What is thermoregulation?
Maintaining constant body temperature
What is hypoglycemia?
Low blood sugar
How does glucose get into the blood?
Eat carbohydrates --> Digest into glucose --> Passes into bloodstream
Movement of solute from high concentration to low concentration through the membrane
Simple Diffusion
Movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to high solute concentration
Osmosis
What is normal body temperature for humans in degrees Celsius?
37 degrees Celsius
(98.6 degrees Fahrenheit)
What is hyperglycemia?
High blood sugar
What are the two hormones that regulate blood glucose levels?
Insulin and Glucagon
Movement of solute from high concentration to low concentration through transport proteins
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of solute from areas of low concentration to high concentration
Active Transport (Requires ATP)
When the body is too warm, list two ways it cools down.
1. Sweating
2. Blood vessels dilate
Why is low blood sugar dangerous?
Body cells can't take in glucose --> Little energy
When blood sugar is too low, what hormone does the pancreas release?
Glucagon
Three types of passive transport
-Simple diffusion
-Facilitated diffusion
-Osmosis
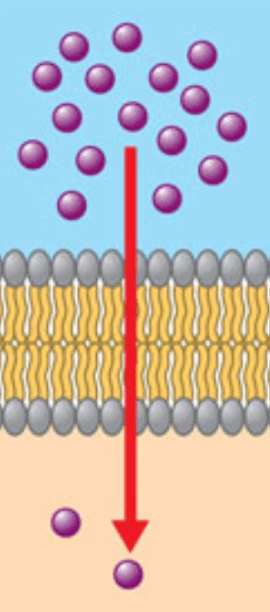
Simple Diffusion
When the body is too cold, list two ways it warms up.
1. Shivering
2. Blood vessels constrict
Why is high blood sugar dangerous?
Too much sugar in blood can damage blood vessels
When blood sugar is too high, what hormone does the pancreas release?
Insulin
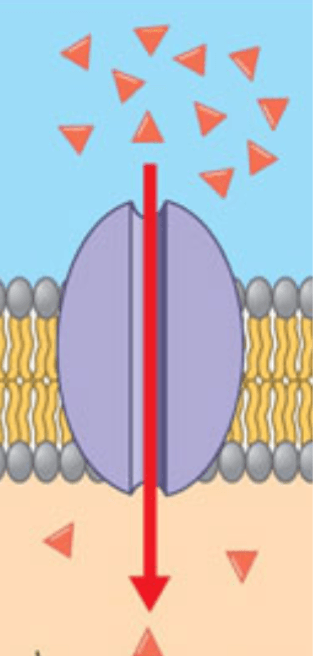
Facilitated Diffusion
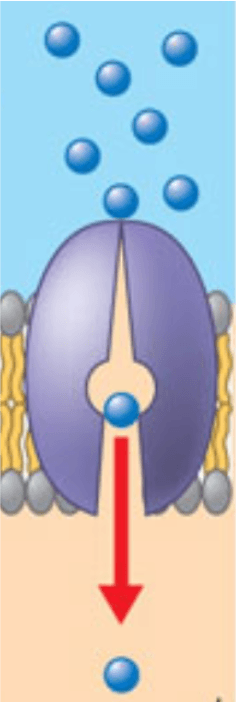
Facilitated Diffusion
Why is it dangerous to be dehydrated? Relate your response to thermoregulation.
Dehydration means little water --> cannot sweat --> cannot cool down
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
A person doesn't produce insulin
How does the body raise blood sugar levels when they are too low?
Pancreas releases glucagon --> Causes stored glucose in glycogen chains in liver to be released into blood
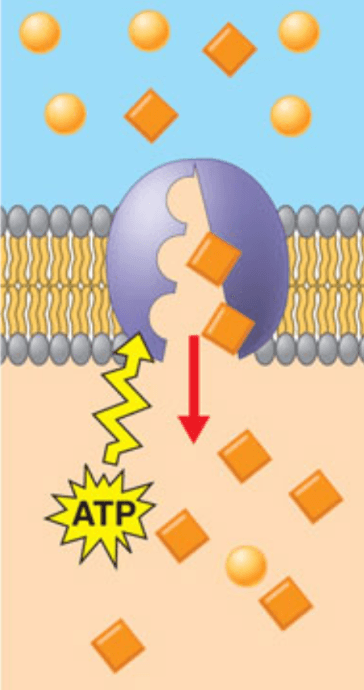
Active Transport
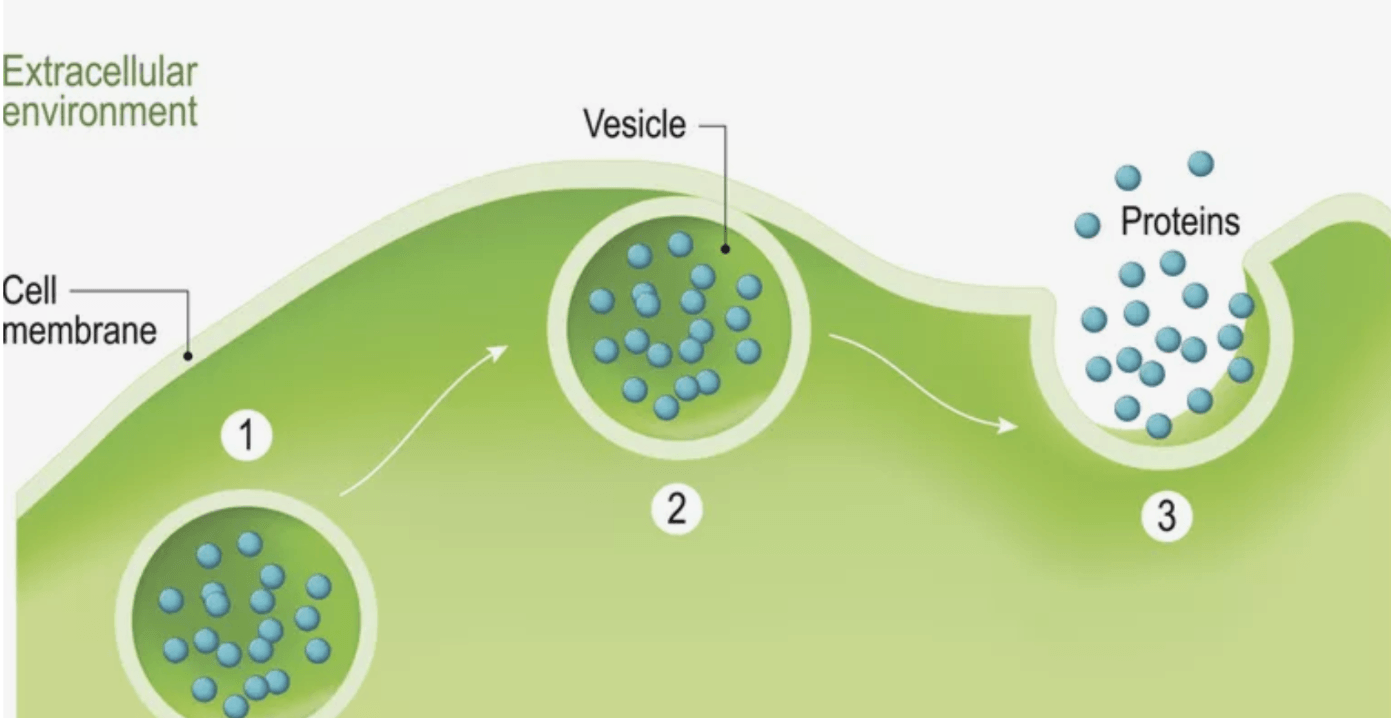
Exocytosis (Requires ATP)
What should a person do while exercising to ensure that they don't overheat?
Drink water (so that they can sweat)
1. In what form is the glucose in food sources such as bread and vegetables?
2. In what form is the glucose in sugary drinks?
1. Starch chains
2. Sucrose
In what form do humans/animals STORE glucose?
Glycogen (in the liver and muscle cells)
Are endocytosis and exocytosis forms of passive or active transport?
Active Transport (require ATP)
What is pinocytosis?
Taking in liquids/dissolved substances into the cell through a vesicle
What is "dilation," and how does it help with thermoregulation?
Dilation: To get larger
When the body is too warm, blood vessels dilate so that they are closer to the skin. Heat from the blood dissipates out of the body through the skin.
When you eat carbohydrates, they get broken down into glucose that enters the blood. What are three things that can happen to that glucose once it's in the blood?
1. Enter body cells for cellular respiration (if insulin is present)
2. Enter muscle/liver cells to be stored in glycogen chains (if insulin is present)
3. Stay in blood (if insulin is NOT present or if there is a lot of glucose in the blood)
What is the treatment for Type 1 Diabetes?
Insulin injections
What is phagocytosis?
Taking in large substances into the cell through a vesicle
Which substances can:
a) pass directly across the membrane
b) only pass through a transport protein
a) Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
b) Glucose