What would you expect iron studies to look like in iron deficiency anemia?
Serum iron - ?, TIBC - ?, Transferrin saturation - ?, Ferritin - ?
Serum iron - low
TIBC - High
Transferrin saturation - low
Ferritin - low
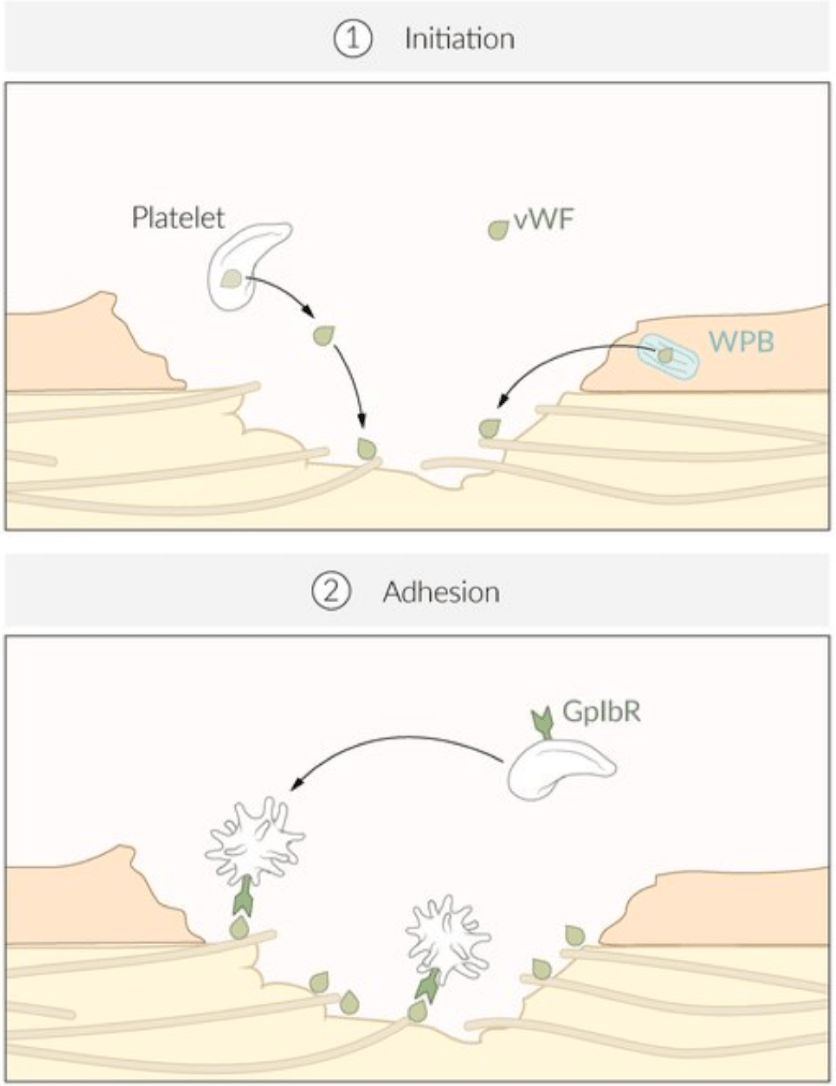
In von Willebrand Disease, patients often have prolonged bleeding time, low levels of vWF, and occasionally a prolonged __(PT or PTT?)__
Von Willebrand Factor binds to subendothelial collagen. Platelets bind to vWF via GpIb. vWF also stabilizes factor VIII --> when vWF levels are low --> factor VIII is less stable --> prolonged PTT
How does hydroxyurea help in sickle cell disease?
Increases HgbF and Decreases HgbS
Recommended for all children with HbSS and HbSB0 to start between 9-42 months of age. Causes expected myelosuppression
What is the most common childhood malignancy?
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Incidence peaks between 2-5 years old
Annual incidence is ~3/100,000
ALL accounts for 75% of all pediatric leukemia cases
A 20 month old presents with ataxia, myoclonic jerking, and abnormal eye movements. An abdominal mass is identified on imaging. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Neuroblastoma
Opsomyoclonus (myoclonic jerking and random eye movements) & ataxia occur in 5% of patients with neuroblastoma. Neuroblastoma is a tumor arising from the neural crest progenitor cells of the sympathetic nervous system. Opsomyoclonus may be the presenting symptom, but the most common presentation is an asymptomatic abdominal mass (mass crosses midline)
How can you differentiate folate deficiency from B12 deficiency on physical exam?
B12 deficiency leads to neurologic symptoms and eventually to irreversible neurologic damage including bilateral paresthesias, decreased proprioception, spastic ataxia, central scotomata, and dementia
What is the factor deficiency in Hemophilia A? Hemophilia B?
A = Factor VIII
B = Factor IX
What is the leading cause of death in adolescents & adults with sickle cell disease?
Acute chest syndrome (ACS)- characterized by the development of a new pulmonary infiltrate with fever, chest pain, tachypnea, or hypoxia. This can progress rapidly to respiratory failure
What factors at time of diagnosis make ALL high risk? *need to get at least 2*
Age <1 yo or >10 yo
WBC > 50,000 on presentation
More than 5 leukemic cells in CSF (CNS3)
What is the most common benign brain tumor in children? Malignant?
Benign- pilocytic astrocytoma- arise from astrocytes, typically occur in the cerebellum
Malignant- medulloblastoma- arise from primitive neuroectodermal cells (undifferentiated cells that are precursors to various types of neurons and glial cells), typically occurs in cerebellum
In what disease process would you see this peripheral smear?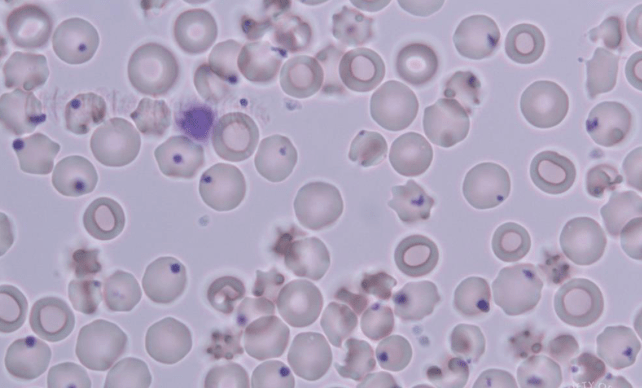
G6PD Deficiency
X-linked, reduced glutathione, RBCs more susceptible to oxidative stress
Can have hemolytic crisis with symptoms including sudden onset of pallor, fatigue, dark urine. Hemolysis can be triggered by infection, drugs (nitrofurantoin, sulfa drugs, antimalarial drugs), certain foods (fava beans!))
What are the 3 first line treatments for ITP?
IVIG
Corticosteroids
Anti-Rh (D) immunoglobulin
What are the 4 types of sickle cell disease?
HbSS - 2 copies of hemoglobin S
HbS/B0 - hemoglobin S from one patent and B0thalassemia from the other parent
HbSC - hemoglobin S from one parent and C from the other
HbS/B+ - hemoglobin S from one parent and B+thalassemia from the other
Which malignancy would have this histologic finding?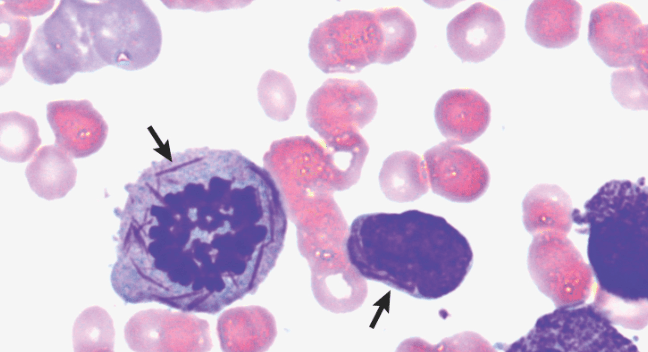
Auer rods
Seen in AML (acute myelogenous leukemia)
A 3 y.o. presents with a painless abdominal mass. He is otherwise asymptomatic. What is the most likely diagnosis?
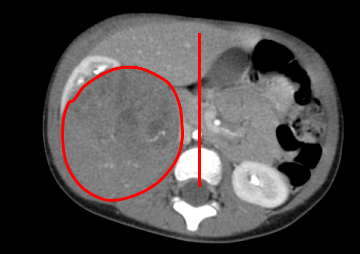
Wilm's tumor- usually presents as an asymptomatic non-tender abdominal mass that rarely crosses midline
Median age of diagnosis is 3 yo
What are 4 causes of macrocytic anemia?
Folate deficiency
B12 deficiency
Medications (hydroxyurea)
Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes
Alcohol use
Hypothyroidism
Liver disease
A neonate is in the NICU for severe intracranial bleed following birth. An X-ray reveals absence of a radius bone but normal thumbs. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Thrombocytopenia-Absent Radius (TAR) Syndrome
Autosomal recessive inherited disorder that presents with severe bleeding in a neonate. Half of all infants are symptomatic in the 1st week of life and 90% are by 4 months of age
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation in the gene encoding ____ globin, causing a substitution that switches _______ to_____
beta
glutamic acid
valine
What is the main differentiating histiologic characteristic of Hodgkin vs non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Hodgkin lymphoma contains Reed Sternberg cells (large cells with multilobulated nuclei)
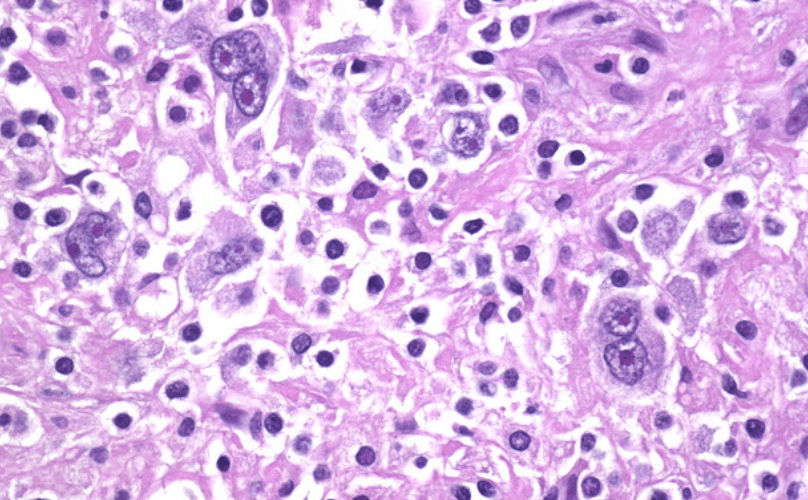
A 15-year-old boy injured his left knee in soccer, and then he has subsequent pain and swelling over the knee. He has been waking up in the middle of the night with pain. X-ray obtained shows the following... What is the most likely diagnosis?
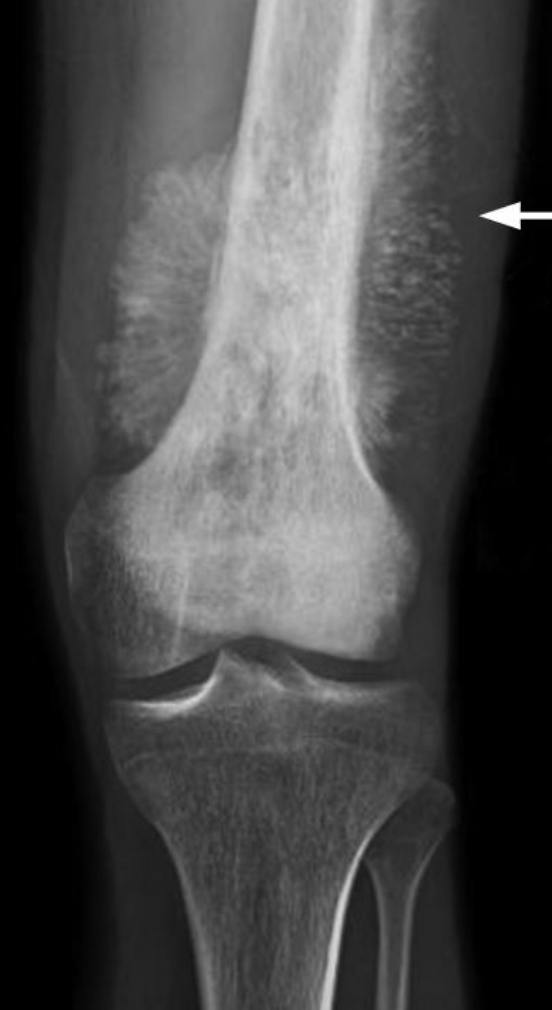
Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone tumor in children. It occurs most often during the adolescent growth spurt with unilateral pain and swelling. Most common sites are the distal femur and proximal tibia. X-ray can show sunburst pattern and Codman triangle (periosteal elevation)
A 9 month old presents with pallor, jaundice, irritability, poor growth, and hepatosplenomegaly. They have microcytic anemia, and Hb electrophoresis only shows Hb F. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Beta thalassemia major- there is essentially no beta globin production (cannot make HbA or A2 --> electrophoresis shows mostly HbF). Patients will be transfusion dependent and often develop iron overload. They have expansion of hematopoietic cells in the liver & spleen, and in the bone marrow (can lead to characteristic "chipmunk facies"

A patient presents with easy bleeding and is found to have thrombocytopenia. Peripheral smear shows giant platelets and platelets do not aggregate during ristocetin test. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome - AR disorder with thrombocytopenia and giant platelets, deficiency of platelet glycoprotein 1b in platelet membrane which prevents aggregation, presents with mucocutaneous bleeding
Ristocetin test - induces the aggregation of platelets, relies on the binding of vWF to the platelet GPIb receptor.
When performing an exchange transfusion for acute chest syndrome, the goal is to decrease Hgb S to less than ___%. You should not exceed a Hb of ____ g/dL (this increases the risk of _____)
30%
10 g/dL
stroke
What is the fastest growing malignant tumor?
Burkitt lymphoma
Type of non-Hodgkins lymphoma, can be associated with EBV infection, commonly originates in Peyer patches in GI system
The tumor can double in 2-3 days so tumor lysis syndrome is common
What disease is associated with hemangioblastomas in the cerebellum, medulla, and spinal cord?
von Hippel- Lindau
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome is caused by mutations in the VHL gene (autosomal dominant), leading to the formation of tumors and cysts in multiple organs. Key manifestations include hemangioblastomas in the brain and spinal cord, renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytomas, and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.