The empiric treatment for most zoonotic infections.
Doxycycline. (ex. Lyme, yersinia pestis, rickettsia, etc.)
A patient presents with flatulence and watery diarrhea following a camping trip. He or she may have drank unfiltered water on the trail.
Giardia
A patient presents with slow-onset shortness of breath for three weeks following a spelunking trip in the Ohio-Mississippi river valley. He or she may have been exposed to bat guano.
Histoplasmosis.

Scientists discover a new strain of bacteria and attempt to characterize the bacteria using laboratory techniques. The bacteria fails to decolorize after addition of hydrochloric acid. What component of the bacteria is responsible for this observation?
Mycolic acid grants this bacteria acid-fastness.
A 4 year old child presents to the clinic with 3 weeks history of cough, runny nose, and fever. After 2 weeks, the runny nose and fever have gone away but the cough has become much worse.
Whooping cough (pertussis) caused by Bordetella pertussis.
- Inspiratory whoop, post cough emesis
- Phase 1: Cold symptoms and cough
- Phase 2: Severe paroxysms of cough
- "The worst cough in my life"
A patient returns from a trip to Mexico presenting with bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and upper right quadrant pain.
Entamoeba histolytica (that has invaded the liver).
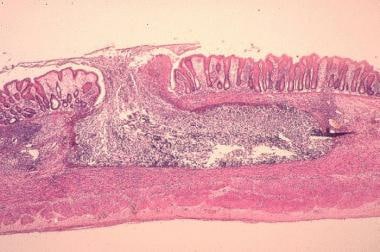
A patient presents with slow onset shortness of breath for three weeks duration following a trip to Arizona mountains.
Coccidioidomycosis.

A child from rural Mississippi presents to the clinic with a swollen and tender inguinal lymph node after a hunting trip.
Yersinia Pestis presenting as bubonic plague. Treat with Streptomycin or Doxycycline (2nd line).
A patient with CD4 count of 100 presents with watery diarrhea. Travel history is negative. The patient drinks unfiltered water.
Cryptosporidium. Infection more common in HIV.
An 80 year old woman suffers a syncopal episode and presents with altered mental status. There is no sign of respiratory distress and cranial CT imaging is benign.
The mechanism by which cholera toxin interacts with host G proteins to cause disease state.
ADP Ribosylation.
ADP ribosylation can lock G proteins in the On or Off state. Check each toxin to see which type of ADP ribosylation is performed and to which G protein (Gi or Gs).
A 25 year old man presents to the ER with abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and lower right quadrant pain. An ultrasound is performed. What is causing his symptoms?
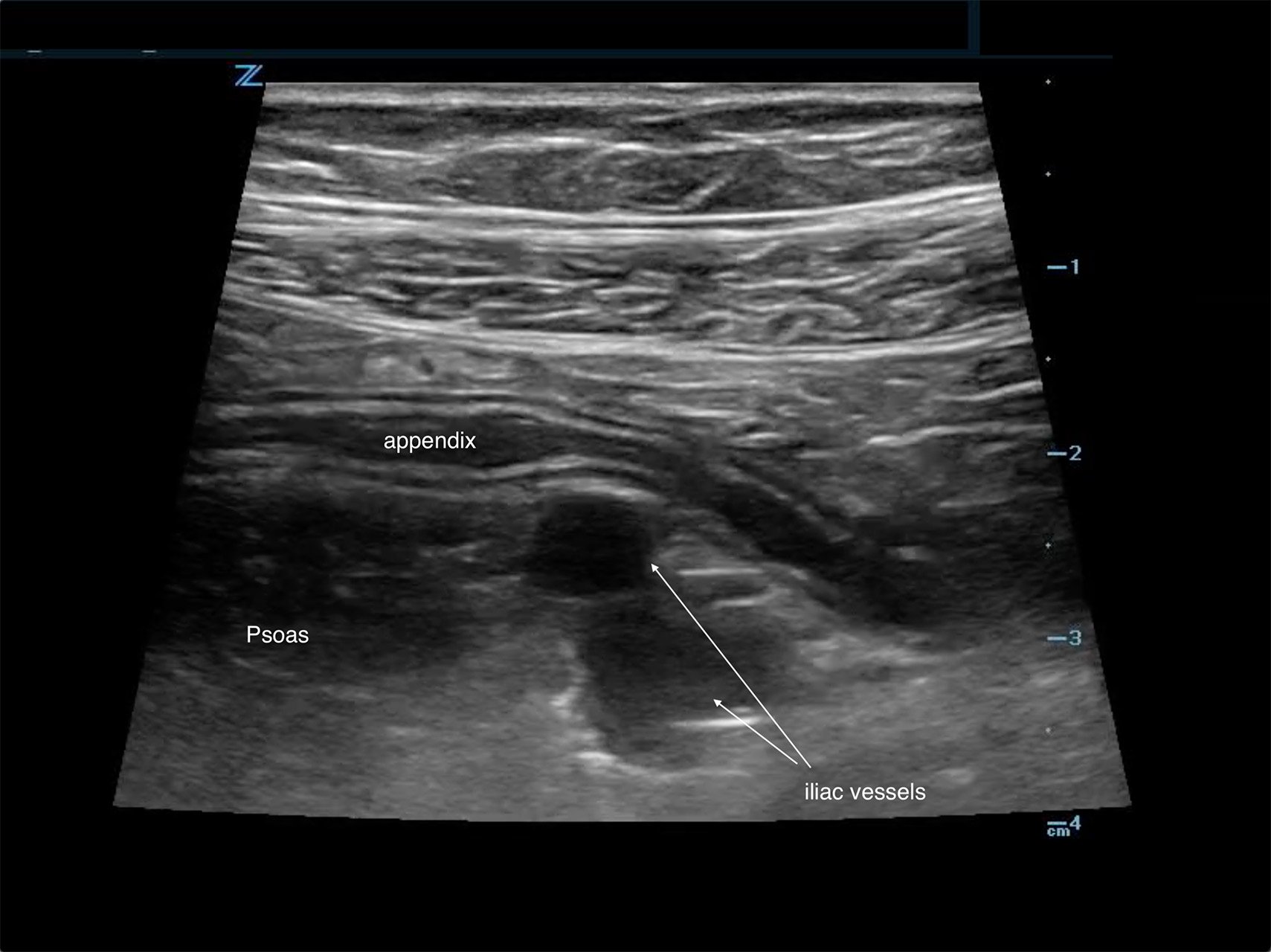
Infection by Yersinia enterocolitica (appendicitis mimic).
A 30 year old G1P0 woman experiences a flu-like illness during her 3rd trimester of pregnancy. No rash is noted. Her fetus suffers a spontaneous abortion. Gram positive bacteria is cultured from a sample of the amniotic fluid.
Listeria monocytogenes causing granulomatosis infantiseptica.
The mechanism by which non-pathogenic strains of cholera become pathogenic to humans.
Lysogenic conversion.
A patient presents to the ER with a severe episode of emesis 2 hours after eating rice leftovers. What is the shape and color of the microorganism responsible for his symptoms?
Bacillus cereus's toxin is causing his symptoms, a gram positive rod.
A patient presents to the clinic with abdominal pain, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, and weight loss. FACS reveals a CD4 count of 47.
MAC