This bone is the most often fractured bone during birth.
What is the clavicle?
Bonus: What is the typical treatment?
Bonus: What is the most common predisposing cause?
Prelabor or prolonged rupture of membranes, maternal fever, maternal group B strep colonization, meconium aspiration, low birth weight or preterm birth, and poor prenatal care are all risk factors for this.
What is neonatal sepsis?
This is the most widely recognized effect of maternal tobacco use.
What is low birth weight?
Infants born between 34 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation are classified as this.
What is late-preterm infant?
Bonus: At what gestational age is an infant considered preterm? At what gestational age is an infant considered postterm?
Infants of diabetic mothers are most at risk for this.
What is hypoglycemia?
Bonus: What is the most common first line treatment for an infant experiencing hypoglycemia?
The highest incidence of neurological injury findings occur in this category of high risk infants.
What is very low birth weight (VLBW) infants?
The nurse may suspect neonatal sepsis if the infant displays some of these signs. List at least three (3).
What is apnea/tachypnea, grunting, nasal flaring, retractions, tachycardia or bradycardia, decreased perfusion, temperature instability (hypothermia or fever), lethargy, irritability, seizures, bulging fontanels, feeding intolerance, abdominal distention, etc.?
The nurse suspects this upon initial observation of the infant.
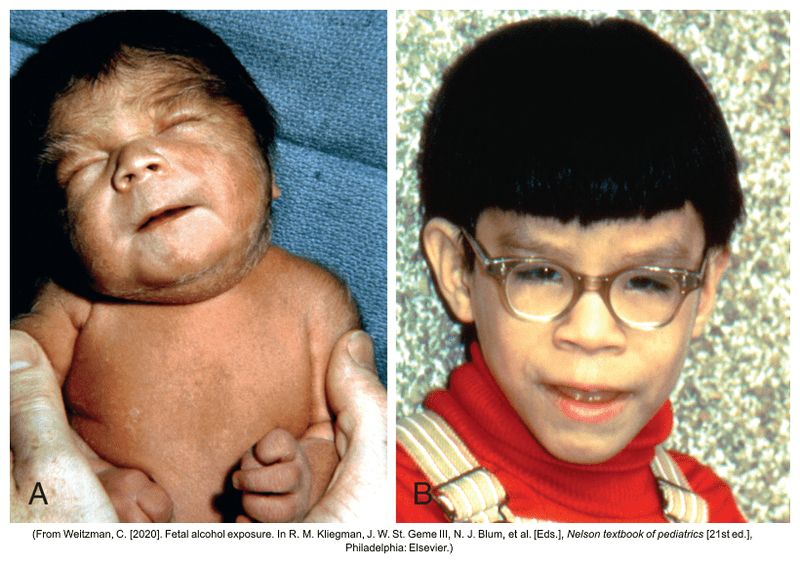
What is fetal alcohol syndrome?
Bonus: What are some neurological and/or behavioral problems associated with this?
What is respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)?
Bonus: What are some common treatments for (RDS)?
This term is used for infants who present with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) in which the weight, length, and head circumference are all affected.
What is symmetric IUGR?
This injury results from forces that alter the normal position and relationship of the arm, shoulder and neck. It usually occurs with shoulder dystocia or a difficult vertex or breech birth.
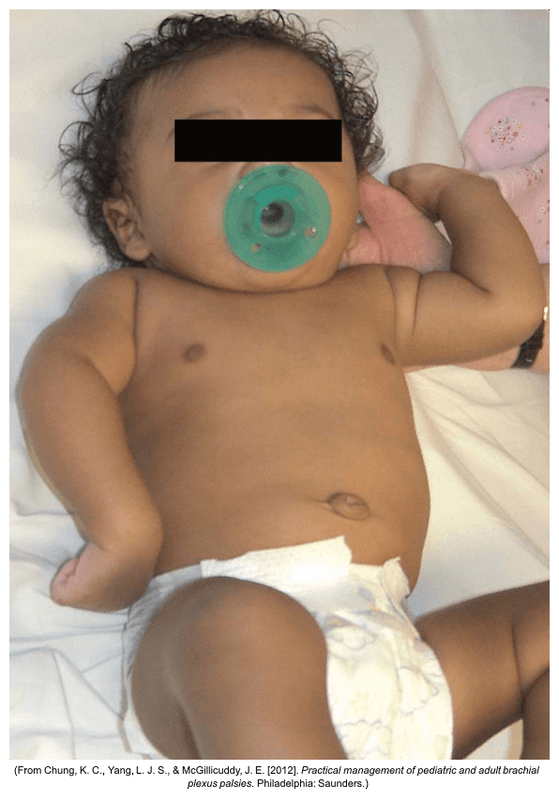
What is Erb Palsy (Erb-Duchenne paralysis)?
Bonus: What is the focus of treatment?
Nursing care of the infant with neonatal sepsis includes these interventions. List at least three (3).
What is identifying risk factors, vigilant assessment, administer antibiotics, administer fluids, breastfeeding or feeding breastmilk, and providing respiratory support?
Bonus: Why is providing breastmilk to the neonate with sepsis considered an important potential intervention?
This is the term used to describe the postnatal drug withdrawal syndrome exhibited by infants exposed to opioids in utero.
What is neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Bonus: What are some signs of neonatal abstinence syndrome the nurse may see in the neonate?
This respiratory complication is a result of aspiration of amniotic fluid containing meconium into the fetal or newborn trachea in utero or at first breath.
What is meconium aspiration syndrome?
This intervention is often used with preterm infants for a variety of reasons including: stress reduction in infants, infant-parent acquaintance, reduced risk for mortality, fostering appropriate neurobehavioral development, and many more benefits.
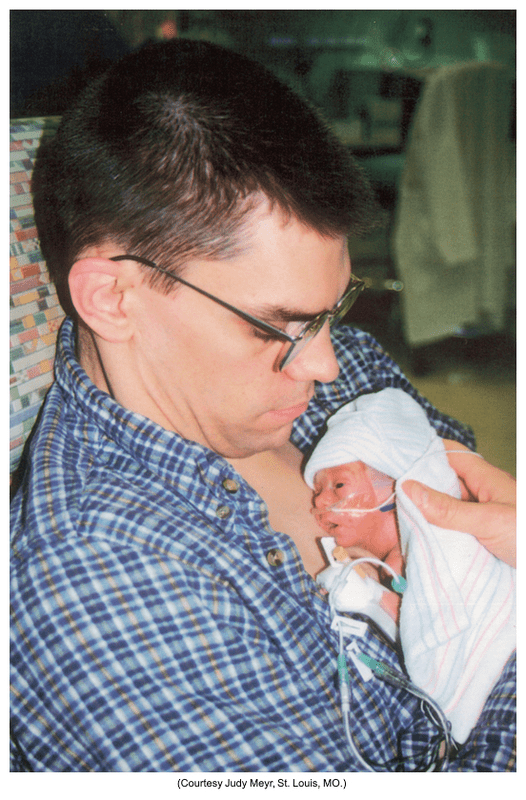
What is kangaroo care?
Due to variable (both increased and decreased) cerebral blood flow, premature infants are highly prone to this type of neurologic injury.
What is periventricular or intraventricular hemorrhage?
Bonus: What are some clinical manifestations? Hint: Think increased ICP.
Some maternal infections can result in fetal loss or malformations. This is the acronym for the common tests that are done if prenatal (congenital) infection is suspected.
What is TORCH complex?
Bonus: What does TORCH stand for?
This medication is contraindicated in infants born to opioid addicted mothers.
What is naloxone (Narcan)?
Distended abdomen, blood in stools, gastric retention, poor feeding, vomiting, and unstable body temperature are a few signs of this acute inflammatory disease of the bowel most prevalent in preterm infants.
What is necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)?
Bonus: What are some treatment options for the infant with NEC?
Universal newborn screening is done to detect a variety of genetic disorders including this one. Infants may have initial clinical manifestations of: poor feeding, respiratory difficulties, cyanosis, constipation, bradycardia, hoarse cry, postterm, and birth weight over 4000g (8lbs 13 oz).
What is congenital hypothyroidism?
Bonus: What are some other inherited conditions that are tested for with newborn screening?
This neurological injury may be caused by intrauterine or postnatal asphyxia resulting in hypoxia or cerebral ischemia. It may be seen in any gestational age infant.
What is hypoxic-ischemic brain injury?
Bonus: What does therapeutic management consist of?
The name of this type of congenital infection.
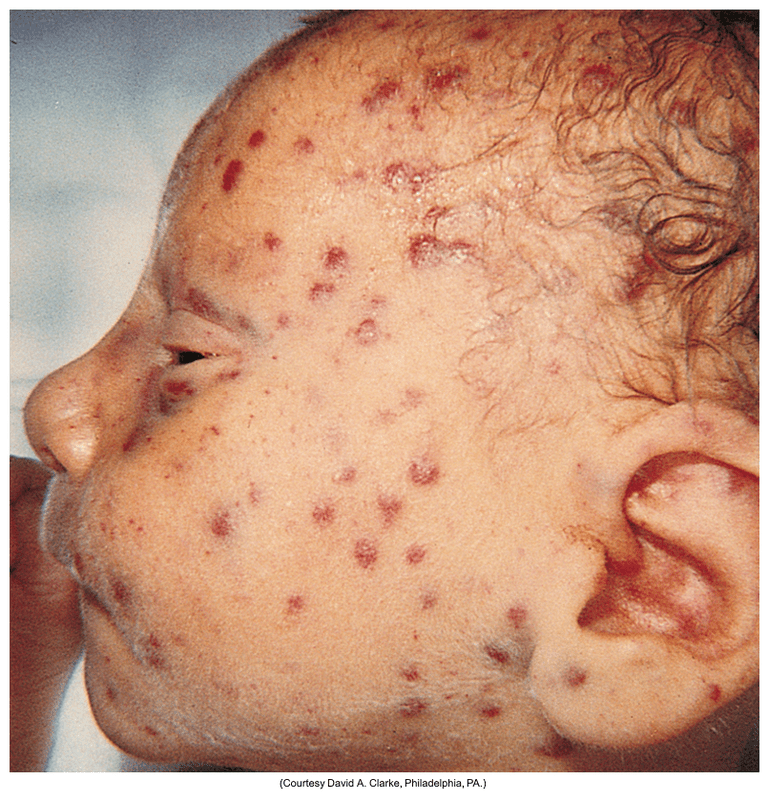
What is Neonatal Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection?
Bonus: What is the typical treatment?
The Eat, Sleep, Console (ESC) model is a newer approach to treating infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome. List at least 1 intervention associated with this model.
What is nonpharmacologic therapy such as vibrotactile stimulation and acupuncture, increasing the involvement of families, using pharmacologic treatment (such as morphine) on PRN basis, temporary prone positioning.
This classification of neonates display common findings such as a wasted physical appearance due to depletion of subcutaneous fat, minimal vernix, absence of lanugo, abundant scalp hair, long fingernails, and meconium staining.
What is postterm infant?
A condition where the mother's immune system attacks the baby's red blood cells. This occurs due to an incompatibility between the mother's and baby's blood types, often related to the Rh factor. Where the mother's body can develop antibodies against the baby's red blood cells, which then cross the placenta and attack the baby's red blood cells, leading to anemia and other complications.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis or hemolytic disease of the newborn?
Bonus: Postnatal treatment includes what?