Medical term for itchiness
Pruritis
This collects high frequency sounds, localizes sound, and is covered by skin
Pinna
If you were to calculate the PTA (pure-tone average) of the following audiogram, which frequencies would you average?
500, 1000, 2000Hz
List the middle ear ossicles in order from most lateral to most medial.
Malleus, Incus, Stapes

The total energy flow combined with the total opposition to energy flow through the middle ear system.
IMMITTANCE
Admittance (come on in!) + Impedance (why are you impeding on my fun?)
[what is measured when assessing the middle ear system]
Stimulation of the external auditory meatus can trigger this normal reflex response.
Coughing
This portion of the temporal bone is located deep in the cranium and houses the otic capsule
Petrous portion
This is most effective for low frequency, high intensity sounds
Acoustic ear reflex or middle ear muscle reflex
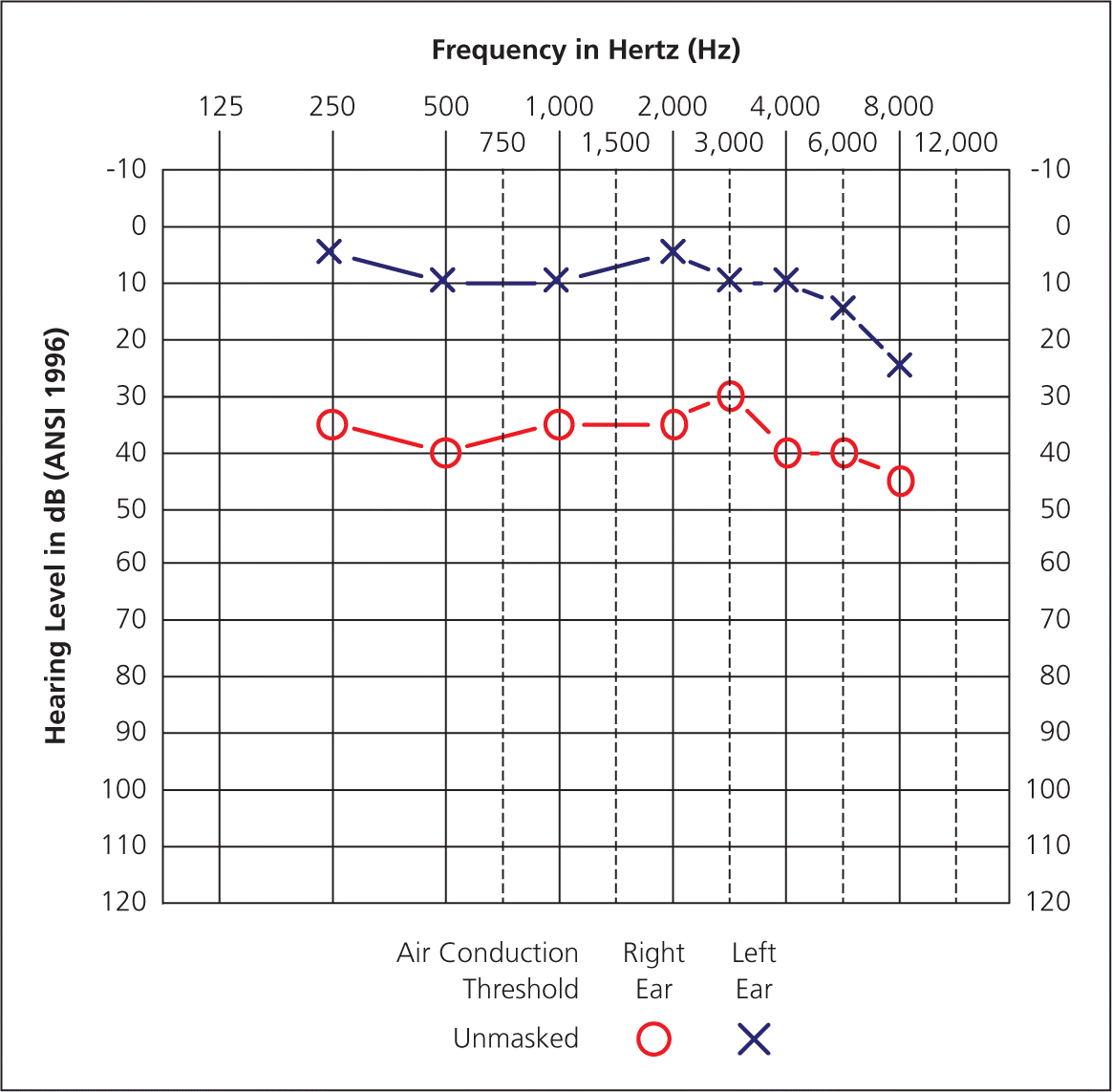
Is this a right or left ear? How do you know?
The cone of light (or the manubrium of the malleus, which points to the anterior fold)

This kind of stimulus triggers the acoustic reflex, a response from these two muscles.
A high-intensity (loud), low-frequency (deep) sound; stapedius and tensor tympani
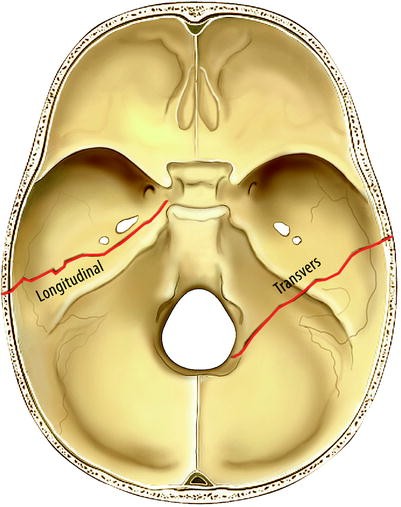
Transverse temporal bone fractures result in this type of hearing loss.
Transverse ➜ sensorineural (across the otic capsule)
Longitudinal ➜ conductive (along the petrous portion's mountain range)
This pathology is caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly originating from an untreated or inadequately treated middle ear infection
Mastoiditis
What is the primary purpose of tympanometry in audiology?
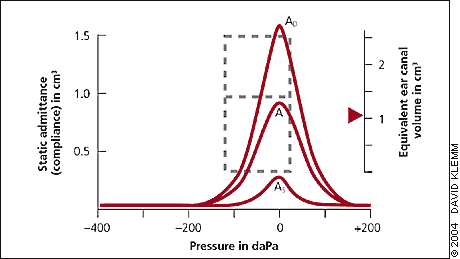 Assess the function of the middle ear system by measuring admittance in response to changes in air pressure
Assess the function of the middle ear system by measuring admittance in response to changes in air pressure
What muscle originates from the anterior wall of the middle ear, is innervated by the trigeminal nerve, and attaches to the malleus?
Tensor Tympani (longer of the two muscles responsible for the acoustic reflex)
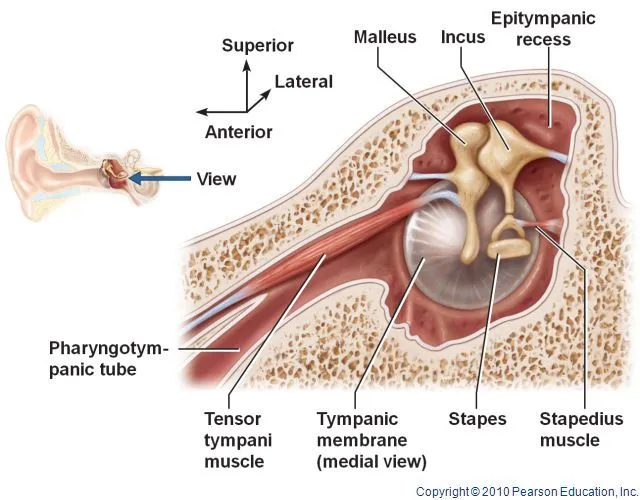
These muscles are responsible for opening the Eustachian Tube.
What are the Tensor veli palatini and Levator veli palatini?
These three congenital outer ear conditions involve underdevelopment or absence of the pinna and/or ear canal. One affects the shape and size of the external ear, another results in a missing ear canal, and the most severe form involves the complete absence of the external ear. Name them.
1. Microtia - congenital underdevelopment of the pinna
2. Atresia - absence/closure of the EAM
3. Anotia - Complete absence of the pinna and EAM
The hinge joint between the temporal bone and the lower jaw
Temporomandibular Joint
Briefly describe what the speech reception threshold is
Testing to find the lowest level a patient responds to speech 50% of the time
The tympanic membrane consists of three layers, from lateral to medial, and is divided into two portions—one smaller and more compliant, the other larger and structurally reinforced. Name these three layers and two portions.
Three Layers (most lateral to medial):
1. cutaneous
2. fibrous
3. membranous
Two parts:
1. Pars Flaccida
2. Pars Tensa
Describe how the parts of the middle ear move during a compression wave.
- Tympanic membrane → moves medially
- Stapes footplate → pushes medially into oval window
- Round window → bulges outwards
- Cochlear/inner ear fluid → displaced
(Process reverses for rarefaction)

A 22-year-old competitive swimmer presents with otalgia, pruritus, and otorrhea in the right ear. Symptoms worsen with manipulation of the pinna. An otoscopy reveals erythema, edema, and yellowish otorrhea in the external auditory canal. What is the likely diagnosis?
Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear)
• Otorrhea: discharge from the ear
• Otalgia: pain in the ear
• Edema: swelling
• Erythema: redness of skin produced by congestion of capillaries
• Pruritis: itching
Out of the 12 cranial nerves, which ones innervate the EAM?
Vth (trigeminal)
VIIth (facial)
IXth (glossopharyngeal)
Xth (vagus)
Describe the type, degree, and configuration
The right ear shows a normal to severe sensorineural hearing loss in a notch configuration.
The left ear shows a mild to severe sensorineural hearing loss in a notch configuration.
Name the six walls of the middle ear cavity.
1. Medial - Labyrinthine
2. Lateral - Membranous
3. Anterior - Carotid
4. Superior - Tegmental
5. Inferior - Jugular
How does the middle ear compensate for impedance between the air-filled middle ear and fluid-filled inner ear? Rank the three mechanisms from most to least contribution.
1. Area Ratio - the size difference between the stapes footplate/oval window and the tympanic membrane (think of a push-pin!) - the most (24dB)
2. Buckling Effect - the buckling of the tympanic membrane, increasing force on malleus - (6dB)
3. Lever Ratio - the orientation of the ossicles that functions like a seesaw/lever - the least (2.4dB)
*Total: 32dB*