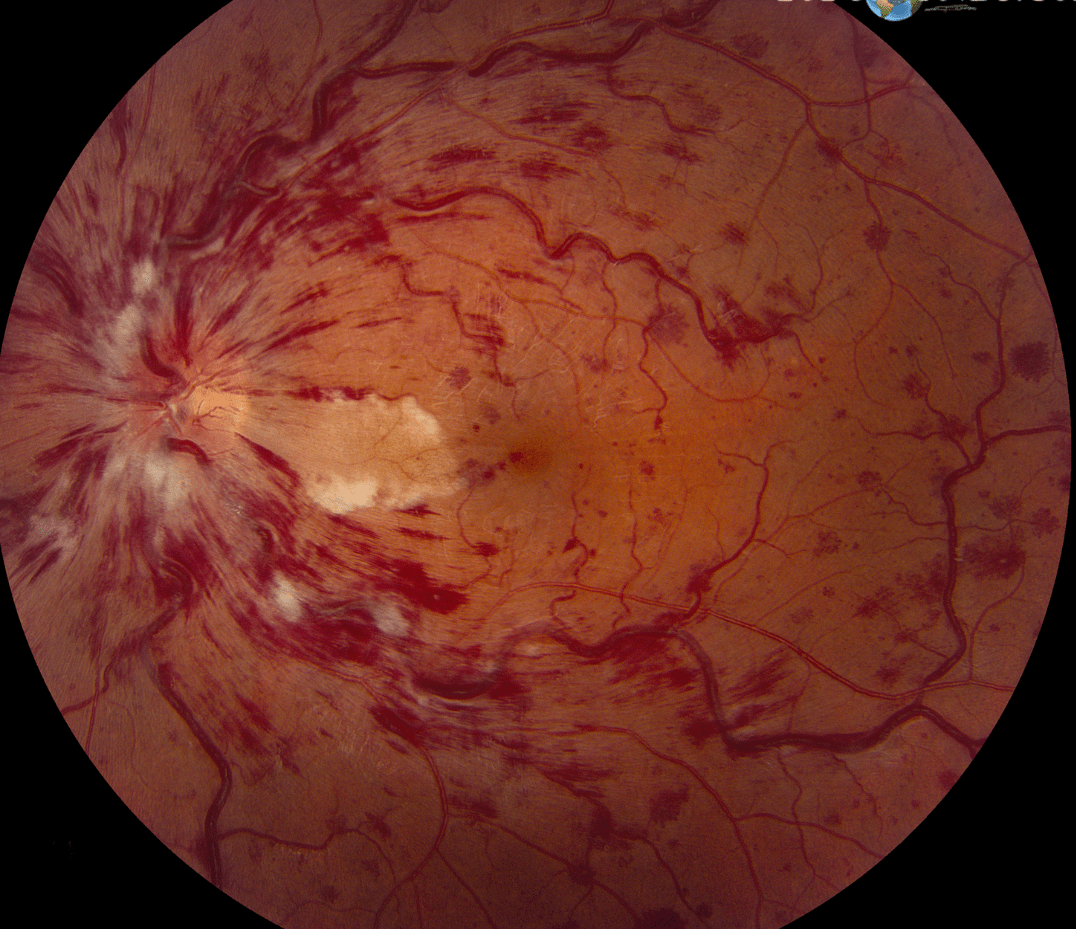
What is a CRVO (central retinal vein occlusion) ?
"Blood and thunder"
What is the primary cause of septal necrosis that results from a button battery lodged in the nose?
What is the electrical current
This rare but deadly complication of cholesteatoma can cause seizures, altered mental status, and a positive Brudzinski’s sign.
What is otogenic meningitis?
This diagnosis shown here causing vesicles and ulcers on the soft palate, uvula and posterior pharyx is most commonly caused by this type of virus?
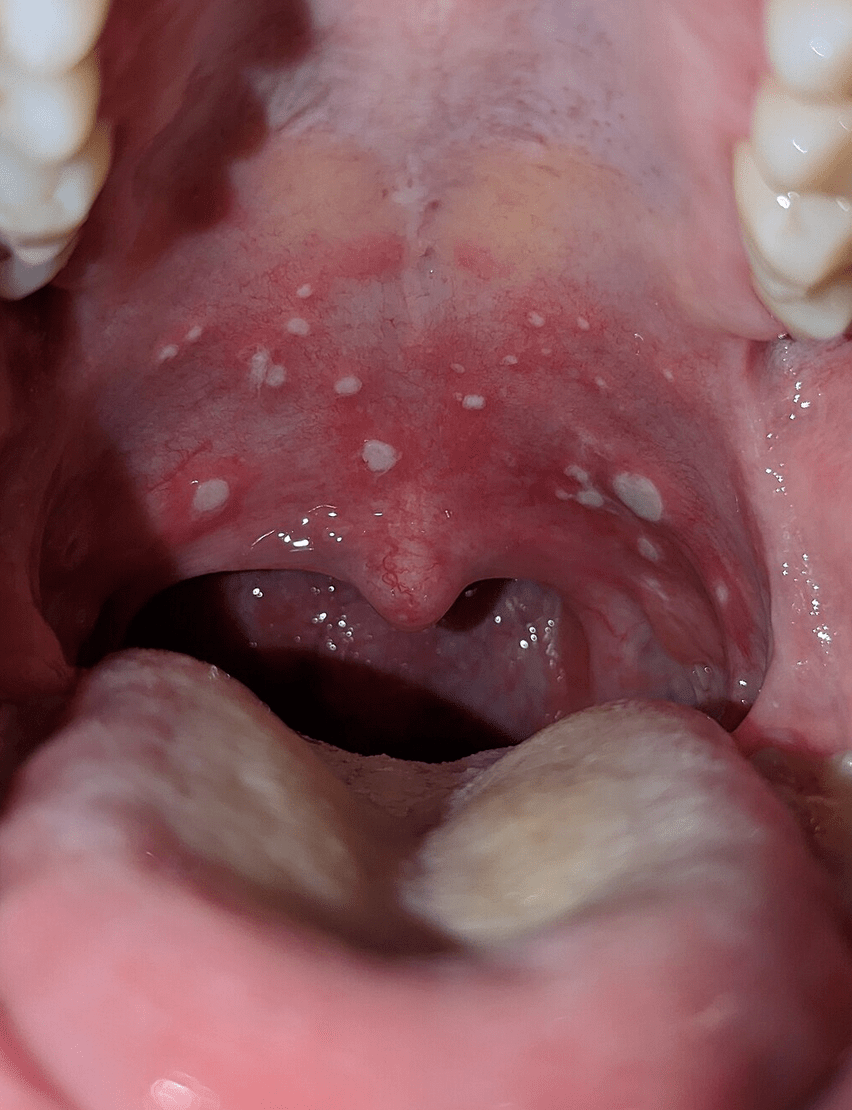
What is coxsackie virus?
Diagnosis: Herpangina
Name 4 critical maneuvers to perform when encountering a patient with a bleeding from a recently placed tracheostomy?
1. Tamponade bleeding by overinflation of tracheostomy cuff
2. Secure airway w/ endotracheal intubation
3. Remove tracheostomy tube
4. Digitally compress innominate artery
Fever, sore throat, atypical lymphocytes, posterior cervical chain.
Diagnosis?
What is Infectious Mononucleosis?
Epstein Barr virus= Human herpes virus 4