The most proximal action of the Cranial Thigh Group
Flex the hip joint
What makes up the external rectus sheath and the internal rectus sheath?
External: aponeurosis of External Abdominal Oblique and Internal Abdominal Oblique
Internal: Aponerosis of the transverse abdominus.
The vein that returns cardiac blood to the right atrium
The great cardiac vein
What is the most caudal irregular bone in the thorax?
Xyphoid Process
The primary function(s) of the Meniscus
1. Shock Absorption
2. Correct the incongruency between Femur and Tibia
What are the heart pressures in the atriums, left ventricle, and right ventricle?
A: 0-4 mmHg
RV: 25 mmHg
LV: 120 mmHg
Originating from the medial condyle of the femur, what is the primary function of this muscle group? Name one muscle from the antagonistic group.
Flex the tarsal and digital joints
Cranial Tibia, Long Digital Extensor, Peroneus Longus
Name the most caudal parietal pleura in the thoracic cavity. What is the major function of the organ that rest beneath this pleura?
Just between the vagosympathetic nerve and the vagus nerve is a junction of neuron cell bodies. Identify this structure and its more dorsal counterpart. What connects these 2 structures?
The middle cervical ganglion and the cervicothoracic ganglion. These are connected by the Ansa Subclavia.
What is unique about T11?
It is the landmark thoracic vertebrae that points directly upward. Only has 1 costal fovea, No Intercapital Ligament
Name the ligament ventral to the Splenius and Transversospinalis system that aids the epaxial muscles.
Name the attachments of this ligament and its difference in the dog and cat.
Nuchal Ligament
Spinous Process of the Axis and T1
Cats do not have a nuchal ligament
List the layers of the pericardium from out to in. Name the type of material that makes up the middle layer.
Mediastinal Pleura, Fibrous Pericardium, Parietal Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium is composed of Collagenous Connective Tissue
Name the specific muscle parts of the cranial thigh group. What is the primary function of this group? Where do they insert? and what is the most proximal action?
vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, illiopsoas
Primary function to extend the stifle joint. Proximal action of flexing the hip joint
Which muscles are utilized in expiration? Name their fiber directions. Is this a passive or forced action? explain the difference.
External Abdominal Oblique
Internal Abdominal Oblique
Transversus Abdominus
Forced Action; difference is when you relax your inspiratory muscles, you will passivley exhale. Abdominal Press is considered forced experiation.
What classification of the autonomic nervous system are the fibers that compose the recurrent laryngeal nerve? Where does the recurrent laryngeal nerve branch from? What does that mean for the for the fibers of this parent nerve?
Parasympaethic fibers.
Branches from the Vagus Nerve and that means the vagus nerve is also a parasympathetic nerve.
Describe the function of the Intercapital Ligaments
Where would these ligaments be present, and what typical disease process occurs where they are not present?
Intercapital Ligaments strengthening effect on the dorsal part of the annulus fibrosis
Present between ribs 2-10; therefore, the cervical, lumbar, and T10-T13 regions... are more likely to develop IVDD.A 7-year-old Siberian Husky presents to the clinic after a rough play sesh at the local park. The patient is observed to have lameness in the left hind limb. It is suspected that there may be damage to the intracapsular ligament that attaches to the cranial tibia. What test is performed to support this suspicion? Explain how to perform this test, and the name of the associated damaged ligament.
Cranial Drawer Test- Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Place fingers on 4 landmarks (head of fibula, tibial tuberosity, patella, and lateral condyle of the femur) and push with thumb to observe signs of cranial movement.
IDENTIFY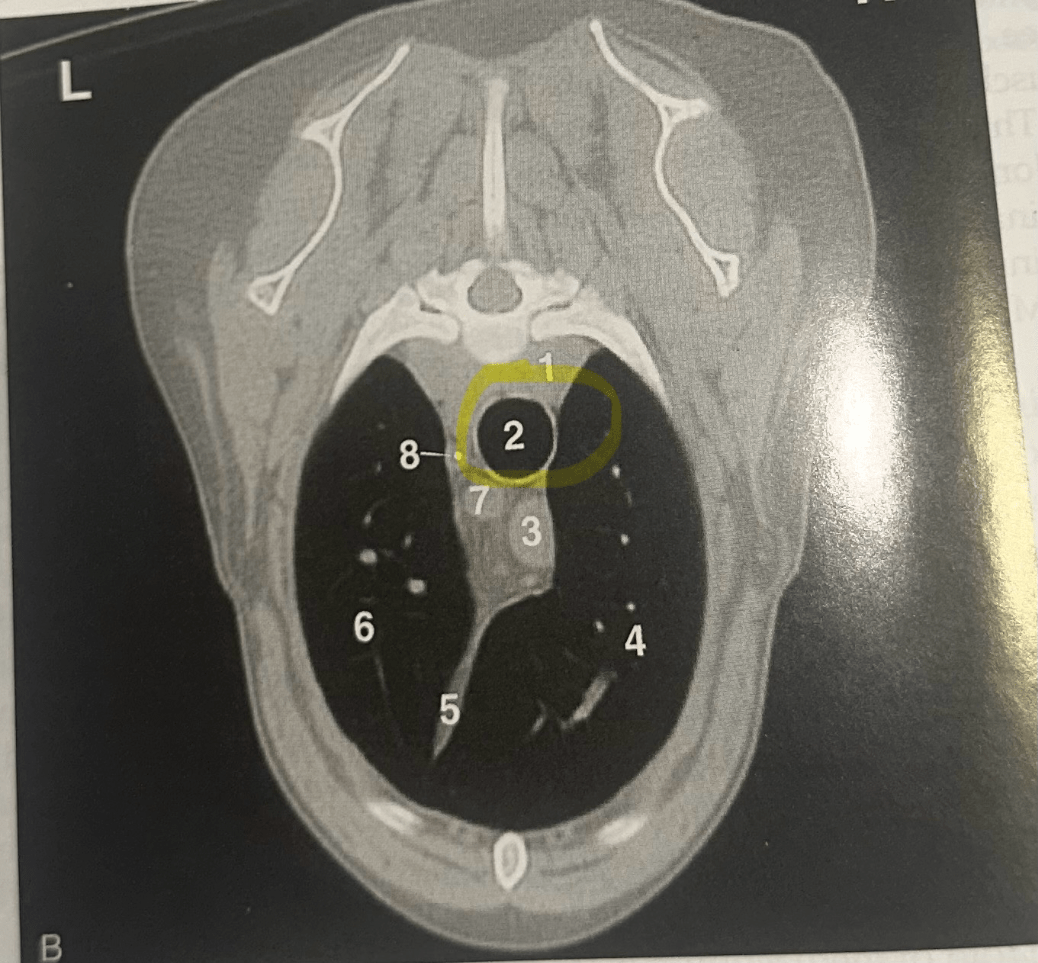
Trachea
which muscle of the rump does not contribute to medial rotation of the limb; where does it originate and where does it insert. what other muscle of the pelvic limb shares a similar origin with this muscle?
Superficial Gluteal Muscle M.
Sacrotuberous lig and sacrum; Biceps Femoris is similar to the sacrotuberous ligament
Inserts on 3rd trochanter;
Name the part of the left lung
Name the parts of the right lung
How many lobular bronchi are present in the right and left lung respectively.
What significant landmark is between the cranial and middle lobe of the right lung?
Left: Cranial head of the cranial lobe, Caudal head of the cranial lobe, Caudal lobe; 2 lobar bronchi
Right: Cranial lobe, Middle lobe, Caudal lobe, accessory lobe; 4 lobar bronchi
The cardiac notch
During a lateral neck surgery, a patient develops shoulder droop and difficulty elevating the scapula. Which cranial nerve is most likely injured, and why might we notice a shoulder droop and difficulty elevating the limb?
The accessory nerve; its the sole innervation of the trapezius
Name the blacked out structure, what runs through this and where does it attach.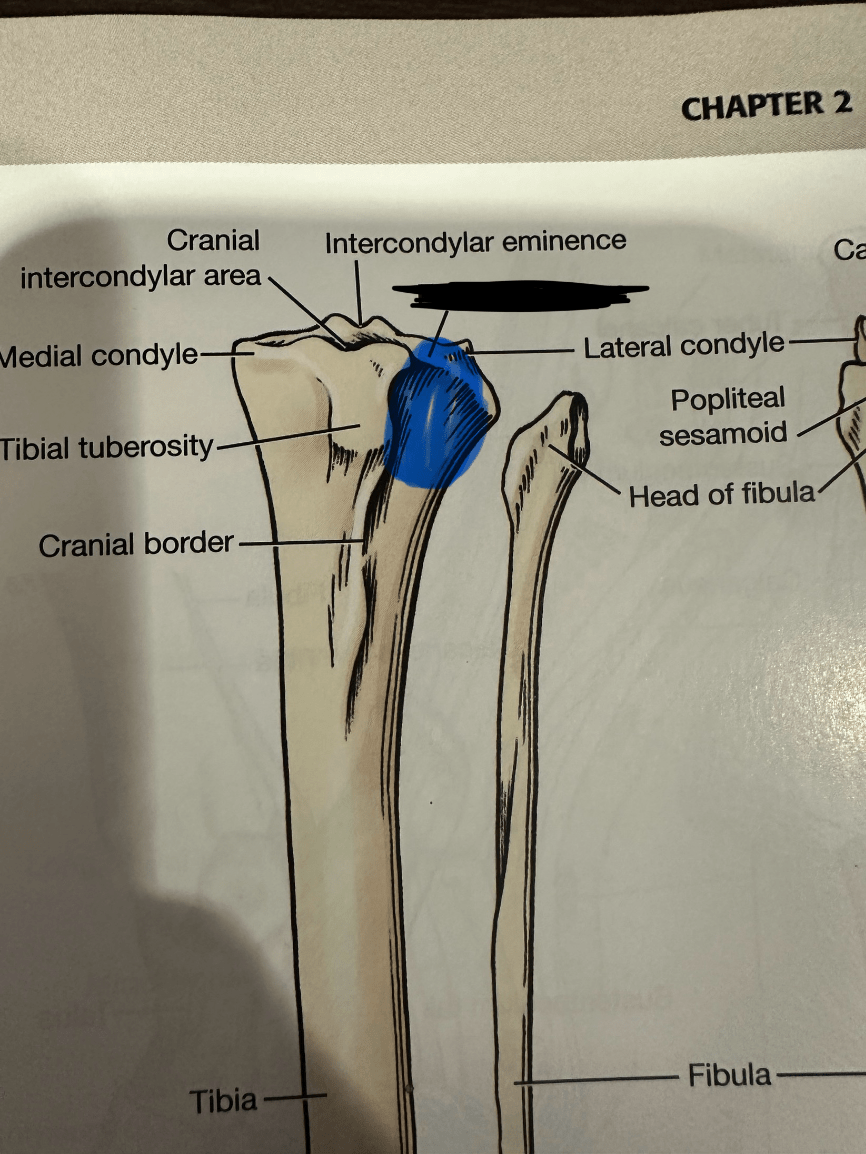
Extensor Groove of Tibia; tendon of origin of the long digital extensor; extensor fossa of femur
The ligament that connects the aorta to the pulmonary trunk is called?
What is the significance of this ligament in utero?
Ligamentum Artieriosum
It serves as the ductus arteriosus in utero and bypasses the pulmonary trunk and goes straight to the aorta.
what structure directs blood flow from the vena cave deep into the atrium?
intervenous tubercle
List all muscles of the crus. Their origins and insertions. Which muscle is not present in dogs but is present in cats?
This Answer is Long and Wordy; we can talk this through after.
Craniolateral: Cranial Tibia; Long Digital Extensor; Peroneus Longus
CT: lateral proximal tibia.... plantar proximal metatarsal 1&2
LDE: Extensor Fossa of Femur.... Extensor Process of Digits
PL: lateral condyle of tibia and proximal fibula.... plantaroproxiomal aspect of metatarsals
Caudal Crus: Gastrocnemius, Superficial Digital Flexor, Deep Digital Flexor, Popliteus; Soleus (only in the cat)
G: Caudal Distal Femur....Tuber Calcanei
SDF: Lateral Supracondylar tuberosity of femur....tuber calcanei and plantar proximal aspects of metacarpals 2-5
DDF: Caudal Aspects of tibia and fibula....distal phalanges
Popliteus: Popliteal Fossa of Femur... proximal medio aspect of the femur
When making a paracostal incision that goes through the lungs and into the heart, name the layers you would go through in order from out to in.
External Intercostal;
Internal Intercostal
Pulmonary/Visceral Pleura
Lung
Pulmonary/Visceral Pleura
Mediastinal Pleura
Fibrous Pericaridum
Parietal Pericardium
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
The transverse foramen is located between C1-C6 and allows for passage of what 3 important structures?
One of these structures carries oxygenated erythrocytes and is a branch of which major vessel?
Vertebral VAN
left subclavian artery
Between which intercostal spaces is the dog heart located? what about the cat?
Between ICS 3-6 in dog; and ribs 4-7 in cats
List the 10 ligaments of the stifle joint.
Which of the extracapsular ligaments are fused to the meniscus of its side?
Lateral Collateral and Medial Collateral (medial is fused to meniscus)
Cranial Cruciate and Caudal Cruciate
Meniscofemoral, Transverse
Meniscotibial (Cranial and Caudal = 4 total)
RA - RV - PT- PA-Lungs-PV-LA-LV-Aorta
Fossa Ovale
Ligamentum Arteriousus