A retrovirus that causes immunosuppression. People with this disease are more susceptable to infections that are normally controlled through immune responses.
HIV disease
p. 218
After acute infection (2 to 4 weeks) the client may expereince these type of symptoms?
Mononucleosis-like syndrome of fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, headache, malaise, nausea, muscle and joint pain, diarrhea, and/or a diffuse rash. They may even develop neurologic complications.
p. 219
What are the two diagnosistic studies to measure the progession of the disease?
Viral load and CD4 counts.
p. 222
What is the goal of drug therapy for HIV?
decrease the viral load, maintain or increase CD4 counts, orbprevent HIV-related symptomsor opportunistic diseases, delay the progression of the disease, prevent transmission.
p. 223
What should the nursing assessment focus on for the client infected with HIV?
Focus on behaviors that put the person at risk for HIV and other sexually trnsmitted and blood-borne infetions. Assess for risky behaviors.
p. 223
This is the mode of transmission of HIV.
infected blood, semen, vaginal secretion, or breast milk, and can be transmitted from an infected mother to a baby.
p. 218
What is this manifestation?

Karposi's sarcoma.
p. 221
What is a window period?
The delay of when a screening test will show a positive result. This delay can be up to 3 weeks.
p. 222
What is the major problem with ART therapy?
That resistance develops rapidly when the drug is not taken properly.
p. 223
HIV is preventable. What are some teaching points that you can educate the public about?
Practicing safe sex with condoms or abstaining from sex.
Educate that alcohol and tobacco can cause immunosupression.
Do not share equipment like needles, syringes
Do not have sexual relations under the influence
p. 225-226
How can the virus not be transmitted?
Hugging, dry kissing, shaking hands, sharing eating utensils, using toilet seats, or casual encouters in any setting. It is not spread in tears, saliva, urine, emesis, sputum, feces, sweat, respiratory droplets, or enteric routes.
p. 219
What is this manifestation?

Thrush.
p. 221
What is the normal range for CD4 cell count?
800-1200 cells/uL.
What is one of the over the counter medications that can interfere with ART therapy?
St. John's Wart, antacids, roton pump inhibitors, and certain supplements.
p. 223
The client and their family may have a wide range of emotions after hearing the diangnosis ?
anxiety, panic, fear, derpression, denial, hopelessness, anger and guilt. The family members may have feelings of loss, anger, powerlessness, depression, and grief, social isolation, the possiblity death and even thoughts of suicide.
p. 227
How does the virus replicate?
Backwards. Going form RNA to DNA.
p. 219
What is this manifestation?
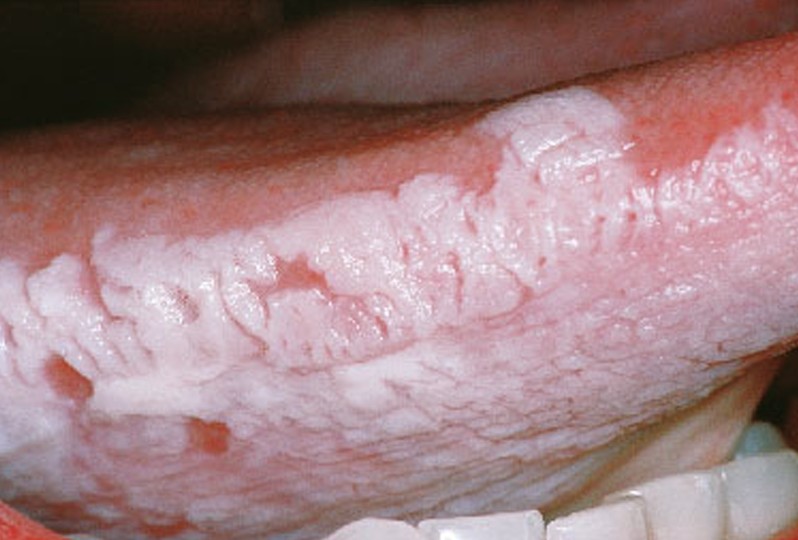
Leukoplakia.
p. 221
What is the CD4 count that is indicatie of AIDS?
<200 cells/uL.
p. 221
What are some measures that you can encourage your client to do to avoid opportunistic infections?
Avoid large crowds, wash hands frequently, get the recommneded vaccines.
p. 223.
ART therapy is very important in order to slow the progression of the disease. What are some key points that the nurse can teach to the client.
The importance of adherance to avoid building drug resistance. The importance of taking the medication at the same time of the day. The client can be assisted in setting reminders on their phones, using pill boxes, and calendars.
p. 228
What is the cell that it destroys?
The CD4 T cells. ( 1 billion per day)
p. 219
This manifestation is harmful to pregnant woman?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
p. 222
What are some other tests that may be monitored?
CBC, Liver function tests.
p. 223
What is a critical component to control the epidemic of HIV?
Prevention.
p. 224
HIV infected persons frequently experience anxiety, fear, diarrhea, pereipheral neuropathy, nausea, vomiting and fatiuge. What is the priority for mangment of fatigue?
To notice the energy patterns and to schedule activities when the client has enough energy and to schedule periods of rest, encourage good sleep habits and to avoid substances such as caffein, noctotine, alcohol, and other medications that may interfere with sleep.
p. 230