You see an infant in your office for their two week well child check. You note that their eyes are jaundice and the direct bilirubin was 0.8 at discharge from the nursery. Repeat bilirubin at the time of the visit is total of 3 and a direct of 1.5. What is the most time sensitive diagnosis.
What is the best next step in management of this patient?
Obtain a direct bilirubin
Treatment of pediatric patients with metabolic associated steatotic liver disease
eliminating sugar-sweetened beverages, reducing processed foods, and 60 minutes of daily physical activity
Which patients to screen for metabolic associated steatotic liver disease and how to screen
Ages 9 and 11 with obesity or overweight and a risk factor (central obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, FH of MASLD.
- Boys: ≥22 U/L
- Girls: ≥26 U/L
Esophageal varices.
A 16 year old patient presents with AST 250, ALT 300, INR 3.0, total bilirubin 5, direct 2. lactate 2.5, bicarb of 18. He is awake, alert and oriented. He was sick last week with influenza but those symptoms have since resolved. What does he meet clinical criteria for?
Acute liver failure
1.5 with encephalopathy
2.0 without
D101/2NS at 90% MTN
A six month old full term healthy female born NSVD attends a well child check, the pregnancy and birth were uncomplicated. Her mother has a PMH significant for untreated hepatitis C, she is HIV negative. At the request of the parent's hepatitis C testing was done at six months of age which demonstrated HCVAB reactive viral load of over 18 million. What is the next step
Repeat HCV antibody at 18 months of age
HCV RNA at 2-6 months
HCV Antibody no sooner then 18 months
A patient with cirrhosis is admitted with fever. What dose and medication will you given them for an antipyretic
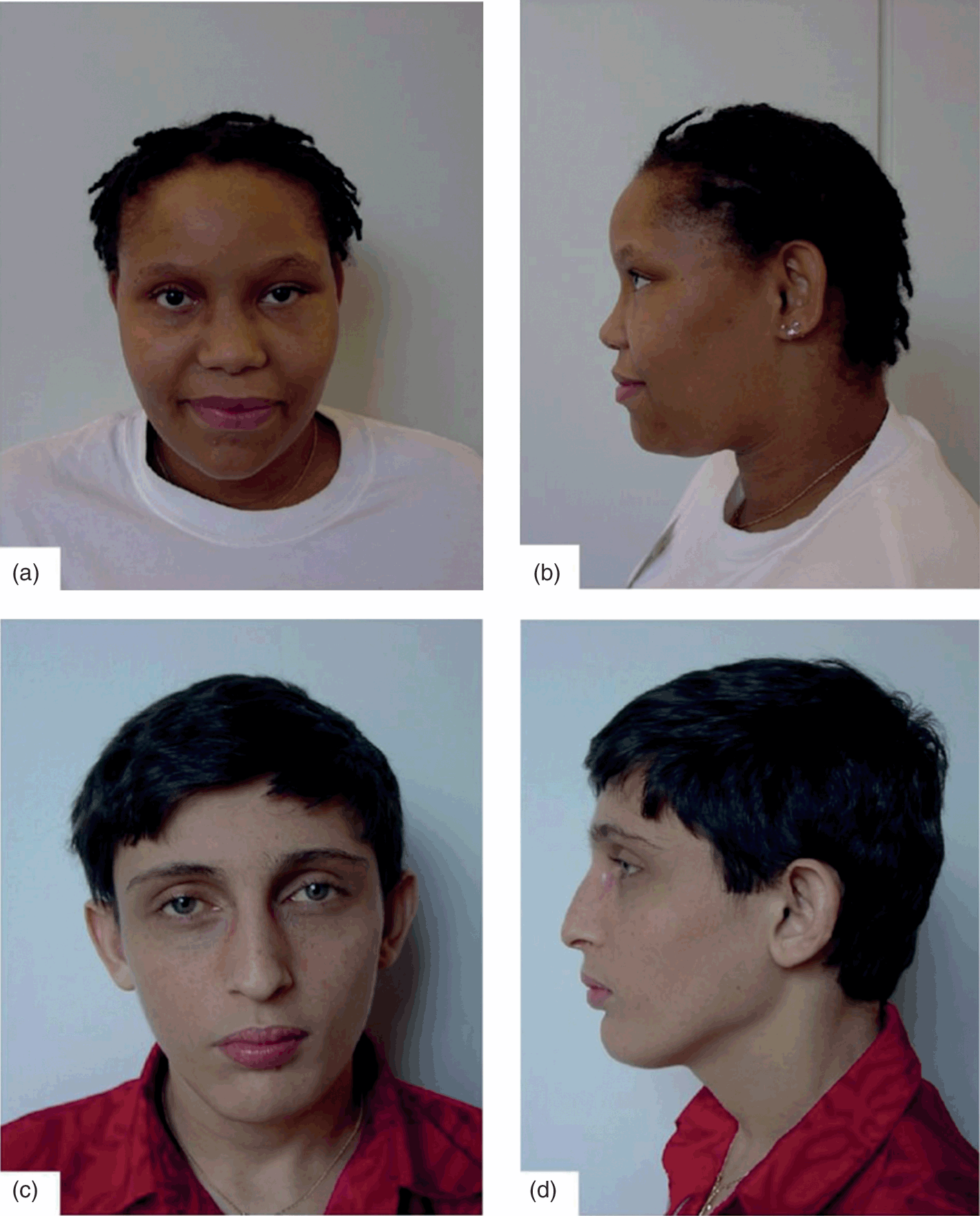 Patient was found to have elevated liver tests on screening. They also have a murmur one exam. What is the likely diagnosis.
Patient was found to have elevated liver tests on screening. They also have a murmur one exam. What is the likely diagnosis.
Alagille syndrome
You are following a 16 year old patient with ulcerative colitis. You note that his eyes have a slight amount of jaundice. You obtain a GGT which is 400, with AST 50, ALT 62. You initiate a workup. Which would be the best next step in his workup and what is the most likely diagnosis.
MRCP
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Which type of formula should an infant with cholestasis be put on?
High MCT containing formula
A 8 year old female presents to the Emergency Room with scleral icterus for 3 days. Labs are significant for AST 250, ALT 300, Total bilirubin 3, direct 1.5, GGT 600 and INR 1.5. There is a strong family history of autoimmune disorders. What tests do you want to send to look for autoimmune hepatitis
ANA, SMA, LKM, IGG
A 15 year old patient with a BMI of 30 presents to your office after routine labs discovered an AST of 100, ALT 150 and INR 1. Other labs are significant for ANA 1:320, SMA 1:160, LKM normal, IGG 2200. What is the best next step in management and what is your top differential for the diagnosis
Liver biopsy
Autoimmune hepatitis
A 14 day old has continued cholestasis. There is a strong FH of emphysema in young individuals. What is blood test do you want to make sure to include in your workup?
A1AT phenotype and level
A 50 day old presents to your clinic with jaundice. On exam the liver edge is firm and palpable Labs are significant for AST 108, ALT 140. Total bilirubin 5, direct bilirubin 3. What do you do?
Send to ER or page hepatology.
14 year old male presents to your clinic for routine physical. He has been well with no recent illnesses. His BMI is at the 98th percentile for age. As part of his screening workup you obtain labs which are significant or AST 68, ALT 79, total bilirubin 0.6, direct 0.2. Best next steps?
Repeat labs in three months with healthy lifestyle recommendations.
A four month old presents to your office after recently having moved from the Dominican Republic. His abdomen is distended with ascites and he has hepatosplenomegaly. He is ultimately diagnosed with biliary atresia. What about his clinical picture worsens his outcome.
Want Kasai done by 30-45 days of life
What is the definition of a draining Kasai operation
Total bilirubin < 2 by 3 months after Kasai
What are the indications for liver transplantation in a child with biliary atresia?
Poor growth
Recurrent infections
Ascites that is difficult to control
Recurrent bleeding episodes that cannot be controlled
lactulose/rifaximin
EMS brings in an 8 year old female with hematemesis with a previous history of esophageal varices. What medication do you want to start to stop the bleeding.
Octreotide bolus and then drop
A 15 year old presents with AST 108, ALT 120. There is a strong family history of both liver disease and psychiatric conditions. What blood test do you want to include in this patients workup for liver disease.
ceruloplasmin
24 hour urinary copper
ophthalmology exam
What is the most common pediatric indication for liver transplant?
Biliary atresia
Which of the following is true?
a) A patient with CLD with an elevated INR is not at risk of developing a venous thromboembolism.
b) A patient with CLD with an elevated INR can experience both thrombosis and bleeding
c) A patient with CLD with an elevated INR is not at an increased risk of bleeding
d) A patient with CLD with an elevated INR is at an increased risk of bleeding.
A patient with CLD with an elevated INR can experience both thrombosis and bleeding