A genotype with two different alleles- one dominant and one recessive.
heterozygous
The mode of inheritance that is a result of two heterozygous parents for a trait producing offspring with 75% of the trait.
complete dominance
Having a widow's peak is dominant. If a woman without a peak marries a man heterozygous for a peak, what % of children will have a peak?
50
The four basic blood types.
What is A, B, AB, and O
Term denoting the actual alleles present for an individual (for a particular gene)
The physical trait you generally see as a result of the genotype of an individual.
phenotype
The mode of inheritance where males are more affected by a trait than females.
X-linked (recessive) inheritance
Fly eye color is X-linked. If a male with white (recessive) eyes mates with a homozygous red--eyed female, what percent of their male offspring will have white eyes? Females?
0% for both
The likely genotype of the parents of four children that all have type AB blood.
What is AA and BB
Black bugs are dominant to blue bugs, cross a blue bug with a black bug. The black bug had a blue bug parent. Show your work/set up and complete the punnett square.
Cross should be between Bb and bb.
When a dominant and recessive allele result in an intermediate phenotype as heterozygotes. FOr example: When a black rat and white rat breed to produce a brown rat.
incomplete dominance
The mode of inheritance in which a person with type A blood marries and person with type B blood and produces children with type AB blood.
Codominant inheritance
***Assess the mode of inheritance of the following pedigree:
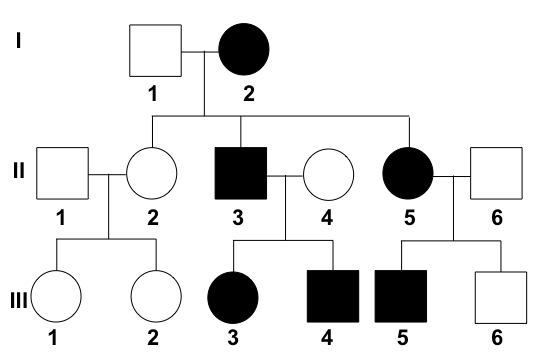
autosomal dominant
The parent genotypes that produce children with all possible blood types.
What is AO and BO
A red and white flower create a pink flower. Cross two pink flowers. Show your work.
PP' x PP'
When a dominant and recessive allele produce a phenotype representing both forms of the phenotype. For example: a black cow and a white cow produce a spotted cow.
codominance
What type of inheritance describes this situation:
A hairless male cat and hairy female cat breed and have kittens. This results in 3 hairy female kittens, 1 hairy male kitten, 3 hairless male kittens, and one hairless female kitten.
Recessive x-linked inheritance
What mode of inheritance where affected dads will always produce affected daughters.

x-linked dominant
Father #1 has type O blood, father #2 has type A blood. The mother has type AB and the child has type AB. Which is the likely father and why?
Father #2, child can only receive either an A or B from mom and needs the alternate from the father. An OO genotype can provide neither.
What is the main reason that x-linked traits appear in males most often?
males only have one X chromosome, so there is not a second X to mask a recessive trait like in females.
A trait that is coded for by multiple allele combinations interacting.
polygenic trait
The mode of inheritance that describes a mating couple without a disease that have 50% homozygous dominant and 50% recessive grandchildren?
autosomal recessive
If 50% of the offspring are homozygous recessive and 50% are heterozygous, what are the parental genotypes?
one is homozygous recessive and the other heterozygous.
Shows that blood typing is considered codominant.
What is the expression of both A and B blood type in AB blood.
Compare and contrast codominance and polygenic inheritance. Can use example to compare.
two alleles both show up in the phenotype of the individual as codominance (ex. red cow and white cow creating roan) and polygenic as interaction of multiple alleles creating a range of phenotypes (ex. height/eye color/hair, etc.)