This cartilage type is found in the External ear
Name the two types of myofibrils.
What are myosin and actin?
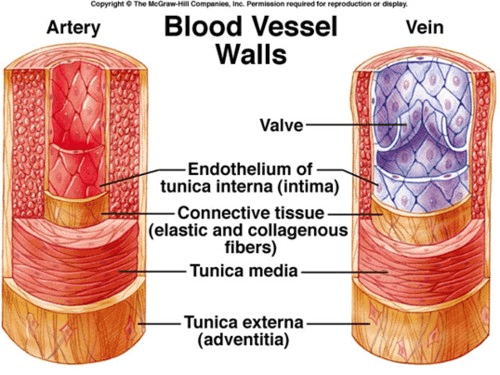
Name the type and size of blood vessel.
What is a large artery?
How to tell: Large tunica media filled with elastic fibers.
This meninge is one cell layer thick.
What is the pia mater (delicate mother?)
This is what serves as the blood-brain barrier!
The apex of the heart is made up of this ventricle.
What is the left? (Great for laterality marker!)
These are the two segments of the respiratory tract.
What are the conducting (nostrils to halfway down bronchioles)
and the respiratory (rest of bronchioles to alveoli)?
Name the small channels that allow osteocytes to communicate with each other.
 What are canaliculi?
What are canaliculi?
This ion is the catalyst for muscle contraction, allowing troponin to unwind the tropomyosin from actin binding sites.
What is calcium? (Ca2+)
This slide comes from this part of the body.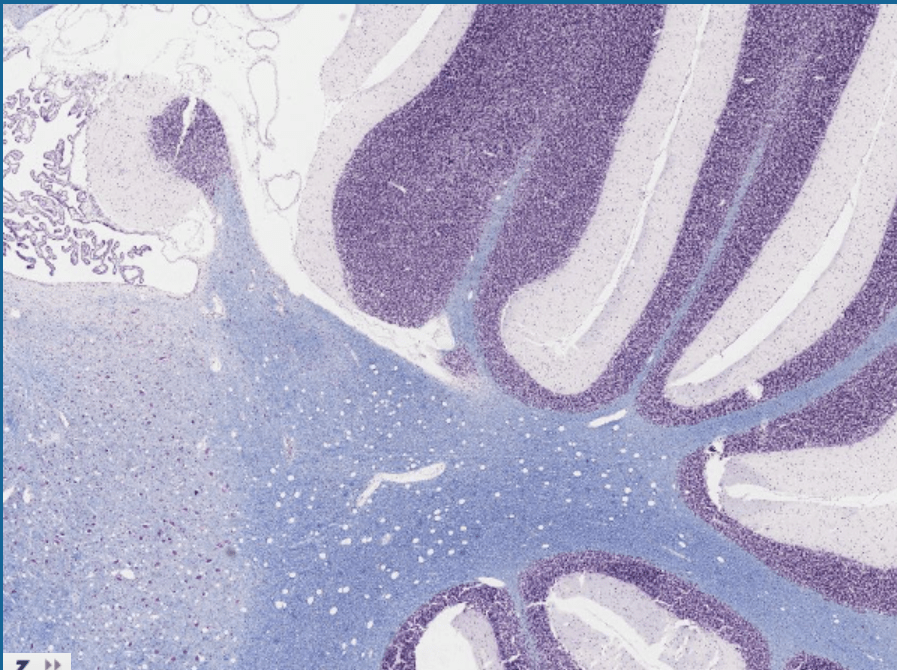
What is the cerebellum?
(How to tell: the folia)
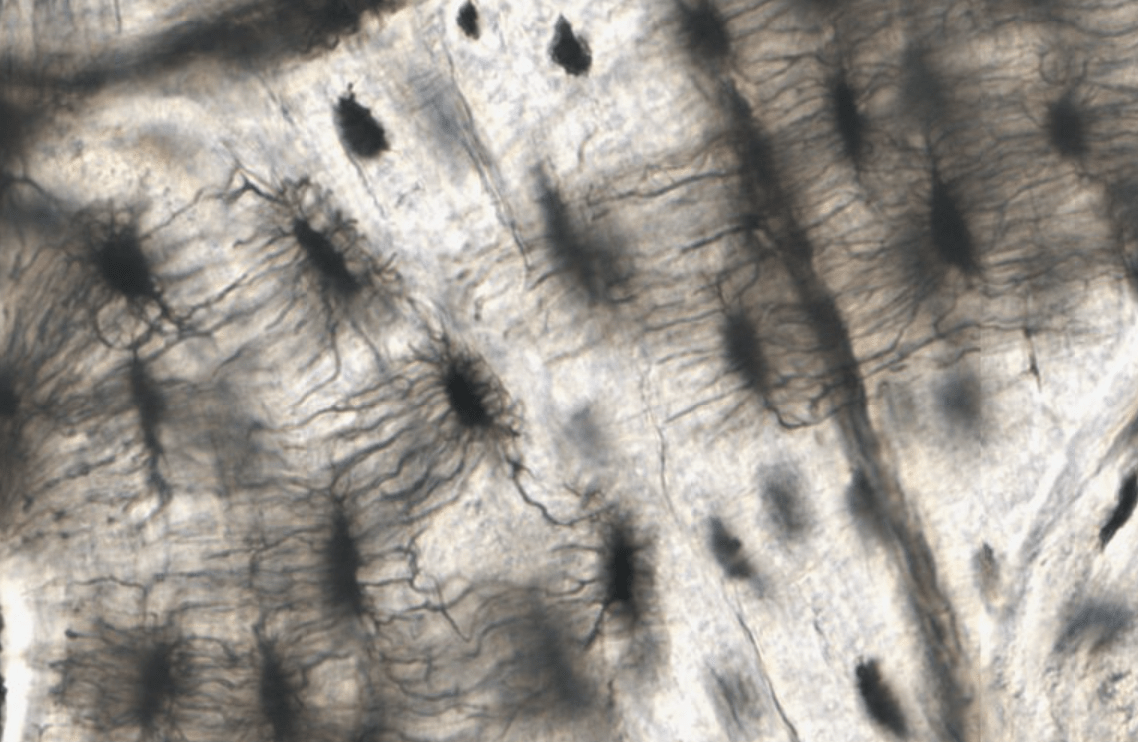
What part of the nervous system are the supportive cells astrocytes and oligodendroglia found?
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
Name the three layers of the cardiovascular system.
Tunica adventitia (connective tissue)
**Tunica media** (smooth muscle)
Tunica intima (endothelium)
In mammals, what shape are the hyaline cartilage rings of the trachea?
What is C-shaped? (Birds have full rings! C-shape is the reason for collapsing trachea!)

This is the embryonic lineage that all connective tissue arises from.
What is mesenchyme/mesoderm?
What is the morphology and action of this tissue?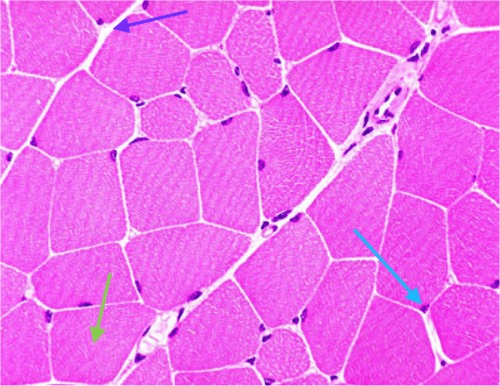
Striated and Voluntary aka Skeletal muscle
How to tell: Striated, nuclei to the periphery
Name the organ this slide is from
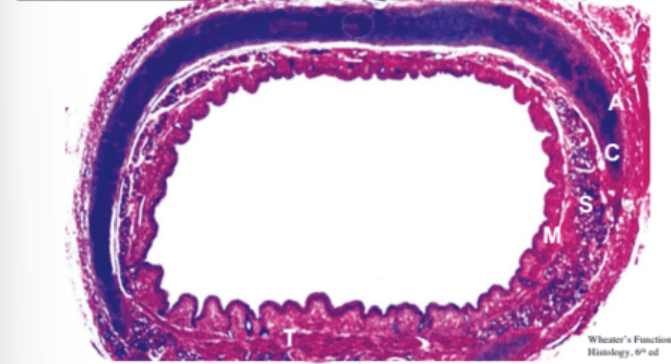
What is the trachea?
A- Adventitia (loose connective tissue!)
C- Cartilage (Hyaline)
S- Submucosa
M- Mucosa
The epineurium is made of this kind of tissue.
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Animals do not have this layer of skin.
What is the stratum lucidum?
Name the clear cells in the picture. What segment of the respiratory tract are they found?

Goblet cells, conducting tract (not present in respiratory tract, great way to tell the difference!)
Name the role of fibrocartilage and at least one place it can be found.
Role- reduce compressive and shearing forces
Places- between intervertebral discs, pelvic symphysis, and articular spaces
Name the two bands in a sarcomere that shrink during muscle contraction.
What are H bands and I bands
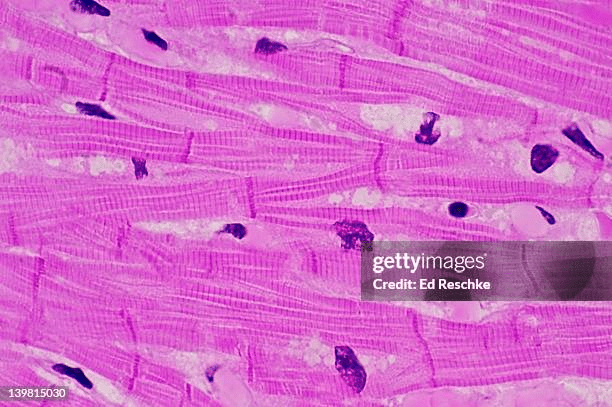 Name the type of muscle found in this picture.
Name the type of muscle found in this picture.
What is involuntary striated muscle?
(How to tell: intercalated discs are characteristic of heart muscle, which is striated and involuntary)
Name the two layers of the grey matter in the cerebellum.
What are the granular (deep) and molecular (superficial)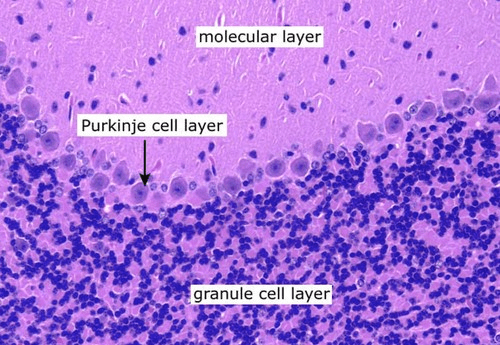 layers?
layers?
This structure of skin is found in the dermis/subcutis.
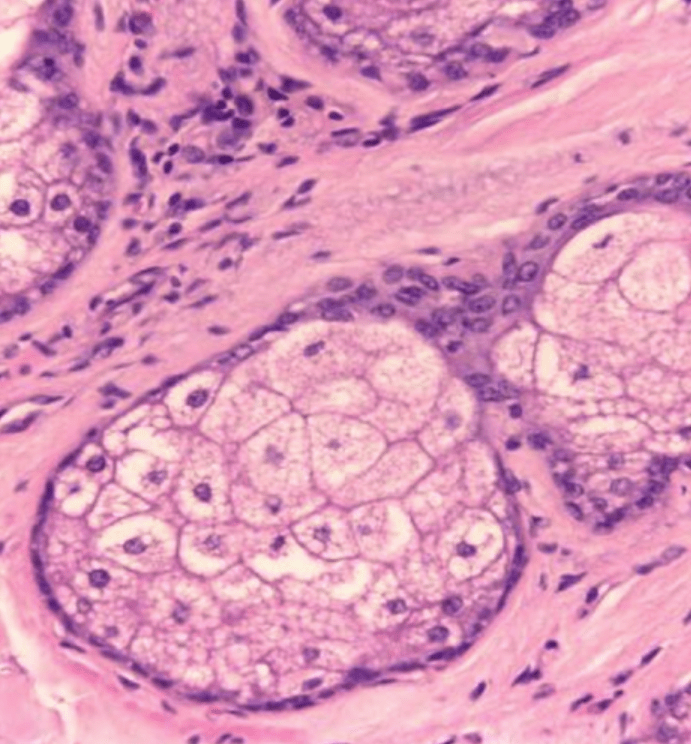
What are sebaceous glands?
What type of endothelium is found in bronchioles?
Simple cuboidal (as opposed to columnar through most of the respiratory tract!)
These cells are cuboidal/polygonal, are basophilic, and have a prominent Golgi Apparatus
What are osteoblasts?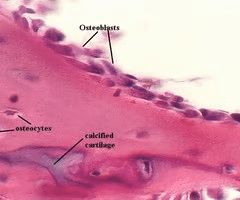
Name the two muscle types that have central nuclei.
What are smooth and cardiac muscle?
Name the tissue. Differentiate between the different layers. What is the name of the structures that separates the two more superficial layers?
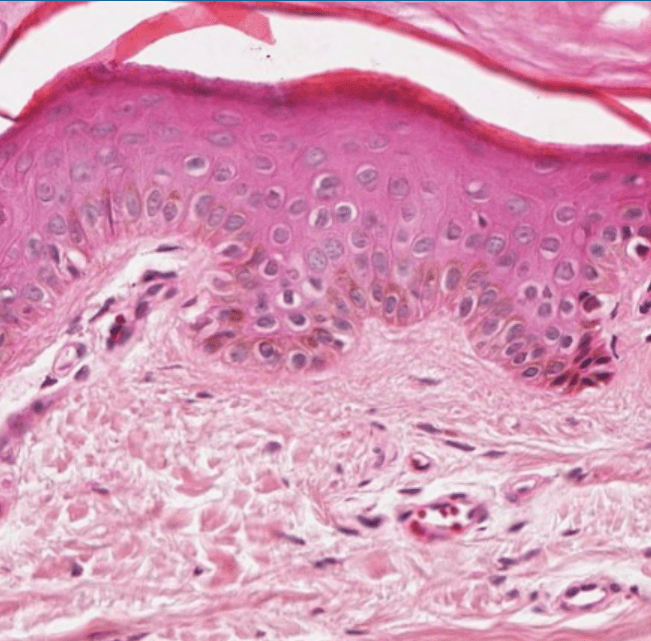
Tissue- Skin/Integument
Different Layers: Epidermis, Dermis, Subcutis
Structure: Dermal papillae/dermal ridges
These cytoplasmic inclusions make a nerve cell look granular.
What are Nissl bodies/substances?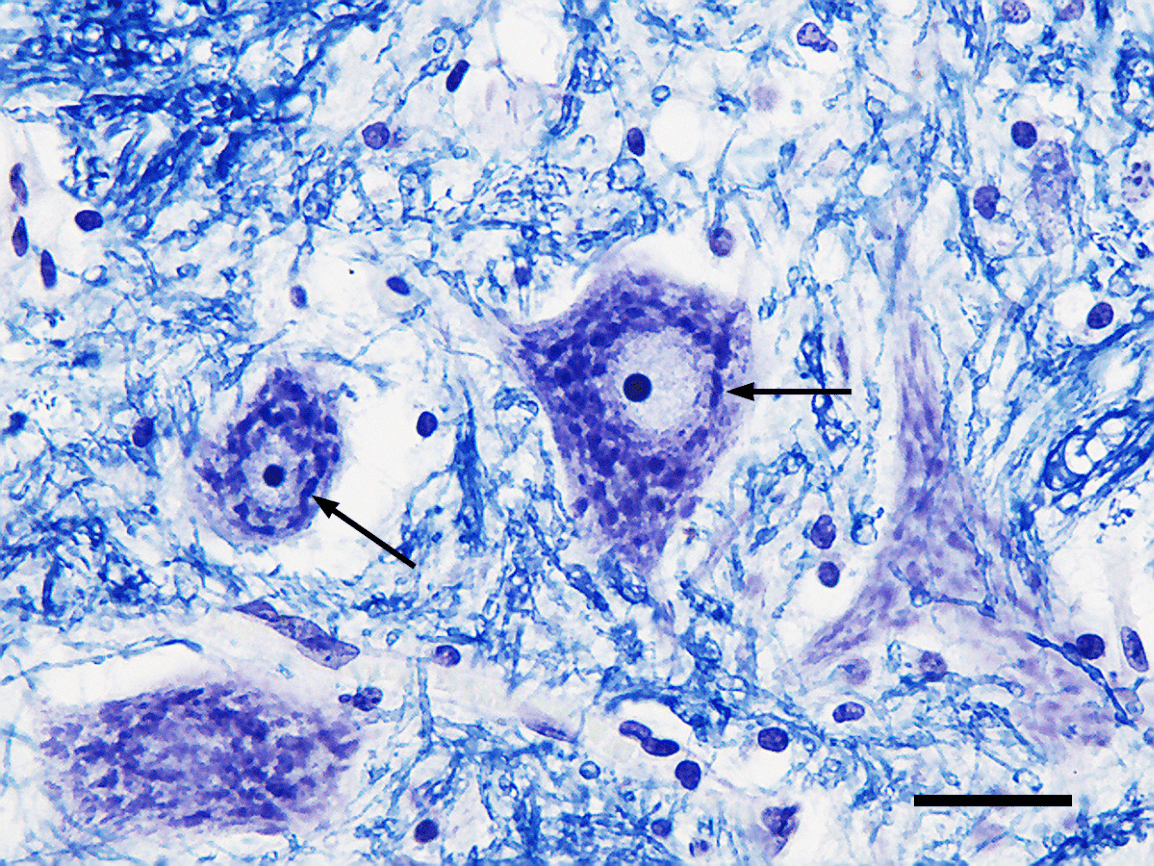
List the valves of the heart.
What are...
Right Atrioventricular Valve (tricuspid)
Pulmonary Valve
Left Atrioventricular Valve (bicuspid or mitral)
Aortic valve
What layer of the trachea are blood vessels found?
Submucosa (second from the lumen)
Name the two types of cartilage growth and what they do.
Appositional- cartilage formed on bone surfaces below perichondrium
Interstitial- formed from existing chondrocytes
Name the two substances (that we've learned so far) that could be in the synaptic vesicles, and what ion stimulates them to be released.
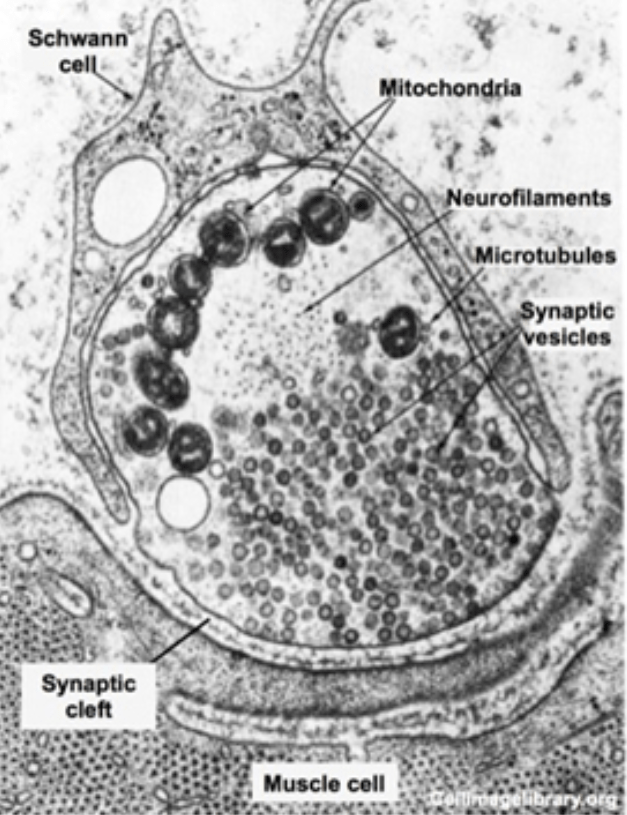
Two substances: Acetylcholine or Norepinephrine
Ion- Calcium (Ca2+)
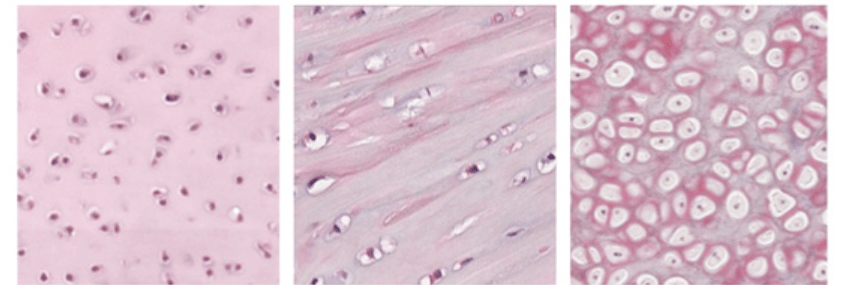
Explain what type of tissue this is and which is which.
Cartilage (connective tissue).
From left to right: Hyaline, Fibro, Elastic
Macrophages in the Central Nervous System are known as this
What are microglia?
Name the location and function of Merkel Cells.
Located in the epidermis (stratum basale) and help with (light) touch sensation. Closely associated with neurons.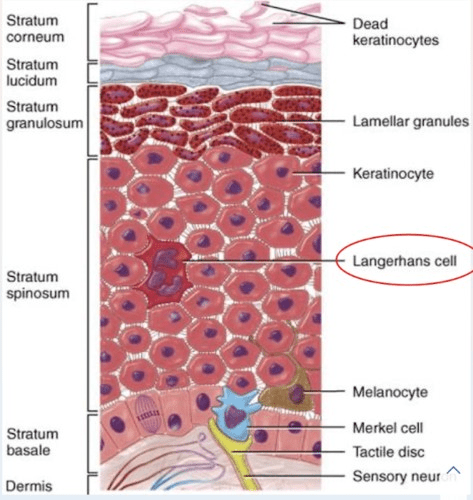
What are clara cells and where are they found?
Cells that secrete lipoproteins to keep tissues from sticking, in the bronchioles and alveolar ducts.
Type II pneumocytes do this for alveolar sacs!
